正文
跟DI容器类似,引入Service Locator目的也在于解耦。虽然和DI放在一起讲,但他与DI是完全不同性质的概念,作用目的也不相同: DI是解决多层依赖的问题;而Service Locator是处理服务定位的问题。一个服务中就会存在多层依赖的问题,可以说DI更底层, Service Locator更上层、更宏观一些。
Service Locator这一模式的优点有:
- Service Locator充当了一个运行时的链接器的角色,可以在运行时动态地修改一个类所要选用的服务, 而不必对类作任何的修改。
- 一个类可以在运行时,有针对性地增减、替换所要用到的服务,从而得到一定程度的优化。
- 实现服务提供方、服务使用方完全的解耦,便于独立测试和代码跨框架复用。
基本功能
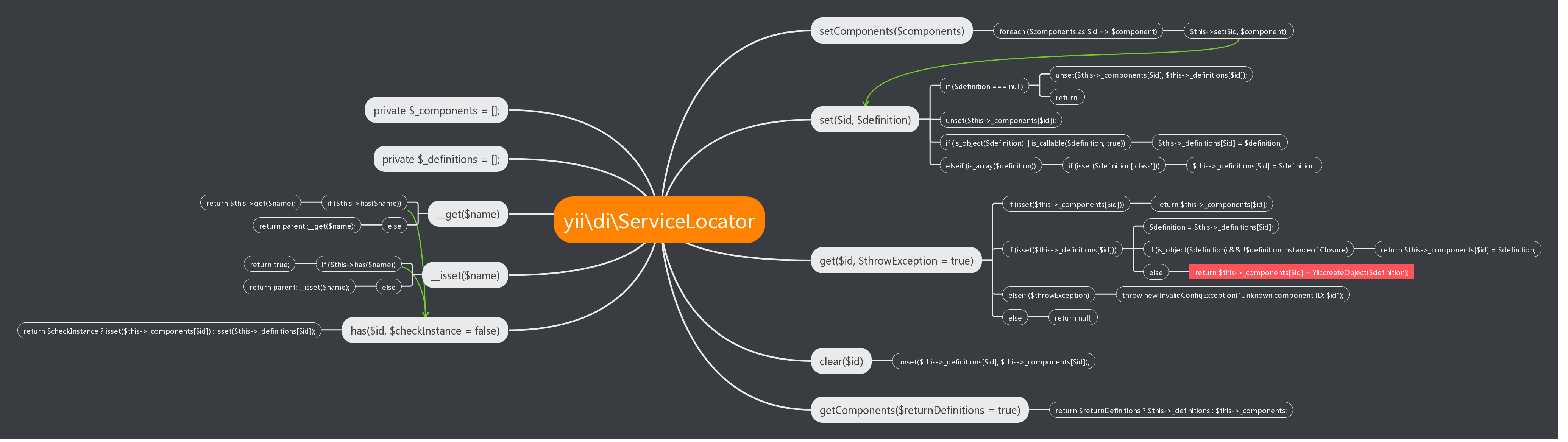
在Yii中Service Locator由 yii\di\ServiceLocator 来实现。 从代码组织上,Yii将Service Locator放到与DI同一层次来对待, 都组织在 yii\di 命名空间下。 下面是Service Locator的源代码:
<?php
namespace yii\di;
use Yii;
use Closure;
use yii\base\Component;
use yii\base\InvalidConfigException;
/**
* ServiceLocator implements a [service locator](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Service_locator_pattern).
*
* To use ServiceLocator, you first need to register component IDs with the corresponding component
* definitions with the locator by calling [[set()]] or [[setComponents()]].
* You can then call [[get()]] to retrieve a component with the specified ID. The locator will automatically
* instantiate and configure the component according to the definition.
*
* For example,
*
* ---php
* $locator = new \yii\di\ServiceLocator;
* $locator->setComponents([
* 'db' => [
* 'class' => 'yii\db\Connection',
* 'dsn' => 'sqlite:path/to/file.db',
* ],
* 'cache' => [
* 'class' => 'yii\caching\DbCache',
* 'db' => 'db',
* ],
* ]);
*
* $db = $locator->get('db'); // or $locator->db
* $cache = $locator->get('cache'); // or $locator->cache
* ---
*
* Because [[\yii\base\Module]] extends from ServiceLocator, modules and the application are all service locators.
*
* For more details and usage information on ServiceLocator, see the [guide article on service locators](guide:concept-service-locator).
*
* @property array $components The list of the component definitions or the loaded component instances (ID =>
* definition or instance).
*
*/
class ServiceLocator extends Component
{
/**
* 用于缓存服务、组件等的实例
* @var array shared component instances indexed by their IDs
*/
private $_components = [];
/**
* 用于保存服务和组件的定义,通常为配置数组,可以用来创建具体的实例
* @var array component definitions indexed by their IDs
*/
private $_definitions = [];
/**
* 重载了 getter 方法,使得访问服务和组件就跟访问类的属性一样。同时,也保留了原来Component的 getter所具有的功能。
* 请留意,ServiceLocator 并未重载 __set(),仍然使用 yii\base\Component::__set()
* Getter magic method.
* This method is overridden to support accessing components like reading properties.
* @param string $name component or property name
* @return mixed the named property value
*/
public function __get($name)
{
if ($this->has($name)) {
return $this->get($name);
} else {
return parent::__get($name);
}
}
/**
* 对比Component,增加了对是否具有某个服务和组件的判断。
* Checks if a property value is null.
* This method overrides the parent implementation by checking if the named component is loaded.
* @param string $name the property name or the event name
* @return bool whether the property value is null
*/
public function __isset($name)
{
if ($this->has($name)) {
return true;
} else {
return parent::__isset($name);
}
}
/**
* 当 $checkInstance === false 时,用于判断是否已经定义了某个服务或组件
* 当 $checkInstance === true 时,用于判断是否已经有了某个服务或组件的实例
* Returns a value indicating whether the locator has the specified component definition or has instantiated the component.
* This method may return different results depending on the value of `$checkInstance`.
*
* - If `$checkInstance` is false (default), the method will return a value indicating whether the locator has the specified
* component definition.
* - If `$checkInstance` is true, the method will return a value indicating whether the locator has
* instantiated the specified component.
*
* @param string $id component ID (e.g. `db`).
* @param bool $checkInstance whether the method should check if the component is shared and instantiated.
* @return bool whether the locator has the specified component definition or has instantiated the component.
* @see set()
*/
public function has($id, $checkInstance = false)
{
return $checkInstance ? isset($this->_components[$id]) : isset($this->_definitions[$id]);
}
/**
* 根据 $id 获取对应的服务或组件的实例
* Returns the component instance with the specified ID.
*
* @param string $id component ID (e.g. `db`).
* @param bool $throwException whether to throw an exception if `$id` is not registered with the locator before.
* @return object|null the component of the specified ID. If `$throwException` is false and `$id`
* is not registered before, null will be returned.
* @throws InvalidConfigException if `$id` refers to a nonexistent component ID
* @see has()
* @see set()
*/
public function get($id, $throwException = true)
{
if (isset($this->_components[$id])) {
return $this->_components[$id];
}
if (isset($this->_definitions[$id])) {
$definition = $this->_definitions[$id];
if (is_object($definition) && !$definition instanceof Closure) {
return $this->_components[$id] = $definition;
} else {
return $this->_components[$id] = Yii::createObject($definition);
}
} elseif ($throwException) {
throw new InvalidConfigException("Unknown component ID: $id");
} else {
return null;
}
}
/**
* 用于注册一个组件或服务,其中 $id 用于标识服务或组件。
* $definition 可以是一个类名,一个配置数组,一个PHP callable,或者一个对象
* Registers a component definition with this locator.
*
* For example,
*
* ---php
* // a class name
* $locator->set('cache', 'yii\caching\FileCache');
*
* // a configuration array
* $locator->set('db', [
* 'class' => 'yii\db\Connection',
* 'dsn' => 'mysql:host=127.0.0.1;dbname=demo',
* 'username' => 'root',
* 'password' => '',
* 'charset' => 'utf8',
* ]);
*
* // an anonymous function
* $locator->set('cache', function ($params) {
* return new \yii\caching\FileCache;
* });
*
* // an instance
* $locator->set('cache', new \yii\caching\FileCache);
* ---
*
* If a component definition with the same ID already exists, it will be overwritten.
*
* @param string $id component ID (e.g. `db`).
* @param mixed $definition the component definition to be registered with this locator.
* It can be one of the following:
*
* - a class name
* - a configuration array: the array contains name-value pairs that will be used to
* initialize the property values of the newly created object when [[get()]] is called.
* The `class` element is required and stands for the the class of the object to be created.
* - a PHP callable: either an anonymous function or an array representing a class method (e.g. `['Foo', 'bar']`).
* The callable will be called by [[get()]] to return an object associated with the specified component ID.
* - an object: When [[get()]] is called, this object will be returned.
*
* @throws InvalidConfigException if the definition is an invalid configuration array
*/
public function set($id, $definition)
{
if ($definition === null) {
unset($this->_components[$id], $this->_definitions[$id]);
return;
}
unset($this->_components[$id]);
if (is_object($definition) || is_callable($definition, true)) {
// an object, a class name, or a PHP callable
$this->_definitions[$id] = $definition;
} elseif (is_array($definition)) {
// a configuration array
if (isset($definition['class'])) {
$this->_definitions[$id] = $definition;
} else {
throw new InvalidConfigException("The configuration for the \"$id\" component must contain a \"class\" element.");
}
} else {
throw new InvalidConfigException("Unexpected configuration type for the \"$id\" component: " . gettype($definition));
}
}
/**
* 删除一个服务或组件
* Removes the component from the locator.
* @param string $id the component ID
*/
public function clear($id)
{
unset($this->_definitions[$id], $this->_components[$id]);
}
/**
* 用于返回Service Locator的 $_components 数组或 $_definitions 数组,同时也是 components 属性的getter函数
* Returns the list of the component definitions or the loaded component instances.
* @param bool $returnDefinitions whether to return component definitions instead of the loaded component instances.
* @return array the list of the component definitions or the loaded component instances (ID => definition or instance).
*/
public function getComponents($returnDefinitions = true)
{
return $returnDefinitions ? $this->_definitions : $this->_components;
}
/**
* 批量方式注册服务或组件,同时也是 components 属性的setter函数
* Registers a set of component definitions in this locator.
*
* This is the bulk version of [[set()]]. The parameter should be an array
* whose keys are component IDs and values the corresponding component definitions.
*
* For more details on how to specify component IDs and definitions, please refer to [[set()]].
*
* If a component definition with the same ID already exists, it will be overwritten.
*
* The following is an example for registering two component definitions:
*
* ---php
* [
* 'db' => [
* 'class' => 'yii\db\Connection',
* 'dsn' => 'sqlite:path/to/file.db',
* ],
* 'cache' => [
* 'class' => 'yii\caching\DbCache',
* 'db' => 'db',
* ],
* ]
* ---
*
* @param array $components component definitions or instances
*/
public function setComponents($components)
{
foreach ($components as $id => $component) {
$this->set($id, $component);
}
}
}
代码可以看出,Service Locator继承自 yii\base\Component ,Component 是Yii中的一个基础类, 提供了属性、事件、行为等基本功能。
Service Locator 通过 __get() 、 __isset() 、 has() 等方法, 扩展了 yii\base\Component 的最基本功能,提供了对于服务和组件的属性化支持。
从功能来看,Service Locator提供了注册服务和组件的 set() 、 setComponents() 等方法, 用于删除的 clear() 。 用于读取的 get() 和 getComponents() 等方法。
看到 setComponents() 和 getComponents() 可知, Service Locator还具有一个可读写的 components 属性。
Service Locator的数据结构
从上面的代码中,可以看到Service Locator维护了两个数组, $_components 和 $_definitions 。这两个数组均是以服务或组件的ID为键的数组。
其中, $_components 用于缓存Service Locator中的组件或服务的实例。 Service Locator 为其提供了getter和setter。 使其成为一个可读写的属性。 $_definitions 用于保存这些组件或服务的定义。这个定义可以是:
- 配置数组。在向Service Locator索要服务或组件时,这个数组会被用于创建服务或组件的实例。 与DI容器的要求类似,当定义是配置数组时, 要求配置数组必须要有 class 元素,表示要创建的是什么类。不然你让Yii调用哪个构造函数?
- PHP callable。每当向Service Locator索要实例时,这个PHP callable都会被调用,其返回值,就是所要的对象。 对于这个PHP callable有一定的形式要求,一是它要返回一个服务或组件的实例。 二是它不接受任何的参数。 至于具体原因,后面会讲到。
- 对象。这个更直接,每当你索要某个特定实例时,直接把这个对象给你就是了。
- 类名。即,使得 is_callable($definition, true) 为真的定义。
yii\di\ServiceLocator::set() 的代码:
public function set($id, $definition)
{
// 当定义为 null 时,表示要从Service Locator中删除一个服务或组件
if ($definition === null) {
unset($this->_components[$id], $this->_definitions[$id]);
return;
}
// 确保服务或组件ID的唯一性
unset($this->_components[$id]);
// 定义如果是个对象或PHP callable,或类名,直接作为定义保存
// 留意这里 is_callable的第二个参数为true,所以,类名也可以。
if (is_object($definition) || is_callable($definition, true)) {
// 定义的过程,只是写入了 $_definitions 数组
$this->_definitions[$id] = $definition;
// 定义如果是个数组,要确保数组中具有 class 元素
} elseif (is_array($definition)) {
if (isset($definition['class'])) {
// 定义的过程,只是写入了 $_definitions 数组
$this->_definitions[$id] = $definition;
} else {
throw new InvalidConfigException("The configuration for the \"$id\" component must contain a \"class\" element.");
}
// 这也不是,那也不是,那么就抛出异常吧
} else {
throw new InvalidConfigException("Unexpected configuration type for the \"$id\" component: ". gettype($definition));
}
}
服务或组件的ID在Service Locator中是唯一的,用于区别彼此。在任何情况下,Service Locator中同一ID只有一个实例、一个定义。 也就是说,Service Locator中,所有的服务和组件,只保存一个单例。 这也是正常的逻辑,既然称为服务定位器, 你只要给定一个ID,它必然返回一个确定的实例。这一点跟DI容器是一样的。
Service Locator 中ID仅起标识作用,可以是任意字符串,但通常用服务或组件名称来表示。 如,以 db 来表示数据库连接,以 cache 来表示缓存组件等。
至于批量注册的 yii\di\ServiceLocator::setCompoents() 只不过是简单地遍历数组,循环调用 set() 而已。
向Service Locator注册服务或组件,其实就是向 $_definitions 数组写入信息而已。
访问Service Locator中的服务
Service Locator重载了 __get() 使得可以像访问类的属性一样访问已经实例化好的服务和组件。 下面是重载的 __get() 方法:
public function __get($name)
{
// has() 方法就是判断 $_definitions 数组中是否已经保存了服务或组件的定义
// 请留意,这个时候服务或组件仅是完成定义,不一定已经实例化
if ($this->has($name)) {
// get() 方法用于返回服务或组件的实例
return $this->get($name);
// 未定义的服务或组件,那么视为正常的属性、行为,
// 调用 yii\base\Component::__get()
} else {
return parent::__get($name);
}
}
在注册好了服务或组件定义之后,就可以像访问属性一样访问这些服务(组件)。 前提是已经完成注册,不要求已经实例化。
访问这些服务或属性,被转换成了调用 yii\di\ServiceLocator::get() 来获取实例。 下面是使用这种形式访问服务或组件的例子:
// 创建一个Service Locator
$serviceLocator = new yii\di\ServiceLocator;
// 注册一个 cache 服务
$serviceLocator->set('cache', [
'class' => 'yii\cache\MemCache',
'servers' => [
... ...
],
]);
// 使用访问属性的方法访问这个 cache 服务
$serviceLocator->cache->flushValues();
// 上面的方法等效于下面这个
$serviceLocator->get('cache')->flushValues();
在Service Locator中,并未重载 __set() 。所以,Service Locator中的服务和组件看起来就好像只读属性一样。
要向Service Locator中“写”入服务和组件,没有 setter 可以使用,需要调用 yii\di\ServiceLocator::set() 对服务和组件进行注册。
这也是为了向 $_definitions 中写服务和组件的定义,不然怎么把属性和组件区分开呢。
通过Service Locator获取实例
与注册服务和组件的简单之极相反,Service Locator在创建获取服务或组件实例的过程要稍微复杂一点。 这一点和DI容器也是很像的。
Service Locator通过 yii\di\ServiceLocator::get() 来创建、获取服务或组件的实例:
public function get($id, $throwException = true)
{
// 如果已经有实例化好的组件或服务,直接使用缓存中的就OK了
if (isset($this->_components[$id])) {
return $this->_components[$id];
}
// 如果还没有实例化好,那么再看看是不是已经定义好
if (isset($this->_definitions[$id])) {
$definition = $this->_definitions[$id];
// 如果定义是个对象,且不是Closure对象,那么直接将这个对象返回
if (is_object($definition) && !$definition instanceof Closure) {
// 实例化后,保存进 $_components 数组中,以后就可以直接引用了
return $this->_components[$id] = $definition;
// 是个数组或者PHP callable,调用 Yii::createObject()来创建一个实例
} else {
// 实例化后,保存进 $_components 数组中,以后就可以直接引用了
return $this->_components[$id] = Yii::createObject($definition);
}
} elseif ($throwException) {
throw new InvalidConfigException("Unknown component ID: $id");
// 即没实例化,也没定义,万能的Yii也没办法通过一个任意的ID,
// 就给你找到想要的组件或服务呀,给你个 null 吧。 表示Service Locator中没有这个ID的服务或组件。
} else {
return null;
}
}
Service Locator创建获取服务或组件实例的过程是:
- 看看缓存数组 $_components 中有没有已经创建好的实例。有的话,皆大欢喜,直接用缓存中的就可以了。
- 缓存中没有的话,那就要从定义开始创建了。
- 如果服务或组件的定义是个对象,那么直接把这个对象作为服务或组件的实例返回就可以了。 但有一点要注意,当使用一个PHP callable定义一个服务或组件时,这个定义是一个Closure类的对象。 这种定义虽然也是对象,但是可不能把这种对象直接当成服务或组件的实例返回。
- 如果定义是一个数组或者一个PHP callable,那么把这个定义作为参数,调用 Yii::createObject() 来创建实例。
在Yii应用中使用Service Locator和DI容器
我们在讲DI容器时,提到了Yii中是把Service Locator和DI容器结合起来用的,Service Locator是建立在DI容器之上的。 那么一个Yii应用,是如何使用Service Locator和DI容器的呢?
DI容器的引入
我们知道,每个Yii应用都有一个入口脚本 index.php 。在其中,有一行不怎么显眼:
require(__DIR__ . '/../../vendor/yiisoft/yii2/Yii.php');
这一行看着普通,也就是引入一个 Yii.php 的文件:
<?php
require(__DIR__ . '/BaseYii.php');
class Yii extends \yii\BaseYii
{
}
spl_autoload_register(['Yii', 'autoload'], true, true);
Yii::$classMap = include(__DIR__ . '/classes.php');
// 重点看这里。创建一个DI 容器,并由 Yii::$container 引用
Yii::$container = new yii\di\Container;
Yii 是一个工具类,继承自 yii\BaseYii 。 但这里对父类的代码没有任何重载,意味之父类和子类在功能上其实是相同的。 但是,Yii提供了让你修改默认功能的机会。 就是自己写一个 Yii 类,来扩展、重载Yii默认的、由 yii\BaseYii 提供的特性和功能。
这里重点看最后一句代码,创建了一个DI容器,并由 Yii::$container 引用。 也就是说, Yii 类维护了一个DI容器, 这是DI容器开始介入整个应用的标志。 同时,这也意味着,在Yii应用中,我们可以随时使用 Yii::$container 来访问DI容器。 一般情况下,如无必须的理由,不要自己创建DI容器,使用 Yii::$container 完全足够。
Application的本质
再看看入口脚本 index.php 的最后两行:
$application = new yii\web\Application($config);
$application->run();
创建了一个 yii\web\Application 实例,并调用其 run() 方法。 那么,这个 yii\web\Application 是何方神圣? 首先, yii\web\Application 继承自 yii\base\Application ,这从 yii\web\Application 的代码可以看出来
class Application extends \yii\base\Application
{
... ...
}
而 yii\base\Application 又继承自 yii\base\Module ,说明所有的Application都是Module
abstract class Application extends Module
{
... ...
}
yii\base\Module 又继承自 yii\di\ServiceLocator
class Module extends ServiceLocator
{
... ...
}
所有的Module都是服务定位器Service Locator,因此,所有的Application也都是Service Locator。
同时,在Application的构造函数中, yii\base\Application::__construct()
public function __construct($config = [])
{
Yii::$app = $this;
... ...
}
第一行代码就把Application当前的实例,赋值给 Yii::$app 了。 这意味着Yii应用创建之后, 可以随时通过 Yii::$app 来访问应用自身,也就是访问Service Locator。
至此,DI容器有了,Service Locator也出现了。那么Yii是如何摆布这两者的呢?这两者又是如何千里姻缘一线牵的呢?
实例创建方法
Service Locator和DI容器的亲密关系就隐藏在 yii\di\ServiceLocator::get() 获取实例时, 调用的 Yii::createObject() 中。
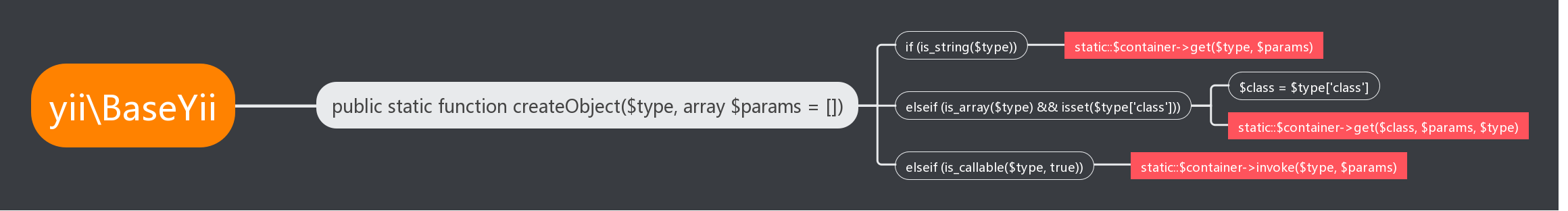
前面我们说到这个 Yii 继承自 yii\BaseYii ,因此这个函数实际上是 BaseYii::createObject() , 其代码如下:
// static::$container 就是上面说的引用了DI容器的静态变量
public static function createObject($type, array $params = [])
{
// 字符串,代表一个类名、接口名、别名。
if (is_string($type)) {
return static::$container->get($type, $params);
// 是个数组,代表配置数组,必须含有 class 元素。
} elseif (is_array($type) && isset($type['class'])) {
$class = $type['class'];
unset($type['class']);
// 调用DI容器的get() 来获取、创建实例
return static::$container->get($class, $params, $type);
// 是个PHP callable则调用其返回一个具体实例。
} elseif (is_callable($type, true)) {
// 是个PHP callable,那就调用它,并将其返回值作为服务或组件的实例返回
return call_user_func($type, $params);
// 是个数组但没有 class 元素,抛出异常
} elseif (is_array($type)) {
throw new InvalidConfigException('Object configuration must be an array containing a "class" element.');
// 其他情况,抛出异常
} else {
throw new InvalidConfigException("Unsupported configuration type: " . gettype($type));
}
}
这个 createObject() 提供了一个向DI容器获取实例的接口, 对于不同的定义,除了PHP callable外, createObject() 都是调用了DI容器的 yii\di\Container::get() , 来获取实例的。 Yii::createObject() 就是Service Locator和DI容器亲密关系的证明, 也是Service Locator构建于DI容器之上的证明。 而Yii中所有的Module, 包括Application都是Service Locator,因此,它们也都构建在DI容器之上。
同时,在Yii框架代码中,只要创建实例,就是调用 Yii::createObject() 这个方法来实现。 可以说,Yii中所有的实例(除了Application,DI容器自身等入口脚本中实例化的),都是通过DI容器来获取的。
同时,我们不难发现, Yii 的基类 yii\BaseYii ,所有的成员变量和方法都是静态的, 其中的DI容器是个静态成员变量 $container 。 因此,DI容器就形成了最常见形式的单例模式,在内存中仅有一份,所有的Service Locator (Module和Application)都共用这个DI容器。 这就节省了大量的内存空间和反复构造实例的时间。
更为重要的是,DI容器的单例化,使得Yii不同的模块共用组件成为可能。 可以想像,由于共用了DI容器,容器里面的内容也是共享的。 因此,你可以在A模块中改变某个组件的状态,而B模块中可以了解到这一状态变化。 但是,如果不采用单例模式, 而是每个模块(Module或Application)维护一个自己的DI容器, 要实现这一点难度会大得多。
所以,这种共享DI容器的设计,是必然的,合理的。
另外,前面我们讲到,当Service Locator中服务或组件的定义是一个PHP callable时,对其形式有一定要求。 一是返回一个实例,二是不接收任何参数。 这在 Yii::createObject() 中也可以看出来。
由于 Yii::createObject() 为 yii\di\ServiceLocator::get() 所调用,且没有提供第二参数,
因此,当使用 Service Locator获取实例时, Yii::createObject() 的 $params 参数为空。
因此,使用 call_user_func($type, $params) 调用这个PHP callable时, 这个PHP callable是接收不到任何参数的。
Yii创建实例的全过程
配置文件中有:
return [
'components' => [
'db' => [
'class' => 'yii\db\Connection',
'dsn' => 'mysql:host=localhost;dbname=yii2advanced',
'username' => 'root',
'password' => '',
'charset' => 'utf8',
],
'cache' => [
'class' => 'yii\caching\MemCache',
'servers' => [
[
'host' => 'cache1.digpage.com',
'port' => 11211,
'weight' => 60,
],
[
'host' => 'cache2.digpage.com',
'port' => 11211,
'weight' => 40,
],
],
],
... ...
],
];
这个数组会被 new yii\web\Application($config)
》 yii\base\Application->__construct($config)
-> yii\base\Component::__construct($config)
》 yii\base\Object::__construct($config)
-> Yii::configure($this, $config)
所调用:
public static function configure($object, $properties)
{
foreach ($properties as $name => $value) {
$object->$name = $value;
}
return $object;
}
然而components 属性不存在,就会使用__set() 方法,最后变成调用Application的 setComponents(),而setComponents在Service Locator下, 这也可以看到Application其实就是一个Service Locator。 setComponents()方法又会遍历传入的配置数组, 然后使用使用 Service Locator 的set() 方法注册服务。
到了这里,就可以了解到:每次在配置文件的 components 项写入配置信息, 最终都是在向Application这个 Service Locator注册服务。
让我们回顾一下,DI容器、Service Locator是如何配合使用的:
- Yii 类提供了一个静态的 $container 成员变量用于引用DI容器。 在入口脚本中,会创建一个DI容器,并赋值给这个 $container 。
- Service Locator通过 Yii::createObject() 来获取实例, 而这个 Yii::createObject() 是调用了DI容器的 yii\di\Container::get() 来向 Yii::$container 索要实例的。 因此,Service Locator最终是通过DI容器来创建、获取实例的。
- 所有的Module,包括Application都继承自 yii\di\ServiceLocator ,都是Service Locator。 因此,DI容器和Service Locator就构成了整个Yii的基础。
可能你会问,Service Locator在注册服务、组件时,又没有向DI容器$container注册依赖。那在 Yii::createObject()从 $container->get() 获取实例的时候, DI容器怎么解析依赖并创建实例呢?
在向DI容器索要一个没有注册过依赖的类型时, DI容器视为这个类型不依赖于任何类型可以直接创建, 或者这个类型的依赖信息容器本身可以通过Reflection API自动解析出来,不用提前注册。
否则DI就要写入依赖,写入依赖有两种方式:
- 第一种是直接用
Yii::$container->set()写入; - 第二种是写在config配置文件中,在
yii\base\Application::__construct($config)->preInit(&$config)时 会调用 ->setContainer($config['container'])->Yii::configure(Yii::$container, $config)写入$container。如
return [
'components' => [
'db' => [...],
'cache' => [...],
... ...
],
'container' => [
'definitions' => [
'yii\widgets\LinkPager' => ['maxButtonCount' => 5],
'yii\web\Request' => 'app\components\Request',
'yii\web\Response' => [
'class' => 'app\components\Response',
'format' => 'json'
],
],
'singletons' => [
'tempFileStorage' => [
['class' => 'app\storage\FileStorage'],
['/var/tempfiles']
],
],
],
... ...
];
yii\base\Application::__construct($config):
public function __construct($config = [])
{
Yii::$app = $this;
static::setInstance($this);
$this->state = self::STATE_BEGIN;
$this->preInit($config);
$this->registerErrorHandler($config);
Component::__construct($config);
}
yii\base\Application::preInit(&$config)
public function preInit(&$config)
{
if (!isset($config['id'])) {
throw new InvalidConfigException('The "id" configuration for the Application is required.');
}
if (isset($config['basePath'])) {
$this->setBasePath($config['basePath']);
unset($config['basePath']);
} else {
throw new InvalidConfigException('The "basePath" configuration for the Application is required.');
}
if (isset($config['vendorPath'])) {
$this->setVendorPath($config['vendorPath']);
unset($config['vendorPath']);
} else {
// set "@vendor"
$this->getVendorPath();
}
if (isset($config['runtimePath'])) {
$this->setRuntimePath($config['runtimePath']);
unset($config['runtimePath']);
} else {
// set "@runtime"
$this->getRuntimePath();
}
if (isset($config['timeZone'])) {
$this->setTimeZone($config['timeZone']);
unset($config['timeZone']);
} elseif (!ini_get('date.timezone')) {
$this->setTimeZone('UTC');
}
if (isset($config['container'])) {
$this->setContainer($config['container']);
unset($config['container']);
}
// merge core components with custom components
foreach ($this->coreComponents() as $id => $component) {
if (!isset($config['components'][$id])) {
$config['components'][$id] = $component;
} elseif (is_array($config['components'][$id]) && !isset($config['components'][$id]['class'])) {
$config['components'][$id]['class'] = $component['class'];
}
}
}
yii\base\Application::setContainer($config)
/**
* Configures [[Yii::$container]] with the $config.
*
* @param array $config values given in terms of name-value pairs
* @since 2.0.11
*/
public function setContainer($config)
{
Yii::configure(Yii::$container, $config);
}
有的版本看不到setContainer()方法,在项目中也没有搜到,应该是在后来发布的版本中被移除了。
源码
yii\di\ServiceLocator 类
<?php
/**
* @link http://www.yiiframework.com/
* @copyright Copyright (c) 2008 Yii Software LLC
* @license http://www.yiiframework.com/license/
*/
namespace yii\di;
use Closure;
use Yii;
use yii\base\Component;
use yii\base\InvalidConfigException;
/**
* ServiceLocator implements a [service locator](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Service_locator_pattern).
*
* To use ServiceLocator, you first need to register component IDs with the corresponding component
* definitions with the locator by calling [[set()]] or [[setComponents()]].
* You can then call [[get()]] to retrieve a component with the specified ID. The locator will automatically
* instantiate and configure the component according to the definition.
*
* For example,
*
*
* $locator = new \yii\di\ServiceLocator;
* $locator->setComponents([
* 'db' => [
* 'class' => 'yii\db\Connection',
* 'dsn' => 'sqlite:path/to/file.db',
* ],
* 'cache' => [
* 'class' => 'yii\caching\DbCache',
* 'db' => 'db',
* ],
* ]);
*
* $db = $locator->get('db'); // or $locator->db
* $cache = $locator->get('cache'); // or $locator->cache
*
*
* Because [[\yii\base\Module]] extends from ServiceLocator, modules and the application are all service locators.
* Modules add [tree traversal](guide:concept-service-locator#tree-traversal) for service resolution.
*
* For more details and usage information on ServiceLocator, see the [guide article on service locators](guide:concept-service-locator).
*
* @property array $components The list of the component definitions or the loaded component instances (ID =>
* definition or instance).
*
* @author Qiang Xue <qiang.xue@gmail.com>
* @since 2.0
*/
class ServiceLocator extends Component
{
/**
* @var array shared component instances indexed by their IDs
*/
private $_components = [];
/**
* @var array component definitions indexed by their IDs
*/
private $_definitions = [];
/**
* Getter magic method.
* This method is overridden to support accessing components like reading properties.
* @param string $name component or property name
* @return mixed the named property value
*/
public function __get($name)
{
if ($this->has($name)) {
return $this->get($name);
}
return parent::__get($name);
}
/**
* Checks if a property value is null.
* This method overrides the parent implementation by checking if the named component is loaded.
* @param string $name the property name or the event name
* @return bool whether the property value is null
*/
public function __isset($name)
{
if ($this->has($name)) {
return true;
}
return parent::__isset($name);
}
/**
* Returns a value indicating whether the locator has the specified component definition or has instantiated the component.
* This method may return different results depending on the value of `$checkInstance`.
*
* - If `$checkInstance` is false (default), the method will return a value indicating whether the locator has the specified
* component definition.
* - If `$checkInstance` is true, the method will return a value indicating whether the locator has
* instantiated the specified component.
*
* @param string $id component ID (e.g. `db`).
* @param bool $checkInstance whether the method should check if the component is shared and instantiated.
* @return bool whether the locator has the specified component definition or has instantiated the component.
* @see set()
*/
public function has($id, $checkInstance = false)
{
return $checkInstance ? isset($this->_components[$id]) : isset($this->_definitions[$id]);
}
/**
* Returns the component instance with the specified ID.
*
* @param string $id component ID (e.g. `db`).
* @param bool $throwException whether to throw an exception if `$id` is not registered with the locator before.
* @return object|null the component of the specified ID. If `$throwException` is false and `$id`
* is not registered before, null will be returned.
* @throws InvalidConfigException if `$id` refers to a nonexistent component ID
* @see has()
* @see set()
*/
public function get($id, $throwException = true)
{
if (isset($this->_components[$id])) {
return $this->_components[$id];
}
if (isset($this->_definitions[$id])) {
$definition = $this->_definitions[$id];
if (is_object($definition) && !$definition instanceof Closure) {
return $this->_components[$id] = $definition;
}
return $this->_components[$id] = Yii::createObject($definition);
} elseif ($throwException) {
throw new InvalidConfigException("Unknown component ID: $id");
}
return null;
}
/**
* Registers a component definition with this locator.
*
* For example,
*
* ```php
* // a class name
* $locator->set('cache', 'yii\caching\FileCache');
*
* // a configuration array
* $locator->set('db', [
* 'class' => 'yii\db\Connection',
* 'dsn' => 'mysql:host=127.0.0.1;dbname=demo',
* 'username' => 'root',
* 'password' => '',
* 'charset' => 'utf8',
* ]);
*
* // an anonymous function
* $locator->set('cache', function ($params) {
* return new \yii\caching\FileCache;
* });
*
* // an instance
* $locator->set('cache', new \yii\caching\FileCache);
* ```
*
* If a component definition with the same ID already exists, it will be overwritten.
*
* @param string $id component ID (e.g. `db`).
* @param mixed $definition the component definition to be registered with this locator.
* It can be one of the following:
*
* - a class name
* - a configuration array: the array contains name-value pairs that will be used to
* initialize the property values of the newly created object when [[get()]] is called.
* The `class` element is required and stands for the the class of the object to be created.
* - a PHP callable: either an anonymous function or an array representing a class method (e.g. `['Foo', 'bar']`).
* The callable will be called by [[get()]] to return an object associated with the specified component ID.
* - an object: When [[get()]] is called, this object will be returned.
*
* @throws InvalidConfigException if the definition is an invalid configuration array
*/
public function set($id, $definition)
{
unset($this->_components[$id]);
if ($definition === null) {
unset($this->_definitions[$id]);
return;
}
if (is_object($definition) || is_callable($definition, true)) {
// an object, a class name, or a PHP callable
$this->_definitions[$id] = $definition;
} elseif (is_array($definition)) {
// a configuration array
if (isset($definition['__class'])) {
$this->_definitions[$id] = $definition;
$this->_definitions[$id]['class'] = $definition['__class'];
unset($this->_definitions[$id]['__class']);
} elseif (isset($definition['class'])) {
$this->_definitions[$id] = $definition;
} else {
throw new InvalidConfigException("The configuration for the \"$id\" component must contain a \"class\" element.");
}
} else {
throw new InvalidConfigException("Unexpected configuration type for the \"$id\" component: " . gettype($definition));
}
}
/**
* Removes the component from the locator.
* @param string $id the component ID
*/
public function clear($id)
{
unset($this->_definitions[$id], $this->_components[$id]);
}
/**
* Returns the list of the component definitions or the loaded component instances.
* @param bool $returnDefinitions whether to return component definitions instead of the loaded component instances.
* @return array the list of the component definitions or the loaded component instances (ID => definition or instance).
*/
public function getComponents($returnDefinitions = true)
{
return $returnDefinitions ? $this->_definitions : $this->_components;
}
/**
* Registers a set of component definitions in this locator.
*
* This is the bulk version of [[set()]]. The parameter should be an array
* whose keys are component IDs and values the corresponding component definitions.
*
* For more details on how to specify component IDs and definitions, please refer to [[set()]].
*
* If a component definition with the same ID already exists, it will be overwritten.
*
* The following is an example for registering two component definitions:
*
* ```php
* [
* 'db' => [
* 'class' => 'yii\db\Connection',
* 'dsn' => 'sqlite:path/to/file.db',
* ],
* 'cache' => [
* 'class' => 'yii\caching\DbCache',
* 'db' => 'db',
* ],
* ]
* ```
*
* @param array $components component definitions or instances
*/
public function setComponents($components)
{
foreach ($components as $id => $component) {
$this->set($id, $component);
}
}
}
yii\di\Container 类
<?php
/**
* @link http://www.yiiframework.com/
* @copyright Copyright (c) 2008 Yii Software LLC
* @license http://www.yiiframework.com/license/
*/
namespace yii\di;
use ReflectionClass;
use ReflectionException;
use ReflectionNamedType;
use ReflectionParameter;
use Yii;
use yii\base\Component;
use yii\base\InvalidConfigException;
use yii\helpers\ArrayHelper;
/**
* Container implements a [dependency injection](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dependency_injection) container.
*
* A dependency injection (DI) container is an object that knows how to instantiate and configure objects and
* all their dependent objects. For more information about DI, please refer to
* [Martin Fowler's article](http://martinfowler.com/articles/injection.html).
*
* Container supports constructor injection as well as property injection.
*
* To use Container, you first need to set up the class dependencies by calling [[set()]].
* You then call [[get()]] to create a new class object. The Container will automatically instantiate
* dependent objects, inject them into the object being created, configure, and finally return the newly created object.
*
* By default, [[\Yii::$container]] refers to a Container instance which is used by [[\Yii::createObject()]]
* to create new object instances. You may use this method to replace the `new` operator
* when creating a new object, which gives you the benefit of automatic dependency resolution and default
* property configuration.
*
* Below is an example of using Container:
*
*
* namespace app\models;
*
* use yii\base\BaseObject;
* use yii\db\Connection;
* use yii\di\Container;
*
* interface UserFinderInterface
* {
* function findUser();
* }
*
* class UserFinder extends BaseObject implements UserFinderInterface
* {
* public $db;
*
* public function __construct(Connection $db, $config = [])
* {
* $this->db = $db;
* parent::__construct($config);
* }
*
* public function findUser()
* {
* }
* }
*
* class UserLister extends BaseObject
* {
* public $finder;
*
* public function __construct(UserFinderInterface $finder, $config = [])
* {
* $this->finder = $finder;
* parent::__construct($config);
* }
* }
*
* $container = new Container;
* $container->set('yii\db\Connection', [
* 'dsn' => '...',
* ]);
* $container->set('app\models\UserFinderInterface', [
* 'class' => 'app\models\UserFinder',
* ]);
* $container->set('userLister', 'app\models\UserLister');
*
* $lister = $container->get('userLister');
*
* // which is equivalent to:
*
* $db = new \yii\db\Connection(['dsn' => '...']);
* $finder = new UserFinder($db);
* $lister = new UserLister($finder);
*
*
* For more details and usage information on Container, see the [guide article on di-containers](guide:concept-di-container).
*
* @property-read array $definitions The list of the object definitions or the loaded shared objects (type or
* ID => definition or instance).
* @property-write bool $resolveArrays Whether to attempt to resolve elements in array dependencies.
*
* @author Qiang Xue <qiang.xue@gmail.com>
* @since 2.0
*/
class Container extends Component
{
/**
* @var array singleton objects indexed by their types
*/
private $_singletons = [];
/**
* @var array object definitions indexed by their types
*/
private $_definitions = [];
/**
* @var array constructor parameters indexed by object types
*/
private $_params = [];
/**
* @var array cached ReflectionClass objects indexed by class/interface names
*/
private $_reflections = [];
/**
* @var array cached dependencies indexed by class/interface names. Each class name
* is associated with a list of constructor parameter types or default values.
*/
private $_dependencies = [];
/**
* @var bool whether to attempt to resolve elements in array dependencies
*/
private $_resolveArrays = false;
/**
* Returns an instance of the requested class.
*
* You may provide constructor parameters (`$params`) and object configurations (`$config`)
* that will be used during the creation of the instance.
*
* If the class implements [[\yii\base\Configurable]], the `$config` parameter will be passed as the last
* parameter to the class constructor; Otherwise, the configuration will be applied *after* the object is
* instantiated.
*
* Note that if the class is declared to be singleton by calling [[setSingleton()]],
* the same instance of the class will be returned each time this method is called.
* In this case, the constructor parameters and object configurations will be used
* only if the class is instantiated the first time.
*
* @param string|Instance $class the class Instance, name, or an alias name (e.g. `foo`) that was previously
* registered via [[set()]] or [[setSingleton()]].
* @param array $params a list of constructor parameter values. Use one of two definitions:
* - Parameters as name-value pairs, for example: `['posts' => PostRepository::class]`.
* - Parameters in the order they appear in the constructor declaration. If you want to skip some parameters,
* you should index the remaining ones with the integers that represent their positions in the constructor
* parameter list.
* Dependencies indexed by name and by position in the same array are not allowed.
* @param array $config a list of name-value pairs that will be used to initialize the object properties.
* @return object an instance of the requested class.
* @throws InvalidConfigException if the class cannot be recognized or correspond to an invalid definition
* @throws NotInstantiableException If resolved to an abstract class or an interface (since 2.0.9)
*/
public function get($class, $params = [], $config = [])
{
if ($class instanceof Instance) {
$class = $class->id;
}
if (isset($this->_singletons[$class])) {
// singleton
return $this->_singletons[$class];
} elseif (!isset($this->_definitions[$class])) {
return $this->build($class, $params, $config);
}
$definition = $this->_definitions[$class];
if (is_callable($definition, true)) {
$params = $this->resolveDependencies($this->mergeParams($class, $params));
$object = call_user_func($definition, $this, $params, $config);
} elseif (is_array($definition)) {
$concrete = $definition['class'];
unset($definition['class']);
$config = array_merge($definition, $config);
$params = $this->mergeParams($class, $params);
if ($concrete === $class) {
$object = $this->build($class, $params, $config);
} else {
$object = $this->get($concrete, $params, $config);
}
} elseif (is_object($definition)) {
return $this->_singletons[$class] = $definition;
} else {
throw new InvalidConfigException('Unexpected object definition type: ' . gettype($definition));
}
if (array_key_exists($class, $this->_singletons)) {
// singleton
$this->_singletons[$class] = $object;
}
return $object;
}
/**
* Registers a class definition with this container.
*
* For example,
*
* ```php
* // register a class name as is. This can be skipped.
* $container->set('yii\db\Connection');
*
* // register an interface
* // When a class depends on the interface, the corresponding class
* // will be instantiated as the dependent object
* $container->set('yii\mail\MailInterface', 'yii\swiftmailer\Mailer');
*
* // register an alias name. You can use $container->get('foo')
* // to create an instance of Connection
* $container->set('foo', 'yii\db\Connection');
*
* // register a class with configuration. The configuration
* // will be applied when the class is instantiated by get()
* $container->set('yii\db\Connection', [
* 'dsn' => 'mysql:host=127.0.0.1;dbname=demo',
* 'username' => 'root',
* 'password' => '',
* 'charset' => 'utf8',
* ]);
*
* // register an alias name with class configuration
* // In this case, a "class" element is required to specify the class
* $container->set('db', [
* 'class' => 'yii\db\Connection',
* 'dsn' => 'mysql:host=127.0.0.1;dbname=demo',
* 'username' => 'root',
* 'password' => '',
* 'charset' => 'utf8',
* ]);
*
* // register a PHP callable
* // The callable will be executed when $container->get('db') is called
* $container->set('db', function ($container, $params, $config) {
* return new \yii\db\Connection($config);
* });
* ```
*
* If a class definition with the same name already exists, it will be overwritten with the new one.
* You may use [[has()]] to check if a class definition already exists.
*
* @param string $class class name, interface name or alias name
* @param mixed $definition the definition associated with `$class`. It can be one of the following:
*
* - a PHP callable: The callable will be executed when [[get()]] is invoked. The signature of the callable
* should be `function ($container, $params, $config)`, where `$params` stands for the list of constructor
* parameters, `$config` the object configuration, and `$container` the container object. The return value
* of the callable will be returned by [[get()]] as the object instance requested.
* - a configuration array: the array contains name-value pairs that will be used to initialize the property
* values of the newly created object when [[get()]] is called. The `class` element stands for the
* the class of the object to be created. If `class` is not specified, `$class` will be used as the class name.
* - a string: a class name, an interface name or an alias name.
* @param array $params the list of constructor parameters. The parameters will be passed to the class
* constructor when [[get()]] is called.
* @return $this the container itself
*/
public function set($class, $definition = [], array $params = [])
{
$this->_definitions[$class] = $this->normalizeDefinition($class, $definition);
$this->_params[$class] = $params;
unset($this->_singletons[$class]);
return $this;
}
/**
* Registers a class definition with this container and marks the class as a singleton class.
*
* This method is similar to [[set()]] except that classes registered via this method will only have one
* instance. Each time [[get()]] is called, the same instance of the specified class will be returned.
*
* @param string $class class name, interface name or alias name
* @param mixed $definition the definition associated with `$class`. See [[set()]] for more details.
* @param array $params the list of constructor parameters. The parameters will be passed to the class
* constructor when [[get()]] is called.
* @return $this the container itself
* @see set()
*/
public function setSingleton($class, $definition = [], array $params = [])
{
$this->_definitions[$class] = $this->normalizeDefinition($class, $definition);
$this->_params[$class] = $params;
$this->_singletons[$class] = null;
return $this;
}
/**
* Returns a value indicating whether the container has the definition of the specified name.
* @param string $class class name, interface name or alias name
* @return bool Whether the container has the definition of the specified name.
* @see set()
*/
public function has($class)
{
return isset($this->_definitions[$class]);
}
/**
* Returns a value indicating whether the given name corresponds to a registered singleton.
* @param string $class class name, interface name or alias name
* @param bool $checkInstance whether to check if the singleton has been instantiated.
* @return bool whether the given name corresponds to a registered singleton. If `$checkInstance` is true,
* the method should return a value indicating whether the singleton has been instantiated.
*/
public function hasSingleton($class, $checkInstance = false)
{
return $checkInstance ? isset($this->_singletons[$class]) : array_key_exists($class, $this->_singletons);
}
/**
* Removes the definition for the specified name.
* @param string $class class name, interface name or alias name
*/
public function clear($class)
{
unset($this->_definitions[$class], $this->_singletons[$class]);
}
/**
* Normalizes the class definition.
* @param string $class class name
* @param string|array|callable $definition the class definition
* @return array the normalized class definition
* @throws InvalidConfigException if the definition is invalid.
*/
protected function normalizeDefinition($class, $definition)
{
if (empty($definition)) {
return ['class' => $class];
} elseif (is_string($definition)) {
return ['class' => $definition];
} elseif ($definition instanceof Instance) {
return ['class' => $definition->id];
} elseif (is_callable($definition, true) || is_object($definition)) {
return $definition;
} elseif (is_array($definition)) {
if (!isset($definition['class']) && isset($definition['__class'])) {
$definition['class'] = $definition['__class'];
unset($definition['__class']);
}
if (!isset($definition['class'])) {
if (strpos($class, '\\') !== false) {
$definition['class'] = $class;
} else {
throw new InvalidConfigException('A class definition requires a "class" member.');
}
}
return $definition;
}
throw new InvalidConfigException("Unsupported definition type for \"$class\": " . gettype($definition));
}
/**
* Returns the list of the object definitions or the loaded shared objects.
* @return array the list of the object definitions or the loaded shared objects (type or ID => definition or instance).
*/
public function getDefinitions()
{
return $this->_definitions;
}
/**
* Creates an instance of the specified class.
* This method will resolve dependencies of the specified class, instantiate them, and inject
* them into the new instance of the specified class.
* @param string $class the class name
* @param array $params constructor parameters
* @param array $config configurations to be applied to the new instance
* @return object the newly created instance of the specified class
* @throws NotInstantiableException If resolved to an abstract class or an interface (since 2.0.9)
*/
protected function build($class, $params, $config)
{
/* @var $reflection ReflectionClass */
list($reflection, $dependencies) = $this->getDependencies($class);
$addDependencies = [];
if (isset($config['__construct()'])) {
$addDependencies = $config['__construct()'];
unset($config['__construct()']);
}
foreach ($params as $index => $param) {
$addDependencies[$index] = $param;
}
$this->validateDependencies($addDependencies);
if ($addDependencies && is_int(key($addDependencies))) {
$dependencies = array_values($dependencies);
$dependencies = $this->mergeDependencies($dependencies, $addDependencies);
} else {
$dependencies = $this->mergeDependencies($dependencies, $addDependencies);
$dependencies = array_values($dependencies);
}
$dependencies = $this->resolveDependencies($dependencies, $reflection);
if (!$reflection->isInstantiable()) {
throw new NotInstantiableException($reflection->name);
}
if (empty($config)) {
return $reflection->newInstanceArgs($dependencies);
}
$config = $this->resolveDependencies($config);
if (!empty($dependencies) && $reflection->implementsInterface('yii\base\Configurable')) {
// set $config as the last parameter (existing one will be overwritten)
$dependencies[count($dependencies) - 1] = $config;
return $reflection->newInstanceArgs($dependencies);
}
$object = $reflection->newInstanceArgs($dependencies);
foreach ($config as $name => $value) {
$object->$name = $value;
}
return $object;
}
/**
* @param array $a
* @param array $b
* @return array
*/
private function mergeDependencies($a, $b)
{
foreach ($b as $index => $dependency) {
$a[$index] = $dependency;
}
return $a;
}
/**
* @param array $parameters
* @throws InvalidConfigException
*/
private function validateDependencies($parameters)
{
$hasStringParameter = false;
$hasIntParameter = false;
foreach ($parameters as $index => $parameter) {
if (is_string($index)) {
$hasStringParameter = true;
if ($hasIntParameter) {
break;
}
} else {
$hasIntParameter = true;
if ($hasStringParameter) {
break;
}
}
}
if ($hasIntParameter && $hasStringParameter) {
throw new InvalidConfigException(
'Dependencies indexed by name and by position in the same array are not allowed.'
);
}
}
/**
* Merges the user-specified constructor parameters with the ones registered via [[set()]].
* @param string $class class name, interface name or alias name
* @param array $params the constructor parameters
* @return array the merged parameters
*/
protected function mergeParams($class, $params)
{
if (empty($this->_params[$class])) {
return $params;
} elseif (empty($params)) {
return $this->_params[$class];
}
$ps = $this->_params[$class];
foreach ($params as $index => $value) {
$ps[$index] = $value;
}
return $ps;
}
/**
* Returns the dependencies of the specified class.
* @param string $class class name, interface name or alias name
* @return array the dependencies of the specified class.
* @throws NotInstantiableException if a dependency cannot be resolved or if a dependency cannot be fulfilled.
*/
protected function getDependencies($class)
{
if (isset($this->_reflections[$class])) {
return [$this->_reflections[$class], $this->_dependencies[$class]];
}
$dependencies = [];
try {
$reflection = new ReflectionClass($class);
} catch (\ReflectionException $e) {
throw new NotInstantiableException(
$class,
'Failed to instantiate component or class "' . $class . '".',
0,
$e
);
}
$constructor = $reflection->getConstructor();
if ($constructor !== null) {
foreach ($constructor->getParameters() as $param) {
if (PHP_VERSION_ID >= 50600 && $param->isVariadic()) {
break;
}
if (PHP_VERSION_ID >= 80000) {
$c = $param->getType();
$isClass = false;
if ($c instanceof ReflectionNamedType) {
$isClass = !$c->isBuiltin();
}
} else {
try {
$c = $param->getClass();
} catch (ReflectionException $e) {
if (!$this->isNulledParam($param)) {
$notInstantiableClass = null;
if (PHP_VERSION_ID >= 70000) {
$type = $param->getType();
if ($type instanceof ReflectionNamedType) {
$notInstantiableClass = $type->getName();
}
}
throw new NotInstantiableException(
$notInstantiableClass,
$notInstantiableClass === null ? 'Can not instantiate unknown class.' : null
);
} else {
$c = null;
}
}
$isClass = $c !== null;
}
$className = $isClass ? $c->getName() : null;
if ($className !== null) {
$dependencies[$param->getName()] = Instance::of($className, $this->isNulledParam($param));
} else {
$dependencies[$param->getName()] = $param->isDefaultValueAvailable()
? $param->getDefaultValue()
: null;
}
}
}
$this->_reflections[$class] = $reflection;
$this->_dependencies[$class] = $dependencies;
return [$reflection, $dependencies];
}
/**
* @param ReflectionParameter $param
* @return bool
*/
private function isNulledParam($param)
{
return $param->isOptional() || (PHP_VERSION_ID >= 70100 && $param->getType()->allowsNull());
}
/**
* Resolves dependencies by replacing them with the actual object instances.
* @param array $dependencies the dependencies
* @param ReflectionClass $reflection the class reflection associated with the dependencies
* @return array the resolved dependencies
* @throws InvalidConfigException if a dependency cannot be resolved or if a dependency cannot be fulfilled.
*/
protected function resolveDependencies($dependencies, $reflection = null)
{
foreach ($dependencies as $index => $dependency) {
if ($dependency instanceof Instance) {
if ($dependency->id !== null) {
$dependencies[$index] = $dependency->get($this);
} elseif ($reflection !== null) {
$name = $reflection->getConstructor()->getParameters()[$index]->getName();
$class = $reflection->getName();
throw new InvalidConfigException("Missing required parameter \"$name\" when instantiating \"$class\".");
}
} elseif ($this->_resolveArrays && is_array($dependency)) {
$dependencies[$index] = $this->resolveDependencies($dependency, $reflection);
}
}
return $dependencies;
}
/**
* Invoke a callback with resolving dependencies in parameters.
*
* This method allows invoking a callback and let type hinted parameter names to be
* resolved as objects of the Container. It additionally allows calling function using named parameters.
*
* For example, the following callback may be invoked using the Container to resolve the formatter dependency:
*
* ```php
* $formatString = function($string, \yii\i18n\Formatter $formatter) {
* // ...
* }
* Yii::$container->invoke($formatString, ['string' => 'Hello World!']);
* ```
*
* This will pass the string `'Hello World!'` as the first param, and a formatter instance created
* by the DI container as the second param to the callable.
*
* @param callable $callback callable to be invoked.
* @param array $params The array of parameters for the function.
* This can be either a list of parameters, or an associative array representing named function parameters.
* @return mixed the callback return value.
* @throws InvalidConfigException if a dependency cannot be resolved or if a dependency cannot be fulfilled.
* @throws NotInstantiableException If resolved to an abstract class or an interface (since 2.0.9)
* @since 2.0.7
*/
public function invoke(callable $callback, $params = [])
{
return call_user_func_array($callback, $this->resolveCallableDependencies($callback, $params));
}
/**
* Resolve dependencies for a function.
*
* This method can be used to implement similar functionality as provided by [[invoke()]] in other
* components.
*
* @param callable $callback callable to be invoked.
* @param array $params The array of parameters for the function, can be either numeric or associative.
* @return array The resolved dependencies.
* @throws InvalidConfigException if a dependency cannot be resolved or if a dependency cannot be fulfilled.
* @throws NotInstantiableException If resolved to an abstract class or an interface (since 2.0.9)
* @since 2.0.7
*/
public function resolveCallableDependencies(callable $callback, $params = [])
{
if (is_array($callback)) {
$reflection = new \ReflectionMethod($callback[0], $callback[1]);
} elseif (is_object($callback) && !$callback instanceof \Closure) {
$reflection = new \ReflectionMethod($callback, '__invoke');
} else {
$reflection = new \ReflectionFunction($callback);
}
$args = [];
$associative = ArrayHelper::isAssociative($params);
foreach ($reflection->getParameters() as $param) {
$name = $param->getName();
if (PHP_VERSION_ID >= 80000) {
$class = $param->getType();
if ($class instanceof \ReflectionUnionType || (PHP_VERSION_ID >= 80100 && $class instanceof \ReflectionIntersectionType)) {
$isClass = false;
foreach ($class->getTypes() as $type) {
if (!$type->isBuiltin()) {
$class = $type;
$isClass = true;
break;
}
}
} else {
$isClass = $class !== null && !$class->isBuiltin();
}
} else {
$class = $param->getClass();
$isClass = $class !== null;
}
if ($isClass) {
$className = $class->getName();
if (PHP_VERSION_ID >= 50600 && $param->isVariadic()) {
$args = array_merge($args, array_values($params));
break;
}
if ($associative && isset($params[$name]) && $params[$name] instanceof $className) {
$args[] = $params[$name];
unset($params[$name]);
} elseif (!$associative && isset($params[0]) && $params[0] instanceof $className) {
$args[] = array_shift($params);
} elseif (isset(Yii::$app) && Yii::$app->has($name) && ($obj = Yii::$app->get($name)) instanceof $className) {
$args[] = $obj;
} else {
// If the argument is optional we catch not instantiable exceptions
try {
$args[] = $this->get($className);
} catch (NotInstantiableException $e) {
if ($param->isDefaultValueAvailable()) {
$args[] = $param->getDefaultValue();
} else {
throw $e;
}
}
}
} elseif ($associative && isset($params[$name])) {
$args[] = $params[$name];
unset($params[$name]);
} elseif (!$associative && count($params)) {
$args[] = array_shift($params);
} elseif ($param->isDefaultValueAvailable()) {
$args[] = $param->getDefaultValue();
} elseif (!$param->isOptional()) {
$funcName = $reflection->getName();
throw new InvalidConfigException("Missing required parameter \"$name\" when calling \"$funcName\".");
}
}
foreach ($params as $value) {
$args[] = $value;
}
return $args;
}
/**
* Registers class definitions within this container.
*
* @param array $definitions array of definitions. There are two allowed formats of array.
* The first format:
* - key: class name, interface name or alias name. The key will be passed to the [[set()]] method
* as a first argument `$class`.
* - value: the definition associated with `$class`. Possible values are described in
* [[set()]] documentation for the `$definition` parameter. Will be passed to the [[set()]] method
* as the second argument `$definition`.
*
* Example:
* ```php
* $container->setDefinitions([
* 'yii\web\Request' => 'app\components\Request',
* 'yii\web\Response' => [
* 'class' => 'app\components\Response',
* 'format' => 'json'
* ],
* 'foo\Bar' => function () {
* $qux = new Qux;
* $foo = new Foo($qux);
* return new Bar($foo);
* }
* ]);
* ```
*
* The second format:
* - key: class name, interface name or alias name. The key will be passed to the [[set()]] method
* as a first argument `$class`.
* - value: array of two elements. The first element will be passed the [[set()]] method as the
* second argument `$definition`, the second one — as `$params`.
*
* Example:
* ```php
* $container->setDefinitions([
* 'foo\Bar' => [
* ['class' => 'app\Bar'],
* [Instance::of('baz')]
* ]
* ]);
* ```
*
* @see set() to know more about possible values of definitions
* @since 2.0.11
*/
public function setDefinitions(array $definitions)
{
foreach ($definitions as $class => $definition) {
if (is_array($definition) && count($definition) === 2 && array_values($definition) === $definition && is_array($definition[1])) {
$this->set($class, $definition[0], $definition[1]);
continue;
}
$this->set($class, $definition);
}
}
/**
* Registers class definitions as singletons within this container by calling [[setSingleton()]].
*
* @param array $singletons array of singleton definitions. See [[setDefinitions()]]
* for allowed formats of array.
*
* @see setDefinitions() for allowed formats of $singletons parameter
* @see setSingleton() to know more about possible values of definitions
* @since 2.0.11
*/
public function setSingletons(array $singletons)
{
foreach ($singletons as $class => $definition) {
if (is_array($definition) && count($definition) === 2 && array_values($definition) === $definition) {
$this->setSingleton($class, $definition[0], $definition[1]);
continue;
}
$this->setSingleton($class, $definition);
}
}
/**
* @param bool $value whether to attempt to resolve elements in array dependencies
* @since 2.0.37
*/
public function setResolveArrays($value)
{
$this->_resolveArrays = (bool) $value;
}
}
yii\BaseYii 类
<?php
/**
* @link http://www.yiiframework.com/
* @copyright Copyright (c) 2008 Yii Software LLC
* @license http://www.yiiframework.com/license/
*/
namespace yii;
use yii\base\InvalidArgumentException;
use yii\base\InvalidConfigException;
use yii\base\UnknownClassException;
use yii\di\Container;
use yii\log\Logger;
/**
* Gets the application start timestamp.
*/
defined('YII_BEGIN_TIME') or define('YII_BEGIN_TIME', microtime(true));
/**
* This constant defines the framework installation directory.
*/
defined('YII2_PATH') or define('YII2_PATH', __DIR__);
/**
* This constant defines whether the application should be in debug mode or not. Defaults to false.
*/
defined('YII_DEBUG') or define('YII_DEBUG', false);
/**
* This constant defines in which environment the application is running. Defaults to 'prod', meaning production environment.
* You may define this constant in the bootstrap script. The value could be 'prod' (production), 'dev' (development), 'test', 'staging', etc.
*/
defined('YII_ENV') or define('YII_ENV', 'prod');
/**
* Whether the application is running in the production environment.
*/
defined('YII_ENV_PROD') or define('YII_ENV_PROD', YII_ENV === 'prod');
/**
* Whether the application is running in the development environment.
*/
defined('YII_ENV_DEV') or define('YII_ENV_DEV', YII_ENV === 'dev');
/**
* Whether the application is running in the testing environment.
*/
defined('YII_ENV_TEST') or define('YII_ENV_TEST', YII_ENV === 'test');
/**
* This constant defines whether error handling should be enabled. Defaults to true.
*/
defined('YII_ENABLE_ERROR_HANDLER') or define('YII_ENABLE_ERROR_HANDLER', true);
/**
* BaseYii is the core helper class for the Yii framework.
*
* Do not use BaseYii directly. Instead, use its child class [[\Yii]] which you can replace to
* customize methods of BaseYii.
*
* @author Qiang Xue <qiang.xue@gmail.com>
* @since 2.0
*/
class BaseYii
{
/**
* @var array class map used by the Yii autoloading mechanism.
* The array keys are the class names (without leading backslashes), and the array values
* are the corresponding class file paths (or [path aliases](guide:concept-aliases)). This property mainly affects
* how [[autoload()]] works.
* @see autoload()
*/
public static $classMap = [];
/**
* @var \yii\console\Application|\yii\web\Application|\yii\base\Application the application instance
*/
public static $app;
/**
* @var array registered path aliases
* @see getAlias()
* @see setAlias()
*/
public static $aliases = ['@yii' => __DIR__];
/**
* @var Container the dependency injection (DI) container used by [[createObject()]].
* You may use [[Container::set()]] to set up the needed dependencies of classes and
* their initial property values.
* @see createObject()
* @see Container
*/
public static $container;
/**
* Returns a string representing the current version of the Yii framework.
* @return string the version of Yii framework
*/
public static function getVersion()
{
return '2.0.45';
}
/**
* Translates a path alias into an actual path.
*
* The translation is done according to the following procedure:
*
* 1. If the given alias does not start with '@', it is returned back without change;
* 2. Otherwise, look for the longest registered alias that matches the beginning part
* of the given alias. If it exists, replace the matching part of the given alias with
* the corresponding registered path.
* 3. Throw an exception or return false, depending on the `$throwException` parameter.
*
* For example, by default '@yii' is registered as the alias to the Yii framework directory,
* say '/path/to/yii'. The alias '@yii/web' would then be translated into '/path/to/yii/web'.
*
* If you have registered two aliases '@foo' and '@foo/bar'. Then translating '@foo/bar/config'
* would replace the part '@foo/bar' (instead of '@foo') with the corresponding registered path.
* This is because the longest alias takes precedence.
*
* However, if the alias to be translated is '@foo/barbar/config', then '@foo' will be replaced
* instead of '@foo/bar', because '/' serves as the boundary character.
*
* Note, this method does not check if the returned path exists or not.
*
* See the [guide article on aliases](guide:concept-aliases) for more information.
*
* @param string $alias the alias to be translated.
* @param bool $throwException whether to throw an exception if the given alias is invalid.
* If this is false and an invalid alias is given, false will be returned by this method.
* @return string|false the path corresponding to the alias, false if the root alias is not previously registered.
* @throws InvalidArgumentException if the alias is invalid while $throwException is true.
* @see setAlias()
*/
public static function getAlias($alias, $throwException = true)
{
if (strncmp((string)$alias, '@', 1) !== 0) {
// not an alias
return $alias;
}
$pos = strpos($alias, '/');
$root = $pos === false ? $alias : substr($alias, 0, $pos);
if (isset(static::$aliases[$root])) {
if (is_string(static::$aliases[$root])) {
return $pos === false ? static::$aliases[$root] : static::$aliases[$root] . substr($alias, $pos);
}
foreach (static::$aliases[$root] as $name => $path) {
if (strpos($alias . '/', $name . '/') === 0) {
return $path . substr($alias, strlen($name));
}
}
}
if ($throwException) {
throw new InvalidArgumentException("Invalid path alias: $alias");
}
return false;
}
/**
* Returns the root alias part of a given alias.
* A root alias is an alias that has been registered via [[setAlias()]] previously.
* If a given alias matches multiple root aliases, the longest one will be returned.
* @param string $alias the alias
* @return string|false the root alias, or false if no root alias is found
*/
public static function getRootAlias($alias)
{
$pos = strpos($alias, '/');
$root = $pos === false ? $alias : substr($alias, 0, $pos);
if (isset(static::$aliases[$root])) {
if (is_string(static::$aliases[$root])) {
return $root;
}
foreach (static::$aliases[$root] as $name => $path) {
if (strpos($alias . '/', $name . '/') === 0) {
return $name;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* Registers a path alias.
*
* A path alias is a short name representing a long path (a file path, a URL, etc.)
* For example, we use '@yii' as the alias of the path to the Yii framework directory.
*
* A path alias must start with the character '@' so that it can be easily differentiated
* from non-alias paths.
*
* Note that this method does not check if the given path exists or not. All it does is
* to associate the alias with the path.
*
* Any trailing '/' and '\' characters in the given path will be trimmed.
*
* See the [guide article on aliases](guide:concept-aliases) for more information.
*
* @param string $alias the alias name (e.g. "@yii"). It must start with a '@' character.
* It may contain the forward-slash '/' which serves as a boundary character when performing
* alias translation by [[getAlias()]].
* @param string $path the path corresponding to the alias. If this is null, the alias will
* be removed. Trailing '/' and '\' characters will be trimmed. This can be
*
* - a directory or a file path (e.g. `/tmp`, `/tmp/main.txt`)
* - a URL (e.g. `http://www.yiiframework.com`)
* - a path alias (e.g. `@yii/base`). In this case, the path alias will be converted into the
* actual path first by calling [[getAlias()]].
*
* @throws InvalidArgumentException if $path is an invalid alias.
* @see getAlias()
*/
public static function setAlias($alias, $path)
{
if (strncmp($alias, '@', 1)) {
$alias = '@' . $alias;
}
$pos = strpos($alias, '/');
$root = $pos === false ? $alias : substr($alias, 0, $pos);
if ($path !== null) {
$path = strncmp($path, '@', 1) ? rtrim($path, '\\/') : static::getAlias($path);
if (!isset(static::$aliases[$root])) {
if ($pos === false) {
static::$aliases[$root] = $path;
} else {
static::$aliases[$root] = [$alias => $path];
}
} elseif (is_string(static::$aliases[$root])) {
if ($pos === false) {
static::$aliases[$root] = $path;
} else {
static::$aliases[$root] = [
$alias => $path,
$root => static::$aliases[$root],
];
}
} else {
static::$aliases[$root][$alias] = $path;
krsort(static::$aliases[$root]);
}
} elseif (isset(static::$aliases[$root])) {
if (is_array(static::$aliases[$root])) {
unset(static::$aliases[$root][$alias]);
} elseif ($pos === false) {
unset(static::$aliases[$root]);
}
}
}
/**
* Class autoload loader.
*
* This method is invoked automatically when PHP sees an unknown class.
* The method will attempt to include the class file according to the following procedure:
*
* 1. Search in [[classMap]];
* 2. If the class is namespaced (e.g. `yii\base\Component`), it will attempt
* to include the file associated with the corresponding path alias
* (e.g. `@yii/base/Component.php`);
*
* This autoloader allows loading classes that follow the [PSR-4 standard](http://www.php-fig.org/psr/psr-4/)
* and have its top-level namespace or sub-namespaces defined as path aliases.
*
* Example: When aliases `@yii` and `@yii/bootstrap` are defined, classes in the `yii\bootstrap` namespace
* will be loaded using the `@yii/bootstrap` alias which points to the directory where the bootstrap extension
* files are installed and all classes from other `yii` namespaces will be loaded from the yii framework directory.
*
* Also the [guide section on autoloading](guide:concept-autoloading).
*
* @param string $className the fully qualified class name without a leading backslash "\"
* @throws UnknownClassException if the class does not exist in the class file
*/
public static function autoload($className)
{
if (isset(static::$classMap[$className])) {
$classFile = static::$classMap[$className];
if (strncmp($classFile, '@', 1) === 0) {
$classFile = static::getAlias($classFile);
}
} elseif (strpos($className, '\\') !== false) {
$classFile = static::getAlias('@' . str_replace('\\', '/', $className) . '.php', false);
if ($classFile === false || !is_file($classFile)) {
return;
}
} else {
return;
}
include $classFile;
if (YII_DEBUG && !class_exists($className, false) && !interface_exists($className, false) && !trait_exists($className, false)) {
throw new UnknownClassException("Unable to find '$className' in file: $classFile. Namespace missing?");
}
}
/**
* Creates a new object using the given configuration.
*
* You may view this method as an enhanced version of the `new` operator.
* The method supports creating an object based on a class name, a configuration array or
* an anonymous function.
*
* Below are some usage examples:
*
* ```php
* // create an object using a class name
* $object = Yii::createObject('yii\db\Connection');
*
* // create an object using a configuration array
* $object = Yii::createObject([
* 'class' => 'yii\db\Connection',
* 'dsn' => 'mysql:host=127.0.0.1;dbname=demo',
* 'username' => 'root',
* 'password' => '',
* 'charset' => 'utf8',
* ]);
*
* // create an object with two constructor parameters
* $object = \Yii::createObject('MyClass', [$param1, $param2]);
* ```
*
* Using [[\yii\di\Container|dependency injection container]], this method can also identify
* dependent objects, instantiate them and inject them into the newly created object.
*
* @param string|array|callable $type the object type. This can be specified in one of the following forms:
*
* - a string: representing the class name of the object to be created
* - a configuration array: the array must contain a `class` element which is treated as the object class,
* and the rest of the name-value pairs will be used to initialize the corresponding object properties
* - a PHP callable: either an anonymous function or an array representing a class method (`[$class or $object, $method]`).
* The callable should return a new instance of the object being created.
*
* @param array $params the constructor parameters
* @return object the created object
* @throws InvalidConfigException if the configuration is invalid.
* @see \yii\di\Container
*/
public static function createObject($type, array $params = [])
{
if (is_string($type)) {
return static::$container->get($type, $params);
}
if (is_callable($type, true)) {
return static::$container->invoke($type, $params);
}
if (!is_array($type)) {
throw new InvalidConfigException('Unsupported configuration type: ' . gettype($type));
}
if (isset($type['__class'])) {
$class = $type['__class'];
unset($type['__class'], $type['class']);
return static::$container->get($class, $params, $type);
}
if (isset($type['class'])) {
$class = $type['class'];
unset($type['class']);
return static::$container->get($class, $params, $type);
}
throw new InvalidConfigException('Object configuration must be an array containing a "class" or "__class" element.');
}
private static $_logger;
/**
* @return Logger message logger
*/
public static function getLogger()
{
if (self::$_logger !== null) {
return self::$_logger;
}
return self::$_logger = static::createObject('yii\log\Logger');
}
/**
* Sets the logger object.
* @param Logger $logger the logger object.
*/
public static function setLogger($logger)
{
self::$_logger = $logger;
}
/**
* Logs a debug message.
* Trace messages are logged mainly for development purposes to see
* the execution workflow of some code. This method will only log
* a message when the application is in debug mode.
* @param string|array $message the message to be logged. This can be a simple string or a more
* complex data structure, such as an array.
* @param string $category the category of the message.
* @since 2.0.14
*/
public static function debug($message, $category = 'application')
{
if (YII_DEBUG) {
static::getLogger()->log($message, Logger::LEVEL_TRACE, $category);
}
}
/**
* Alias of [[debug()]].
* @param string|array $message the message to be logged. This can be a simple string or a more
* complex data structure, such as an array.
* @param string $category the category of the message.
* @deprecated since 2.0.14. Use [[debug()]] instead.
*/
public static function trace($message, $category = 'application')
{
static::debug($message, $category);
}
/**
* Logs an error message.
* An error message is typically logged when an unrecoverable error occurs
* during the execution of an application.
* @param string|array $message the message to be logged. This can be a simple string or a more
* complex data structure, such as an array.
* @param string $category the category of the message.
*/
public static function error($message, $category = 'application')
{
static::getLogger()->log($message, Logger::LEVEL_ERROR, $category);
}
/**
* Logs a warning message.
* A warning message is typically logged when an error occurs while the execution
* can still continue.
* @param string|array $message the message to be logged. This can be a simple string or a more
* complex data structure, such as an array.
* @param string $category the category of the message.
*/
public static function warning($message, $category = 'application')
{
static::getLogger()->log($message, Logger::LEVEL_WARNING, $category);
}
/**
* Logs an informative message.
* An informative message is typically logged by an application to keep record of
* something important (e.g. an administrator logs in).
* @param string|array $message the message to be logged. This can be a simple string or a more
* complex data structure, such as an array.
* @param string $category the category of the message.
*/
public static function info($message, $category = 'application')
{
static::getLogger()->log($message, Logger::LEVEL_INFO, $category);
}
/**
* Marks the beginning of a code block for profiling.
*
* This has to be matched with a call to [[endProfile]] with the same category name.
* The begin- and end- calls must also be properly nested. For example,
*
* ```php
* \Yii::beginProfile('block1');
* // some code to be profiled
* \Yii::beginProfile('block2');
* // some other code to be profiled
* \Yii::endProfile('block2');
* \Yii::endProfile('block1');
* ```
* @param string $token token for the code block
* @param string $category the category of this log message
* @see endProfile()
*/
public static function beginProfile($token, $category = 'application')
{
static::getLogger()->log($token, Logger::LEVEL_PROFILE_BEGIN, $category);
}
/**
* Marks the end of a code block for profiling.
* This has to be matched with a previous call to [[beginProfile]] with the same category name.
* @param string $token token for the code block
* @param string $category the category of this log message
* @see beginProfile()
*/
public static function endProfile($token, $category = 'application')
{
static::getLogger()->log($token, Logger::LEVEL_PROFILE_END, $category);
}
/**
* Returns an HTML hyperlink that can be displayed on your Web page showing "Powered by Yii Framework" information.
* @return string an HTML hyperlink that can be displayed on your Web page showing "Powered by Yii Framework" information
* @deprecated since 2.0.14, this method will be removed in 2.1.0.
*/
public static function powered()
{
return \Yii::t('yii', 'Powered by {yii}', [
'yii' => '<a href="http://www.yiiframework.com/" rel="external">' . \Yii::t('yii',
'Yii Framework') . '</a>',
]);
}
/**
* Translates a message to the specified language.
*
* This is a shortcut method of [[\yii\i18n\I18N::translate()]].
*
* The translation will be conducted according to the message category and the target language will be used.
*
* You can add parameters to a translation message that will be substituted with the corresponding value after
* translation. The format for this is to use curly brackets around the parameter name as you can see in the following example:
*
* ```php
* $username = 'Alexander';
* echo \Yii::t('app', 'Hello, {username}!', ['username' => $username]);
* ```
*
* Further formatting of message parameters is supported using the [PHP intl extensions](https://www.php.net/manual/en/intro.intl.php)
* message formatter. See [[\yii\i18n\I18N::translate()]] for more details.
*
* @param string $category the message category.
* @param string $message the message to be translated.
* @param array $params the parameters that will be used to replace the corresponding placeholders in the message.
* @param string $language the language code (e.g. `en-US`, `en`). If this is null, the current
* [[\yii\base\Application::language|application language]] will be used.
* @return string the translated message.
*/
public static function t($category, $message, $params = [], $language = null)
{
if (static::$app !== null) {
return static::$app->getI18n()->translate($category, $message, $params, $language ?: static::$app->language);
}
$placeholders = [];
foreach ((array) $params as $name => $value) {
$placeholders['{' . $name . '}'] = $value;
}
return ($placeholders === []) ? $message : strtr($message, $placeholders);
}
/**
* Configures an object with the initial property values.
* @param object $object the object to be configured
* @param array $properties the property initial values given in terms of name-value pairs.
* @return object the object itself
*/
public static function configure($object, $properties)
{
foreach ($properties as $name => $value) {
$object->$name = $value;
}
return $object;
}
/**
* Returns the public member variables of an object.
* This method is provided such that we can get the public member variables of an object.
* It is different from "get_object_vars()" because the latter will return private
* and protected variables if it is called within the object itself.
* @param object $object the object to be handled
* @return array the public member variables of the object
*/
public static function getObjectVars($object)
{
return get_object_vars($object);
}
}
/vendor/yiisoft/yii2/Yii.php 文件
<?php
/**
* @link http://www.yiiframework.com/
* @copyright Copyright (c) 2008 Yii Software LLC
* @license http://www.yiiframework.com/license/
*/
require __DIR__ . '/BaseYii.php';
/**
* Yii is a helper class serving common framework functionalities.
*
* It extends from [[\yii\BaseYii]] which provides the actual implementation.
* By writing your own Yii class, you can customize some functionalities of [[\yii\BaseYii]].
*
* @author Qiang Xue <qiang.xue@gmail.com>
* @since 2.0
*/
class Yii extends \yii\BaseYii
{
}
spl_autoload_register(['Yii', 'autoload'], true, true);
Yii::$classMap = require __DIR__ . '/classes.php';
Yii::$container = new yii\di\Container();
参考资料
深入理解Yii2.0 » Yii 模式 » 服务定位器(Service Locator)
http://www.digpage.com/service_locator.html#service-locator
https://www.kancloud.cn/kancloud/yii-in-depth/50772
Closure 类 https://www.php.net/manual/zh/class.closure.php
is_callable https://www.php.net/manual/zh/function.is-callable.php
Yii 2.0 权威指南 关键概念(Key Concepts): 依赖注入容器(Dependency Injection Container) https://www.yiichina.com/doc/guide/2.0/concept-di-container
Yii 2.0 权威指南 关键概念(Key Concepts): 服务定位器(Service Locator) https://www.yiichina.com/doc/guide/2.0/concept-service-locator