正文
什么是算法
直白地说,算法就是任何明确定义的计算过程,它接收一些值或集合作为输入,并产生一些值或集合作为输出。这样,算法就是将输入转换为输出的一系列计算过程。 来源:Thomas H. Cormen, Chales E. Leiserson (2009), 《算法导论第三版》。
简而言之,我们可以说算法就是用来解决一个特定任务的一系列步骤(是的,不止计算机在使用算法,人类也同样如此)。目前,一个有效的算法应该含有三个重要特性:
- 它必须是有限的:如果你设计的算法永无休止地尝试解决问题,那么它是无用的。
- 它必须具备明确定义的指令:算法的每一步都必须准确定义,在任何场景下指令都应当没有歧义。
- 它必须是有效的:一个算法被设计用以解决某个问题,那么它就应当能解决这个问题,并且仅仅使用纸和笔就能证明该算法是收敛的。
对数
log10100 相当于问:将多少个10相乘的结果为100?答案当然是2个了。 因此log10100=2,即对数运算是幂运算的逆运算:
| left | right |
|---|---|
| 23 = 8 | log28 = 3 |
| 24 = 16 | log216 = 4 |
| 25 = 32 | log232 = 5 |
| 26 = 64 | log264 = 6 |
| 27 = 128 | log2128 = 7 |
运行时间
以二分查找为例,使用它可节省多少时间呢?简单查找,逐个地检查数字,如果列表包含100个数字,最多需要猜100次。
换而言之最多需要猜测的次数与列表长度相同,这被称为线性时间(linear time),而二分查找则不同,如果列表包含100个元素,
最多需要7次,如果列表包含40亿个数字,最多需猜32次,二分查找的运行时间为对数时间 O(log) 。
大O表示法
大O表示法是一种特殊的表示法 ,指出了算法的速度有多快。
在这种情况下,知道这些算法的速度有快有慢:
- 算法的运行时间以不同的速度增加
- 例如简单查找与二分查找的区别
| 元素 | 简单查找 | 二分查找 |
|---|---|---|
| 100个元素 | 100ms | 7ms |
| 10000个元素 | 10s | 14ms |
| 1 000 000 000 个元素 | 11天 | 30ms |
-
大O表示法指出了算法有多快,例如列表包含
n个元素,简单查找需要检查每个元素,因此需要执行n次操作。 使用大O表示法,这个运行时间为O(n),二分查找需要执行log2n次操作,使用大O表示为O(log n) -
一些常见的大O运行时间
O(log n),也叫对数时间,这样的算法包括二分算法。O(n),也叫线性时间,这样的算法包括简单查找。O(n * log n),快速排序。- O(n2) ,选择排序。
O(n!),即阶乘时间。
注意
- 算法的速度指的并非时间,而是操作数的增速
- 谈论算法的速度时间时,我们说的是随着输入的增加,其运行时间将以什么样的速度增加
- 算法的运行时间用大O表示法表示
O(log n)比O(n)快,当需要搜索的元素越多时,前者比后者快的越多
编写解决实际问题的程序过程
- 如何用数据形式描述问题,即将问题抽象为一个数学模型
- 问题所涉及到的数据量的大小及数据之间的关系
- 如何在计算机中储存数据及体现数据之间的关系
- 处理数据时需要对数据执行的操作
- 编写的程序的性能是否良好
数据(Data)
- 数据 :是客观事物的符号表示,在计算机科学中指的是所有能输入到计算机中并被计算机程序处理的符号的总称。
- 数据元素(Data Element) :是数据的基本单位,在程序中通常作为一个整体来进行考虑和处理。一个数据元素可由若干个数据项(Data Item)组成。
- 数据项(Data Item) :是数据的不可分割的最小单位。数据项是对客观事物某一方面特性的数据描述。
- 数据对象(Data Object) ::是性质相同的数据元素的集合,是数据的一个子集。如字符集合C=
{‘A’,’B’,’C,…}。 - 数据结构 :相互之间具有一定联系的数据元素的集合。
- 数据的逻辑结构 :数据元素之间的相互关系称为逻辑结构。
- 数据操作 :对数据要进行的运算。
- 数据类型(Data Type) :指的是一个值的集合和定义在该值集上的一组操作的总称。
数据的逻辑结构有四种基本类型
- 集合 :结构中数据元素之间除了“属于同一个集合”外,再也没有其他的关系
- 线性结构 :结构中的数据元素存在一对一的关系
- 树形结构 :结构中的数据元素存在一对多的关系
- 网状或者图状结构 :结构中的数据元素存在多对多的关系
数据结构的储存方式
由数据元素之间的关系在计算机中有两种不同的表示方法——顺序表示和非顺序表示,从而导出两种储存方式,顺序储存结构和链式储存结构
- 顺序存储结构 :用数据元素在存储器中的相对位置来表示数据元素之间的逻辑结构(关系),数据元素存放的地址是连续的
- 链式存储结构 :在每一个数据元素中增加一个存放另一个元素地址的指针(pointer),用该指针来表示数据元素之间的逻辑结构(关系),数据元素存放的地址是否连续没有要求
数据的逻辑结构和物理结构是密不可分的两个方面,一个算法的设计取决于所选定的逻辑结构,而算法的实现依赖于所采用的存储结构
算法(Algorithm)
是对特定问题求解方法(步骤)的一种描述,是指令的有限序列,其中每一条指令表示一个或多个操作。
算法具有以下五个特性
- 有穷性: 一个算法必须总是在执行有穷步之后结束,且每一步都在有穷时间内完成
- 确定性:算法中每一条指令必须有确切的含义,不存在二义性,且算法只有一个入口和一个出口
- 可行性: 一个算法是能行的,即算法描述的操作都可以通过已经实现的基本运算执行有限次来实现
- 输入: 一个算法有零个或多个输入,这些输入取自于某个特定的对象集合
- 输出: 一个算法有一个或多个输出,这些输出是同输入有着某些特定关系的量
算法和程序是两个不同的概念
一个计算机程序是对一个算法使用某种程序设计语言的具体实现。算法必须可终止意味着不是所有的计算机程序都是算法。
评价一个好的算法有以下几个标准
- 正确性(Correctness ): 算法应满足具体问题的需要
- 可读性(Readability): 算法应容易供人阅读和交流,可读性好的算法有助于对算法的理解和修改
- 健壮性(Robustness): 算法应具有容错处理,当输入非法或错误数据时,算法应能适当地作出反应或进行处理,而不会产生莫名其妙的输出结果
- 通用性(Generality): 算法应具有一般性 ,即算法的处理结果对于一般的数据集合都成立
效率与存储量需求: 效率指的是算法执行的时间;存储量需求指算法执行过程中所需要的最大存储空间,一般地,这两者与问题的规模有关
算法的时间复杂度
算法中基本操作重复执行的次数是问题规模n的某个函数,其时间量度记作T(n)=O(f(n)),称作算法的渐近时间复杂度(Asymptotic Time complexity),简称时间复杂度
算法的空间复杂度
是指算法编写成程序后,在计算机中运行时所需存储空间大小的度量,记作:S(n)=O(f(n)),其中n为问题规模
递归和循环的简单比较
- 从程序上看,递归表现为自己调用自己,循环则没有这样的形式。
- 递归是从问题的最终目标出发,逐渐将复杂问题化为简单问题,并且简单的问题的解决思路和复杂问题一样,同时存在基准情况,就能最终求得问题,是逆向的。而循环是从简单问题出发,一步步的向前发展,最终求得问题,是正向的。
- 任意循环都是可以用递归来表示的,但是想用循环来实现递归(除了单向递归和尾递归),都必须引入栈结构进行压栈出栈。
- 一般来说,非递归的效率高于递归。而且递归函数调用是有开销的,递归的次数受堆栈大小的限制。
简易结构
用 PHP 的方式实现的各类算法合集:
├──Package
│ ├── Sort 排序篇
│ │ ├── BubbleSort.php 冒泡排序
│ │ ├── HeapSort.php 堆排序
│ │ ├── MBaseSort.php 基数排序 MSD
│ │ ├── LBaseSort.php 基数排序 LSD
│ │ ├── QuickSort.php 快速排序
│ │ ├── ShuttleSort.php 飞梭排序
│ │ ├── ShellSort.php 希尔排序
│ │ ├── MergeSort.php 归并排序
│ │ ├── InsertSort.php 插入排序
│ │ └── SelectSort.php 选择排序
│ │
│ ├── Query 查找篇
│ │ ├── BinaryQuery.php 二分查找
│ │ ├── InsertQuery.php 插入查找
│ │ ├── FibonacciQuery.php 斐波那契查找
│ │ ├── BFSQuery.php 广度优先查找
│ ├── Kmp.php 算法导论-KMP算法
│ ├── DijkstraQuery.php 迪克斯特拉算法
│ │ └── QulickQuery.php 快速查找
│ │
│ ├── Structure 数据结构
│ │ ├── StackExample.php 堆栈 先进后出 LIFO (Last In First Out)
│ │ ├── LinearChain.php 线性表 单链存储
│ │ └── LinearOrder.php 线性表 顺序存储
│ │ └── BinarySearchTree.php 二叉搜索树
│ │
│ ├── Tools 小工具集
│ │ └── SystemSwitch.php 堆栈实现进制转换
│ │
│ └── Other 其他
│ ├── MonkeyKing.php 约瑟夫环
│ ├── DynamicProgramming.php 动态规划
│ ├── Fibonacci.php 斐波那契数列
│ ├── StealingApples.php 偷苹果求余
│ ├── HanoiGames.php 汉诺塔游戏
│ ├── BidirectionalQueue.php 双向队列
│ ├── ColorBricks.php 彩色砖块
│ ├── GetCattle.php 牛年求牛
│ ├── OnlyNumbers.php 求唯一数
│ ├── PokerGames.php 洗扑克牌
│ ├── Interval.php 抽奖区间算法
│ ├── Maze.php 迷宫寻址算法
│ ├── AntsClimb.php 蚂蚁爬杆算法
│ ├── Encryption.php 对称加密算法
│ ├── ElevatorDispatch.php 编程之美-电梯调度算法
│ ├── PointInTriangle.php 向量叉集计算点是否在三角形中
│ ├── TraversalOfBinary.php 二叉树非递归遍历算法实现
│ ├── Knapsack.php 贪心算法之背包问题实现
│ └── BigSmallReplace.php Hello World 输出 Olleh Dlrow
│ └── Solution.php Facebook面试题之岛屿周长算法
│ └── RotationSort.php Facebook面试题之顺时针回旋算法
│ └── Square.php Facebook面试题之判断四个点能否组成正方形算法
│ └── Prim.php Prim算法(最小生成树算法)
│ └── CartesianProduct.php 笛卡尔积算法
│ └── Square.php 面试题之平面任意四点能否组成一个矩形
│ └── Judge.php 面试题之扑克牌中任选五张判断是不是顺子
│ └── Factorial.php 面试题之N的阶乘末尾有多少个0
| └── HashTable.php HashTable
│
├──LICENSE
└──README.md
https://ibaiyang.github.io/blog/php/2019/07/30/PHP-算法-查找篇.html
https://ibaiyang.github.io/blog/php/2019/07/30/PHP-算法-数据结构.html
当然
用 PHP 实现算法并替代官方提供的函数是愚蠢的事情 .但这并不代表斟酌算法就是件无意义的事 , 每个算法都是一种思想的结晶 , 学习优秀的思想 , 开拓思维, 加油(ง •̀_•́)ง
数组转换相关函数:is_array(), explode(), implode(), split(), preg_split(), unset()。
对数组进行排序 PHP官方 排序函数属性:
| 函数名称 | 排序依据 | 数组索引键保持 | 排序的顺序 | 相关函数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| array_multisort() | 值 | 键值关联的保持,数字类型的不保持 | 第一个数组或者由选项指定 | array_walk() |
| asort() | 值 | 是 | 由低到高 | arsort() |
| arsort() | 值 | 是 | 由高到低 | asort() |
| ksort() | 键 | 是 | 由低到高 | asort() |
| krsort() | 键 | 是 | 由高到低 | ksort() |
| natcasesort() | 值 | 是 | 自然排序,大小写不敏感 | natsort() |
| natsort() | 值 | 是 | 自然排序 | natcasesort() |
| sort() | 值 | 否 | 由低到高 | rsort() |
| rsort() | 值 | 否 | 由高到低 | sort() |
| shuffle() 值 | 否 | 随机 | array_rand() | |
| uasort() | 值 | 是 | 由用户定义 | uksort() |
| uksort() | 键 | 是 | 由用户定义 | uasort() |
| usort() | 值 | 否 | 由用户定义 | uasort() |
排序篇
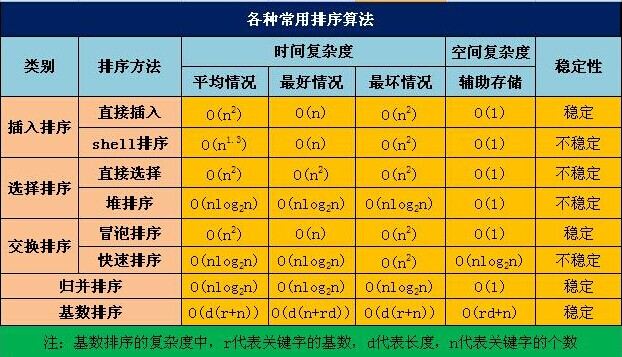
各种排序算法的时间、空间复杂度、稳定性对比分析:
冒泡排序
冒泡排序(Bubble Sort),是一种计算机科学领域的较简单的排序算法。它重复地走访过要排序的数列,一次比较两个元素, 如果他们的顺序错误就把他们交换过来。走访数列的工作是重复地进行直到没有再需要交换,也就是说该数列已经排序完成。 这个算法的名字由来是因为越大的元素会经由交换慢慢“浮”到数列的顶端。
说是冒泡,就是小的冒泡上来。
<?php
/**
* 冒泡排序(数组排序)
* @param $array
* @return bool | array
*/
function bubbleSort($array)
{
$count = count($array);
if ($count <= 0) {
return false;
}
for ($i = 0 ; $i < $count; $i++) {
for ($j = $count - 1; $j > $i; $j--) {
if ($array[$j] < $array[$j - 1]) {
$tmp = $array[$j];
$array[$j] = $array[$j - 1];
$array[$j - 1] = $tmp;
}
}
}
return $array;
}
举例:
<?php
$array = array(8, 4, 10, 2, 6);
$array = bubbleSort($array);
print_r($array); // 输出 Array ( [0] => 2 [1] => 4 [2] => 6 [3] => 8 [4] => 10 )
打印一下过程:
0 1 2 3 4 -> 0 1 2 3 4
// $i = 0
8, 4, 10, 2, 6 -> 8, 4, 10, 2, 6 // $j = 4
8, 4, 10, 2, 6 -> 8, 4, 2, 10, 6 // $j = 3
8, 4, 2, 10, 6 -> 8, 2, 4, 10, 6 // $j = 2
8, 2, 4, 10, 6 -> 2, 8, 4, 10, 6 // $j = 1
// $i = 1
2, 8, 4, 10, 6 -> 2, 8, 4, 6, 10 // $j = 4
2, 8, 4, 6, 10 -> 2, 8, 4, 6, 10 // $j = 3
2, 8, 4, 6, 10 -> 2, 4, 8, 6, 10 // $j = 2
// $i = 2
2, 4, 8, 6, 10 -> 2, 4, 8, 6, 10 // $j = 4
2, 4, 8, 6, 10 -> 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 // $j = 3
// $i = 3
2, 4, 6, 8, 10 -> 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 // $j = 4
// $i = 4
// $j = 4 for循环不进入
// $i = 5 for循环不进入
特别说明,里面有两次循环,内层循环的目的是把最小的数向最前面互换,外层循环的目的是把前面已经排好序的数跳过,然后用内层循环继续选择后面最小的数。
总结可以看出,就是小的不断往前排,最小的先到最前面。
这种写法,与上面的本质是一样的:
/**
* bubbleSort
*
* @param array $container
* @return array
*/
function bubbleSort(array $container) {
$count = count($container);
for ($i = $count - 1; $i >= 1; $i--) {
for ($j = $count - 1; $j >= $count - $i; $j--) {
if ($container[$j] < $container[$j - 1]) {
$temp = $container[$j];
$container[$j] = $container[$j - 1];
$container[$j - 1] = $temp;
}
}
}
return $container;
}
打印一下过程:
0 1 2 3 4 -> 0 1 2 3 4
// $i = 4
8, 4, 10, 2, 6 -> 8, 4, 10, 2, 6 // $j = 4
8, 4, 10, 2, 6 -> 8, 4, 2, 10, 6 // $j = 3
8, 4, 2, 10, 6 -> 8, 2, 4, 10, 6 // $j = 2
8, 2, 4, 10, 6 -> 2, 8, 4, 10, 6 // $j = 1
// $i = 3
2, 8, 4, 10, 6 -> 2, 8, 4, 6, 10 // $j = 4
2, 8, 4, 6, 10 -> 2, 8, 4, 6, 10 // $j = 3
2, 8, 4, 6, 10 -> 2, 4, 8, 6, 10 // $j = 2
// $i = 2
2, 4, 8, 6, 10 -> 2, 4, 8, 6, 10 // $j = 4
2, 4, 8, 6, 10 -> 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 // $j = 3
// $i = 1
2, 4, 6, 8, 10 -> 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 // $j = 4
// $i = 0 for循环不进入
还有下面这种沉底的算法,前后两个数比较,把大的数交换到下面,循环一轮后,最大的数就到最底部了。 下一轮循环就没有必要对刚才沉到最底部的数字进行比较,以此类推得到最终排序。
/**
* bubbleSort
*
* @param array $container
* @return array
*/
function bubbleSort(array $container)
{
$count = count($container);
for ($i = 1; $i < $count; $i++) {
for ($j = 0; $j < $count - $i; $j++) {
if ($container[$j] > $container[$j+1]) {
$temp = $container[$j];
$container[$j] = $container[$j+1];
$container[$j+1] = $tmp;
}
}
}
return $container;
}
快速排序
快速排序(Quicksort)也叫二分法排序,是对冒泡排序的一种改进。 它的基本思想是:通过一趟排序将要排序的数据分割成独立的两部分,其中一部分的所有数据都比另外一部分的所有数据都要小, 然后再按此方法对这两部分数据分别进行快速排序,整个排序过程可以递归进行,以此达到整个数据变成有序序列。
快速排序的思路是选取一个基准,然后逐个对比,比基准小的放左边,比基准大的放右边, 使用递归(recursive)再分别对比分割后的左右小集群,不断缩小对比范围,最后合并返回。
/**
* QuickSort
*
* @param array $container
* @return array
*/
function QuickSort(array $container)
{
$count = count($container);
if ($count <= 1) {
// 基线条件为空或者只包含一个元素,只需要原样返回数组
return $container;
}
$pivot = $container[0]; // 基准值 pivot
$left = $right = [];
for ($i = 1; $i < $count; $i++) {
if ($container[$i] < $pivot) {
$left[] = $container[$i];
} else {
$right[] = $container[$i];
}
}
$left = QuickSort($left);
$right = QuickSort($right);
return array_merge($left, [$container[0]], $right);
}
快速排序使用分而治之【 divide and conquer,D&C 】的策略,是一种解决问题的思路,D&C 解决问题的过程包括两个步骤:
- 找出基线条件,这种条件必须尽可能简单
- 不断将问题分解(或者说缩小规模),直到符合基线条件
举例:
$array = array(8, 4, 10, 2, 6);
$array = QuickSort($array);
print_r($array); // 输出 Array ( [0] => 2 [1] => 4 [2] => 6 [3] => 8 [4] => 10 )
打印一下过程:
Array ( [0] => 8 [1] => 4 [2] => 10 [3] => 2 [4] => 6 )
Array ( [0] => 4 [1] => 2 [2] => 6 )
Array ( [0] => 2 )
Array ( [0] => 6 )
Array ( [0] => 10 )
特别说明,里面用到了递归,核心思想是取一个数,划分左右,不断缩小,不断合并,然后排序完成。
插入排序
插入排序基本操作就是将一个数据插入到已经排好序的有序数据中,从而得到一个新的、个数加一的有序数据,算法适用于少量数据的排序, 时间复杂度为O(n^2)。是稳定的排序方法。插入排序的基本思想是:每步将一个待排序的纪录,按其关键码值的大小插入前面已经排序的文件中适当位置上, 直到全部插入完为止。
插入排序的思路是每次往后走一步,对前面的数字进行排序,因为前面数字已经排好序,所以这一次只要把新加入进来的数字找到目标位置插入进去就好了。 如此,直到最后一步。
/**
* InsertSort
*
* @param array $container
* @return array
*/
function InsertSort(array $container)
{
$count = count($container);
if ($count <= 0) {
return false;
}
for($i = 1; $i < $count; $i++) {
$j = $i;
while ($j >= 1) {
if ($container[$j] < $container[$j -1]) {
$temp = $container[$j - 1];
$container[$j -1] = $container[$j];
$container[$j] = $temp;
} else {
break;
}
$j--;
}
}
return $container;
}
同样的原理,只是把while换成了for:
function InsertSort($array) {
$count = count($array);
if ($count <= 0) {
return false;
}
for($i = 1 ; $i < $count; $i++) {
for($j = $i; $j >= 1; $j--) {
if ($array[$j] < $array[$j - 1]) {
$tmp = $array[$j - 1];
$array[$j - 1] = $array[$j];
$array[$j] = $tmp;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
return $array;
}
还有这种思路,与上面细微差别是先确定这个数的具体位置,后加入这个位置,优点是赋值次数减少,提升运算效率:
function InsertSort(array $container) {
$count = count($container);
for ($i = 1; $i < $count; $i++) {
$temp = $container[$i];
$j = $i - 1;
while ($j >= 0 && $container[$j] > $temp) {
$container[$j+1] = $container[$j];
$j--;
}
if ($i != $j+1) {
$container[$j+1] = $temp;
}
}
return $container;
}
上面这种while循环时,每次都要 $j 都要自减到0,优化一下:
function InsertSort(array $container) {
$count = count($container);
for ($i = 1; $i < $count; $i++) {
$temp = $container[$i];
$j = $i - 1;
while ($j >= 0) {
if ($container[$j] > $temp) {
$container[$j+1] = $container[$j];
$j--;
} else {
break;
}
}
if ($i != $j+1) {
$container[$j+1] = $temp;
}
}
return $container;
}
把while换成for:
<?php
function InsertSort(array $container) {
$count = count($container);
for ($i = 1; $i < $count; $i++) {
$temp = $container[$i];
for ($j = $i-1; $j >= 0; $j--) {
if ($container[$j] > $temp) {
$container[$j+1] = $container[$j];
// 进入这个 if 后,最后就会执行一次 $j--
} else {
break;
}
}
// 这里注意,上面最后break前 $j-- 了一次
if ($i != $j+1) {
$container[$j+1] = $temp;
}
}
return $container;
}
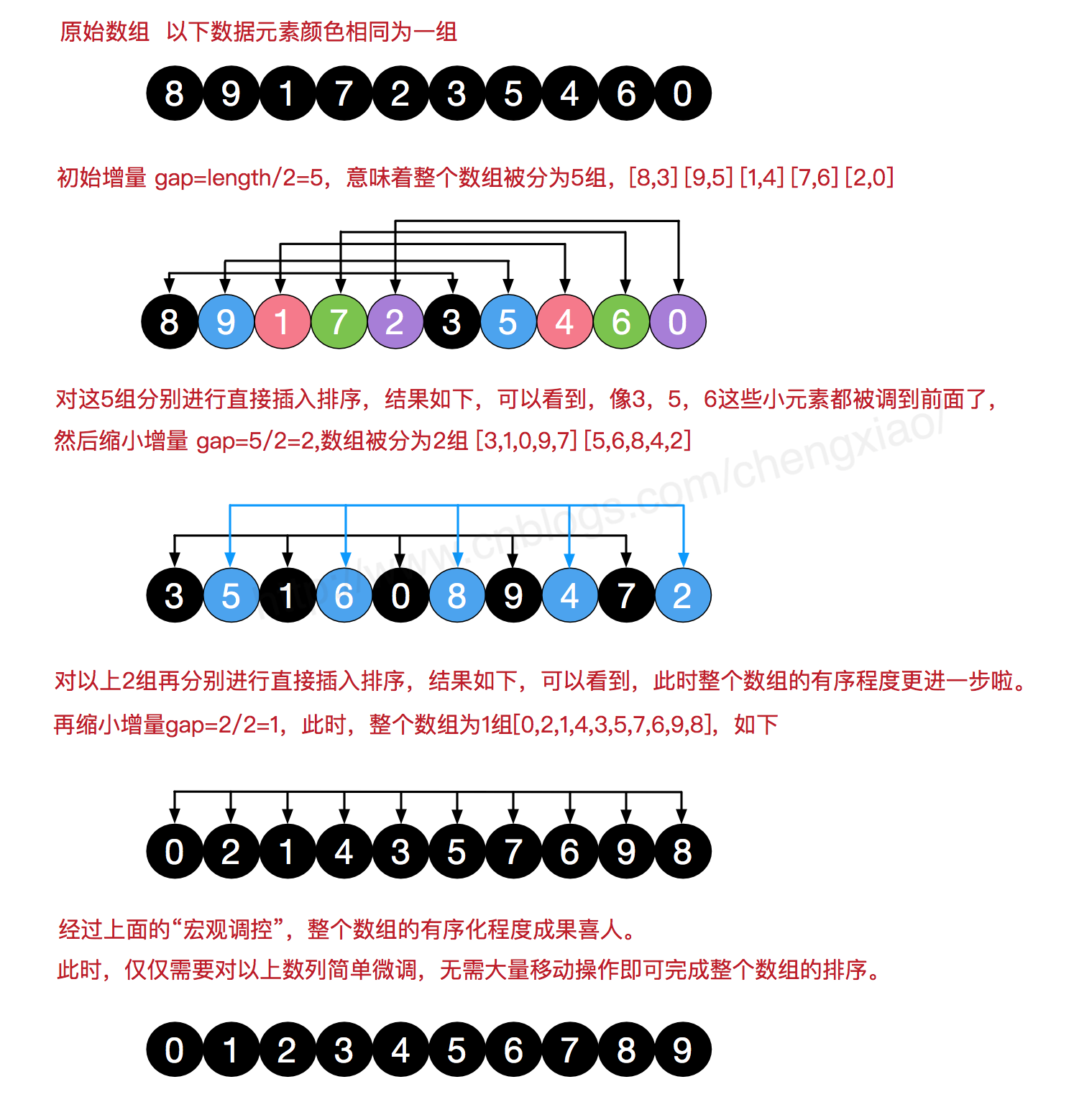
希尔排序
希尔排序(Shell Sort)是插入排序的一种。也称缩小增量排序,是直接插入排序算法的一种更高效的改进版本。希尔排序是非稳定排序算法。 希尔排序是把记录按下标的一定增量分组,对每组使用直接插入排序算法排序;随着增量逐渐减少,每组包含的关键词越来越多, 当增量减至1时,整个文件恰被分成一组,算法便终止。
<?php
/**
* ShellSort
*
* @param array $container
* @return array
*/
function ShellSort(array $container)
{
$count = count($container);
// 缩小间隔,如 5->2 , 2->1
for ($increment = intval($count / 2); $increment > 0; $increment = intval($increment / 2)) {
// 从间隔值处,往后运算
for ($i = $increment; $i < $count; $i++) {
$temp = $container[$i];
// 对同一组中的各数值从后向前进行比较并修改值
for ($j = $i; $j >= $increment; $j -= $increment) {
if ($temp < $container[$j - $increment]) {
$container[$j] = $container[$j - $increment];
} else {
break;
}
}
// $container[$j] = $temp;
// 避免多余赋值操作
if ($j != $i) {
$container[$j] = $temp;
}
}
}
return $container;
}
选择排序
选择排序(Selection sort)是一种简单直观的排序算法。它的工作原理是每一次从待排序的数据元素中选出最小(或最大)的一个元素, 存放在序列的起始位置,直到全部待排序的数据元素排完。 选择排序是不稳定的排序方法。
选择排序的思路是,从左边开始寻找最小的数交换位置,这样最左边这个数就是最小的,接下来再看第二位应该放的数字,依次向右前进, 直到最后一位完成数字从小到大排序。
/**
* SelectSort
*
* @param array $container
* @return array
*/
function SelectSort(array $container)
{
$count = count($container);
for ($i = 0; $i < $count; $i++){
$k = $i;
for ($j = $i + 1; $j < $count; $j++){
if ($container[$j] < $container[$k]) {
$k = $j;
}
}
if($k != $i){
$temp = $container[$i];
$container[$i] = $container[$k];
$container[$k] = $temp;
}
}
return $container;
}
内层for的意思是:整体选出最小值的键,然后与外层循环到的值进行交换。这应该就是选择排序中“选择”的含义。
再看下下面这个方法:
function SelectSort(array $container)
{
$count = count($container);
for ($i = 0; $i < $count; $i++){
for ($j = $i + 1; $j < $count; $j++){
if ($container[$j] < $container[$i]){
$temp = $container[$i];
$container[$i] = $container[$j];
$container[$j] = $temp;
}
}
}
return $container;
}
这里是内层for的意思是:如果接下来一个值比刚才交换的那个值要小,则进行交换,依次把最小的那个值交换上去。
选择排序是不稳定的排序方法(比如序列[5, 5, 3]第一次就将第一个[5]与[3]交换,导致第一个5挪动到第二个5后面)。
堆排序
堆(heap)是计算机科学中一类特殊的数据结构的统称,通常是一个可以被看做一棵树的数组对象。
关于堆:
- 堆总是一棵完全二叉树(下面):
- 堆中某个节点的值总是不大于或不小于其父节点的值;
- 将根节点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根节点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。
数据结构:
# 从1开始
堆 {k1,k2,ki,…,kn} {ki <= k2i, ki <= k(2i+1)} | {ki >= k2i, ki >= (k2i+1)}, (i = 1,2,3,4...n/2)
# 从0开始
堆 {k0,k1,k2,ki,…,kn} {ki <= k(2i+1), ki <= k(2i+2)} | {ki >= k(2i+1), ki >= k(2i+2)}, (i = 0,1,2,3,4...[ceil(n/2)-1])
完全二叉树 除最后一层外,每一层上的节点数均达到最大值;在最后一层上只缺少右边的若干结点。
小根堆实现图:
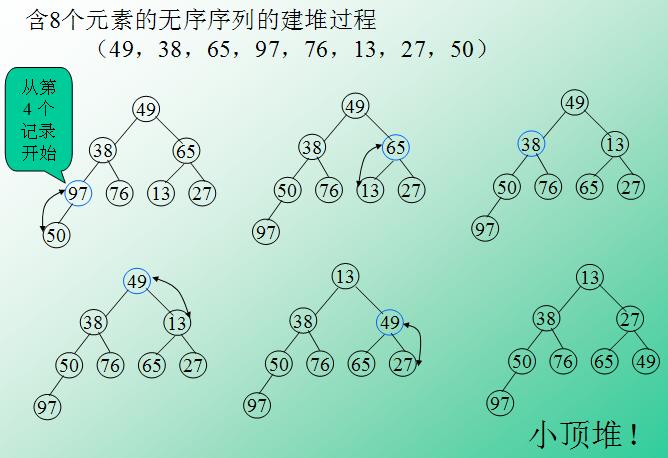
堆排序算法:堆排序就是利用堆进行排序的方法,它的基本思想是(假设利用大根堆):将待排序的序列构造成一个大根堆。 此时,整个序列的最大值就是堆顶的根节点。将它移走(其实就是将其与堆数组的末尾元素交换,此时末尾元素就是最大值), 然后将剩余的 n - 1 个序列重新构造成一个堆,这样就会得到 n 个元素中的次小的值。如此反复执行,便能得到一个有序序列了。
因为建堆的时间复杂度是 O(n)(调用一次);调整堆的时间复杂度是 logn,调用了 n-1 次;总体上来说,堆排序的时间复杂度是 O(nlogn)。
大根堆排序类:
<?php
class heapSort
{
/**
* @var int
*/
protected $count;
/**
* @var array
*/
protected $data;
/**
* HeapSort constructor.
*
* @param array $data
*/
public function __construct(array $data){
$this->count = count($data);
$this->data = $data;
}
/**
* Action
*
* @return array
*/
public function run() {
$this->createHeap();
while ($this->count > 0) {
/* 这是一个大顶堆 , 所以堆顶的节点必须是最大的,根据此特点 , 每次都将堆顶数据移到最后一位,然后对剩余数据节点再次建造堆就可以 */
$this->swap($this->data[0], $this->data[--$this->count]);
$this->buildHeap($this->data, 0, $this->count);
}
return $this->data;
}
/**
* 创建一个堆
*/
public function createHeap() {
// $i = floor($this->count / 2) + 1;
$i = floor($this->count / 2);
// 从 数组 的第 $i-1 个节点开始至 数组长度为0 结束 , 递归的将其 ( 包括其子节点 ) 转化为一个堆
while ($i--) {
$this->buildHeap($this->data, $i, $this->count);
}
}
/**
* 将 数组 转换为 第 $i 个节点 为根的大顶堆
*
* @param $data
* @param $i
* @param $count
*/
public function buildHeap(array &$data, $i, $count) {
if (false === $i < $count) {
return;
}
// 获取左 / 右节点
$right = ($left = 2 * $i + 1) + 1;
$max = $i;
// 如果左子节点大于当前节点 , 那么记录左节点键名
if ($left < $count && $data[$i] < $data[$left]) {
$max = $left;
}
// 如果右节点大于刚刚记录的 $max , 那么再次交换
if ($right < $count && $data[$max] < $data[$right]) {
$max = $right;
}
if ($max !== $i && $max < $count) {
$this->swap($data[$i], $data[$max]);
$this->buildHeap($data, $max, $count);
}
}
/**
* 交换空间
*
* @param $left
* @param $right
*/
public function swap(&$left, &$right) {
list($left, $right) = array ($right, $left);
}
}
示例:
$array = array (4, 21, 41, 2, 53, 1, 213, 31, 21, 423, 56);
$result = (new heapSort($array))->run();
print_r($result);
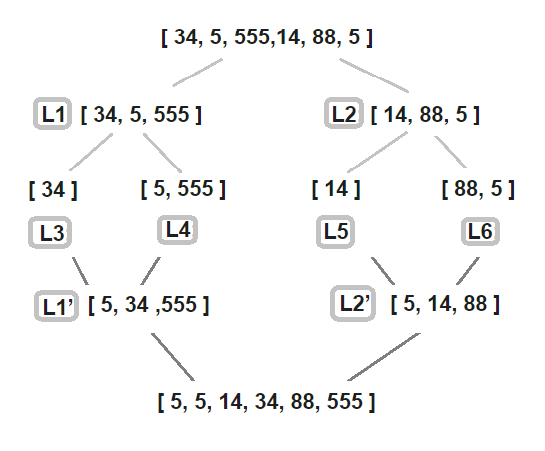
归并排序
归并排序是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法,该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。 将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;即先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列段间有序。若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为二路归并。
<?php
class MergeSort
{
private $arr;
/**
* MergeSort constructor.
* @param array $arr 待排序的数组
*/
public function __construct(array $arr)
{
$this->arr = $arr;
}
/**
* 开始递归函数的一个驱动函数
*/
public function run()
{
$this->mSort($this->arr, 0, count($this->arr) - 1);
}
/**
* 获取数组
* @return array
*/
public function getArr()
{
return $this->arr;
}
/**
* 实际实现归并排序的程序
*
* @param $arr array 需要排序的数组
* @param $left int 子序列的左下标值
* @param $right int 子序列的右下标值
*/
public function mSort(&$arr, $left, $right)
{
if ($left < $right) {
echo $left . ' - ' . $right .PHP_EOL;
//说明子序列内存在多余1个的元素,那么需要拆分,分别排序,合并
//计算拆分的位置,长度/2 去整
$center = floor(($left + $right) / 2);
//递归调用对左边进行再次排序:
$this->mSort($arr, $left, $center);
//递归调用对右边进行再次排序
$this->mSort($arr, $center + 1, $right);
//合并排序结果
$this->mergeArray($arr, $left, $center, $right);
}
}
/**
* 将两个有序数组合并成一个有序数组
*
* @param &$arr , 待排序的所有元素
* @param $left , 排序子数组A的开始下标
* @param $center , 排序子数组A与排序子数组B的中间下标,也就是数组A的结束下标
* @param $right , 排序子数组B的结束下标(开始为$center+1)
*/
public function mergeArray(&$arr, $left, $center, $right)
{
echo '| ' . $left . ' - ' . $center . ' - ' . $right . ' - ' . implode(',', $arr);
//设置两个起始位置标记
$a_i = $left;
$b_i = $center + 1;
$temp = [];
while ($a_i <= $center && $b_i <= $right) {
//当数组A和数组B都没有越界时,取小的那个,循环交叉对比取值
if ($arr[ $a_i ] < $arr[ $b_i ]) {
$temp[] = $arr[ $a_i++ ];
} else {
$temp[] = $arr[ $b_i++ ];
}
}
//判断 数组A内的元素是否都用完了,没有的话将其全部插入到C数组内:
while ($a_i <= $center) {
$temp[] = $arr[ $a_i++ ];
}
//判断 数组B内的元素是否都用完了,没有的话将其全部插入到C数组内:
while ($b_i <= $right) {
$temp[] = $arr[ $b_i++ ];
}
echo ' - ' . implode(',', $temp) . PHP_EOL;
//将$arrC内排序好的部分,写入到$arr内:
for ($i = 0, $len = count($temp); $i < $len; $i++) {
$arr[ $left + $i ] = $temp[ $i ];
}
}
}
$a = [34,5,55,14,88,5];
$t = new MergeSort($a);
$t->run();
print_r($t->getArr());
输出:
0 - 5
0 - 2
0 - 1
| 0 - 0 - 1 - 34,5,55,14,88,5 - 5,34
| 0 - 1 - 2 - 5,34,55,14,88,5 - 5,34,55
3 - 5
3 - 4
| 3 - 3 - 4 - 5,34,55,14,88,5 - 14,88
| 3 - 4 - 5 - 5,34,55,14,88,5 - 5,14,88
| 0 - 2 - 5 - 5,34,55,5,14,88 - 5,5,14,34,55,88
Array
(
[0] => 5
[1] => 5
[2] => 14
[3] => 34
[4] => 55
[5] => 88
)
飞梭排序
飞梭排序是冒泡排序的轻微变形。不同的地方在于,飞梭排序是从低到高,然后从高到低,来回排序,而冒泡排序则仅从低到高去比较序列里的每个元素。
先对数组从左到右进行沉底排序(升序),则最大的元素去到最右端;
再对数组从右到左进行冒泡排序(降序),则最小的元素去到最左端;
以此类推,依次改变冒泡的方向,并不断缩小未排序元素的范围,直到最后一个元素结束。
<?php
/**
* ShuttleSort
*
* @param array $data
* @return array
*/
function ShuttleSort(array $data) {
/**
* 替换方法
*
* @param array $data
* @param $i
* @param $j
* @return array
*/
$swap = function (array &$data, $i, $j) {
$temp = $data[$i];
$data[$i] = $data[$j];
$data[$j] = $temp;
return $data;
};
$count = count($data);
$left = 0;
$right = $count - 1;
while ($left < $right) {
// 从左到右
$lastRight = 0;
for ($i = $left; $i < $right; $i++) {
if ($data[$i] > $data[$i + 1]) {
$swap($data, $i, 1 + $i);
$lastRight = $i;
}
}
$right = $lastRight;
// 从右到左
$lastLeft = 0;
for ($j = $right; $left < $j; $j--) {
if ($data[$j - 1] > $data[$j]) {
$swap($data, $j - 1, $j);
$lastLeft = $j;
}
}
$left = $lastLeft;
}
return $data;
}
中文数字排序
class ChineseTextNumberSort
{
/**
* @var string text
*/
const CHINESE_DIGITAL_MATCHING = '/\x{96f6}|\x{4e00}|\x{4e8c}|\x{4e09}|\x{56db}|\x{4e94}|\x{516d}|\x{4e03}|\x{516b}|\x{4e5d}|\x{5341}/ui';
/**
* @var string regular rules [! order can not arbitrarily change]
*/
const MODEL_REGULAR_A = <<<REGEXPS
/^\x{7b2c}(\x{4e00}|\x{4e8c}|\x{4e09}|\x{56db}|\x{4e94}|\x{516d}|\x{4e03}|\x{516b}|\x{4e5d}|\x{5341}){1}(\x{7ae0}|\x{8282}|\x{8bfe}|\x{5355}\x{5143})([\f\n\r\t\v]|\x09|\s){1}+/u
REGEXPS;
const MODEL_REGULAR_D = '/^(\d{1,2})(\x{9875})\-{1}/u';
const MODEL_REGULAR_E = '/^(\d{1,2})\-/i';
const MODEL_REGULAR_F = '/^(\d{1,2})([\f\n\r\t\v]|\x09|\s)+/i';
const MODEL_REGULAR_G = '/^(\d{1,2})(\x{3001}{1})+/u';
const MODEL_REGULAR_H = '/\x{518c}(\d{1,2})(\s){1}(\x{ff1a}|\:){1}/u';
const MODEL_REGULAR_I = '/([\f\n\r\t\v]|\x09|\s){1}(\d+)/i';
const MODEL_REGULAR_B = '/^\d{1,2}+/i';
const MODEL_REGULAR_C = '/^\d{1,2}([\f\n\r\t\v]|\x09|\s){1}+/i';
/**
* 解析文本到十位
*
* @param $text
* @return false|float|int|string
*/
public function parsingText($text)
{
$structure = '';
$mapping = array ('零', '一', '二', '三', '四', '五', '六', '七', '八', '九', '十');
preg_match_all(static::CHINESE_DIGITAL_MATCHING, $text, $structure, PREG_PATTERN_ORDER);
if (empty($structure[0])) {
return 0;
}
$currentNum = 0;
foreach ($structure[0] as $plane => $matchNum) {
if ($matchNum === '十') {
if ($plane === 0) {
$currentNum += 10;
continue;
}
if ($plane === 1) {
$index = array_search($structure[0][0], $mapping);
$currentNum -= $index;
$currentNum += $index * 10;
continue;
}
}
$index = array_search($matchNum, $mapping);
$currentNum += $index;
}
return $currentNum;
}
/**
* isChinese
*
* @param $text
* @return bool
*/
public function isCompletelyChinese($text)
{
return boolval(preg_match('/^[\x7f-\xff]+$/', $text));
}
/**
* regularModel
*
* @param $regularModel
* @param $text
* @return bool
*/
public function regularModel($regularModel, $text)
{
return boolval(preg_match($regularModel, $text));
}
/**
* extractModel
*
* @param $regularModel
* @param $text
* @return string
* @throws \Exception
*/
public function extractModel($regularModel, $text)
{
$result = '';
if (preg_match($regularModel, $text, $result)) {
return trim($result[$this->modelMappingIndex($regularModel)]);
}
throw new Exception('The matching error');
}
/**
* modelMappingIndex
*
* @param $regularModel
* @return int|mixed
*/
protected function modelMappingIndex($regularModel)
{
return array (
static::MODEL_REGULAR_A => 1,
static::MODEL_REGULAR_B => 0,
static::MODEL_REGULAR_C => 0,
static::MODEL_REGULAR_D => 1,
static::MODEL_REGULAR_E => 1,
static::MODEL_REGULAR_F => 1,
static::MODEL_REGULAR_G => 1,
static::MODEL_REGULAR_H => 1,
static::MODEL_REGULAR_I => 2
)[$regularModel] ?? 1;
}
/**
* chineseConversionNum
*
* @param $text
* @return mixed
*/
public function chineseConversionNum($text)
{
if ($this->regularModel(static::CHINESE_DIGITAL_MATCHING, $text)) {
$mapping = array ('零', '一', '二', '三', '四', '五', '六', '七', '八', '九', '十');
return array_search($text, $mapping);
}
return ltrim($text, 0);
}
/**
* getAllModelRegular
*
* @return array
* @throws \ReflectionException
*/
public function getAllModelRegular()
{
$constants = (new \ReflectionClass(__CLASS__))->getConstants();
$collection = array ();
foreach ($constants as $key => $value) {
if (strpos($key, 'MODEL_REGULAR_') !== false) {
$collection[$key] = $value;
}
}
return $collection;
}
/**
* modelAnalysis
*
* @param $text
* @return int|string
* @throws \ReflectionException
*/
public function modelAnalysis($text)
{
foreach ($this->getAllModelRegular() as $item) {
if ($this->regularModel($item, $text)) {
return $item;
}
}
throw new Exception('Model Analysis of the failure !');
}
/**
* textAnalysis
*
* @param $text
* @return int
*/
public function textAnalysis($text)
{
try {
return (int)$this->chineseConversionNum($this->extractModel(
$this->modelAnalysis($text),
$text
)
);
} catch (Exception $e) {
return 0;
}
}
/**
* chineseTextList
*
* @param array $list
* @return array
*/
public function chineseTextListSorter(array $list)
{
$container = $generate = array ();
foreach ($list as $item) {
$container[] = $this->textAnalysis($item);
}
if (count($container) !== count($list)) {
return $list;
}
uksort($list, function ($left, $right) use ($container) {
if ($left == $right) {
return 0;
}
return $container[$left] < $container[$right] ? -1 : 1;
});
return array_values($list);
}
}
小工具集
堆栈实现进制转换
<?php
/**
* SystemSwitch
*
* -------------------------------------------------------------
* 十进制整数转换为二、八、十六进制整数 n = (n div d) * d + n mod d
* -------------------------------------------------------------
*/
class SystemSwitch
{
/**
* @var array
*/
protected $systemGather;
/**
* @var int
*/
protected $input;
/**
* @var mixed
*/
protected $output;
/**
* SystemSwitch constructor.
*
* @param $input
* @param $output
*/
public function __construct($input, $output)
{
$this->systemGather = array (2, 8, 16);
$this->input = $input;
$this->output = $output;
}
public function run()
{
$before = $this->input;
$stack = new StackExample();
while ($this->input != 0) {
$mod = $this->input % $this->output;
$stack->setPushStack($mod);
$this->input = (int)($this->input - $mod) / $this->output;
}
$output = '';
if ($this->output == 16) {
$output .= '0x';
} else if ($this->output == 8) {
$output .= '0';
}
foreach ($stack->getAllPopStack() as $value) {
if ($this->output == 16) {
switch ($value) {
case 10:
$value = 'A';
break;
case 11:
$value = 'B';
break;
case 12:
$value = 'C';
break;
case 13:
$value = 'D';
break;
case 14:
$value = 'E';
break;
case 15:
$value = 'F';
break;
}
}
$output .= $value;
}
// 因为输出语句会自动将整型的数转换为10进制输出
// 也即如果转换后的结果为0xff,直接将0xff输出会得到255,所以返回一数组
return array (
'before' => $before, // 转换之前
'after' => intval($output, $this->output), // 转换后的整型数(整型)
'string' => $output // 转换后的整型数的字符串表示(字符串型)
);
}
}
// load the stack
define("DS", DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR);
require_once dirname(__DIR__) . DS . 'Structure' . DS . 'StackExample.php';
$systemObj = new SystemSwitch(6, 16);
$result = $systemObj->run();
var_dump($result);
上面 StackExample 可以先看数据结构堆栈部分理解一下。
YieldExample
先说下自己过去对 yield 的理解:有人说php中通过yield实现了对协程的支持,我不赞成这一点, 至少协程的一个表现是:当A任务执行中等待时,系统会自动切到B任务进行执行,一段时间后又切回A任务继续执行。 但在 yield 实现中,并不是自动切换,而是通过我们写的 yield 暂时跳出本任务; 其次并不是自动跳回来继续执行,而是B任务运行结束,或者执行了迭代器的send方法后。
不断学习后,发现上面理解的错误之处:协程可以理解为纯用户态的线程,其通过协作而不是抢占来进行切换。 虽然在PHP语言本身级别未实现一个完善的协程解决方案,但通过yield关键字,增加了迭代生成器和对协程的支持。
可以参阅下 https://ibaiyang.github.io/blog/php/2020/07/01/PHP-Socket初探.html#17-php中的yield上
这么说过后,再看下面的例子,应该会好理解很多。
<?php
/**
* YieldExample
*
* -------------------------------------------------------------
* 思路分析:笔记局 ,觉得需要认真学习的 Yield
* -------------------------------------------------------------
* [由来]
* PHP从5.5引入了yield关键字,增加了迭代生成器和协程的支持,但并未在语言本身级别实现一个完善的协程解决方案。
* PHP协程也是基于Generator,Generator可以视为一种“可中断”的函数,而 yield 构成了一系列的“中断点”。
* PHP 协程没有resume关键字,而是“在使用的时候唤起”协程。了解如何在PHP中实现协程,首先要解决迭代生成器。
* PHP > 手册 > 语言参考 > 生成器 http://php.net/manual/zh/language.generators.overview.php
* -------------------------------------------------------------
* [概念]
* “协程”(Coroutine)概念最早由 Melvin Conway 于1958年提出。
* 协程可以理解为纯用户态的线程,其通过协作而不是抢占来进行切换。
* 相对于进程或者线程,协程所有的操作都可以在用户态完成,创建和切换的消耗更低。
* 总的来说,协程为协同任务提供了一种运行时抽象,这种抽象非常适合于协同多任务调度和数据流处理。
* 在现代操作系统和编程语言中,因为用户态线程切换代价比内核态线程小,协程成为了一种轻量级的多任务模型。
* -------------------------------------------------------------
* [协程与进程线程的区别]
* 对于操作系统来说只有进程和线程,协程的控制由应用程序显式调度,非抢占式的
* 协程的执行最终靠的还是线程,应用程序来调度协程选择合适的线程来获取执行权
* 切换非常快,成本低。一般占用栈大小远小于线程(协程KB级别,线程MB级别),
* 所以可以开更多的协程,协程比线程更轻量级
* -------------------------------------------------------------
*/
/**
* 协程生产器
*
* @param $start
* @param $end
* @param int $step
* @return \Generator
*/
$SyncFactory = function ($start, $end, $step = 1) {
for ($i = $start; $i <= $end; $i += $step) {
yield $i;
}
};
/**
* 普通的生产器
*
* @param $start
* @param $end
* @param int $step
*/
$UsualFactory = function ($start, $end, $step = 1) {
for ($i = $start; $i <= $end; $i += $step) {
//var_dump($i);
}
};
$SyncFactory(1, 100000); //class Generator#2 , PHP 协程没有resume关键字,而是“在使用的时候唤起”协程,
// Generator 这个东西是从 generators返回的, http://php.net/manual/zh/class.generator.php
$UsualFactory(1, 100000);
/**
* 从编程角度上看,协程的思想本质上就是控制流的主动让出(yield)和恢复(resume)机制,迭代器常被用来实现协程,
* 所以大部分的语言实现的协程中都有yield关键字,比如Python、PHP、Lua。但也有特殊比如Go就使用的是通道来通信。
*/
foreach ($SyncFactory(1, 10) as $value) {
echo $value . "\n"; // 我理解的是相当于开了10协程跑这次输出操作
} // 那就尝试将它唤醒吧
<?php
/**
* [中断点]
* 我们从生成器认识协程需要认识到:生成器是一种具有中断点的函数,而yield构成了中断点。
* 比如, 你调用$xrange->rewind(),那么xrange()里的代码就会运行到控制流第一次出现yield的地方,
* 而函数内传递给yield语句的值,即为迭代的当前值,可以通过$xrange->current()获取。
* [PHP中的协程实现]
* PHP的协程支持是在迭代生成器的基础上,增加了可以回送数据给生成器的功能,从而达到双向通信即:
* -------------------------------------------------------------
* >>> 生成器<---数据--->调用者 <<<
* -------------------------------------------------------------
*/
echo '/* ------------------------- Yield接收与发送数据 ------------------------- */';
/**
* 容器接收示例
*/
function container()
{
$test = yield "Hello ";
var_dump($test);
$test = yield "World ";
var_dump($test);
}
$container = container(); // 这里又进化成 Generator对象了,还记得SPL 那一坨么? 传送门 [http://php.net/manual/zh/book.spl.php]
var_dump($container->key()); // 返回当前产生的键,int(0)
var_dump($container->current()); // 返回当前产生的值,string(6) "Hello "
$container->next(); // 生成器继续执行 ,$test 未收到 回来的数据,所以 var_dump($test); 输出NULL
var_dump($container->key()); // int(1)
var_dump($container->current()); // string(6) "World "
$container->send('强势占位'); // string(12) "强势占位"
var_dump($container->key()); // null
var_dump($container->current()); // null
if (!$container->valid()) {
echo "我被关闭了" . PHP_EOL;
}
<?php
echo '/* ------------------------- 协程与任务调度 ------------------------- */';
/**
* yield指令提供了任务中断自身的一种方法,然后把控制交回给任务调度器。
* 而PHP语言本身只是提供程序中断的功能,至于任务调度器需要我们自己实现,
* 同时协程在运行多个其他任务时,yield还可以用来在任务和调度器之间进行通信。
*/
/**
* PHP协程任务
* 简单的定义具有任何ID标识的协程函数,如一个轻量级的协程函数示例代码
* @form http://wiki.phpboy.net/doku.php?id=2017-07:54-PHP_Yield协程从入门到精通.md
*
* @version 1.0
*/
class Task
{
protected $taskId;
protected $coroutine;
protected $sendValue = null;
protected $beforeFirstYield = true;
/**
* Task constructor.
*
* @param $taskId
* @param \Generator $coroutine
*/
public function __construct($taskId, Generator $coroutine)
{
$this->taskId = $taskId;
$this->coroutine = $coroutine;
}
/**
* setSendValue
*
* @param $sendValue
*/
public function setSendValue($sendValue)
{
$this->sendValue = $sendValue;
}
/**
* 跑起来的巨人
*
* @return mixed
*/
public function run()
{
if ($this->beforeFirstYield) {
$this->beforeFirstYield = false;
return $this->coroutine->current();
} else {
$retval = $this->coroutine->send($this->sendValue);
$this->sendValue = null;
return $retval;
}
}
/**
* getTaskId
*
* @return mixed
*/
public function getTaskId()
{
return $this->taskId;
}
/**
* 协程关了没?
*
* @return bool
*/
public function isFinished()
{
return !$this->coroutine->valid();
}
}
/**
* PHP协程调度器
* 简单来说,是可以在多个任务之间相互协调,及任务之间相互切换的一种进程资源的分配器。
* 调度器的实现方式有多种,大致分为两类:一是,队列;二是,定时器
*
* @version 1.0
*/
class Scheduler
{
protected $maxTaskId = 0;
protected $taskMap = []; // taskId => task
protected $taskQueue;
public function __construct()
{
// http://php.net/manual/zh/class.splqueue.php
$this->taskQueue = new SplQueue();
}
/**
* 创建一个task 开启一个协程
*
* @param \Generator $coroutine
* @return int
*/
public function newTask(Generator $coroutine)
{
$tid = ++$this->maxTaskId;
$task = new Task($tid, $coroutine);
$this->taskMap[$tid] = $task;
$this->schedule($task);
return $tid;
}
/**
* 队列入队
*
* @param \Task $task
*/
public function schedule(Task $task)
{
$this->taskQueue->enqueue($task);
}
/**
* 消费队列内容
*/
public function run()
{
GLOBAL $i;
while (!$this->taskQueue->isEmpty()) {
// 出队列
$task = $this->taskQueue->dequeue();
$retval = $task->run(); // 跑Task 中的 run
echo "Scheduler runtime:" . ++$i . " retval is:\n";
if ($retval instanceof SystemCall) {
$retval($task, $this); // 如果为函数调用则这样跑起来
continue;
}
if ($task->isFinished()) { // 结束了就删掉
unset($this->taskMap[$task->getTaskId()]);
} else {
$this->schedule($task); // 那就回炉重造
}
}
}
}
class SystemCall
{
protected $callback;
public function __construct(callable $callback)
{
$this->callback = $callback;
}
/**
* 以函数方式调用
*
* @param \Task $task
* @param \Scheduler $scheduler
* @return mixed
*/
public function __invoke(Task $task, Scheduler $scheduler)
{
$callback = $this->callback;
return $callback($task, $scheduler);
}
}
/**
* newTask()方法创建一个新任务,然后把这个任务放入任务map数组里,接着它通过把任务放入任务队列里来实现对任务的调度。
* 接着run()方法扫描任务队列,运行任务,如果一个任务结束了,那么它将从队列里删除,否则它将在队列的末尾再次被调度。
*/
function getTaskId()
{
return new SystemCall(function (Task $task, Scheduler $scheduler) {
$task->setSendValue($task->getTaskId());
$scheduler->schedule($task);
});
}
function task($max)
{
$tid = (yield getTaskId());
for ($i = 0; $i < $max; $i++) {
echo "this is task $tid iteration $i .\n";
yield;
}
}
$scheduler = new Scheduler();
$scheduler->newTask(task(3));
$scheduler->newTask(task(3));
/*
function testYield()
{
yield getTaskId();
}
var_dump(testYield()->current());
输出:
object(SystemCall)#8 (1) {
["callback":protected]=>
object(Closure)#9 (1) {
["parameter"]=>
array(2) {
["$task"]=>
string(10) ""
["$scheduler"]=>
string(10) ""
}
}
}
*/
$scheduler->run();
/*
输出:
Scheduler runtime:1 retval is:
Scheduler runtime:2 retval is:
this is task 1 iteration 0 .
Scheduler runtime:3 retval is:
this is task 2 iteration 0 .
Scheduler runtime:4 retval is:
this is task 1 iteration 1 .
Scheduler runtime:5 retval is:
this is task 2 iteration 1 .
Scheduler runtime:6 retval is:
this is task 1 iteration 2 .
Scheduler runtime:7 retval is:
this is task 2 iteration 2 .
Scheduler runtime:8 retval is:
Scheduler runtime:9 retval is:
Scheduler runtime:10 retval is:
*/
function task1() {
for ($i = 1; $i <= 10; ++$i) {
echo "This is task 1 iteration $i.\n";
yield;
}
}
function task2() {
for ($i = 1; $i <= 5; ++$i) {
echo "This is task 2 iteration $i.\n";
yield;
}
}
$scheduler->newTask(task1(21));
$scheduler->newTask(task2(21));
$scheduler->run();
/*
输出:
This is task 1 iteration 1.
Scheduler runtime:11 retval is:
This is task 2 iteration 1.
Scheduler runtime:12 retval is:
This is task 1 iteration 2.
Scheduler runtime:13 retval is:
This is task 2 iteration 2.
Scheduler runtime:14 retval is:
This is task 1 iteration 3.
Scheduler runtime:15 retval is:
This is task 2 iteration 3.
Scheduler runtime:16 retval is:
This is task 1 iteration 4.
Scheduler runtime:17 retval is:
This is task 2 iteration 4.
Scheduler runtime:18 retval is:
This is task 1 iteration 5.
Scheduler runtime:19 retval is:
This is task 2 iteration 5.
Scheduler runtime:20 retval is:
This is task 1 iteration 6.
Scheduler runtime:21 retval is:
Scheduler runtime:22 retval is:
This is task 1 iteration 7.
Scheduler runtime:23 retval is:
This is task 1 iteration 8.
Scheduler runtime:24 retval is:
This is task 1 iteration 9.
Scheduler runtime:25 retval is:
This is task 1 iteration 10.
Scheduler runtime:26 retval is:
Scheduler runtime:27 retval is:
*/
<?php
// 最后回顾一下知识点,协程不一定能提高速度,但它一定能节约到内存
/**
* 协程创建
*
* @param $start
* @param $limit
* @param int $step
* @return \Generator
*/
function xrange($start, $limit, $step = 1)
{
for ($i = $start; $i <= $limit; $i += $step) {
yield $i;
}
}
$max = 999999;
// 没有使用协程
$c = new codeStatus(true);
$c->timeStart();
$simpleStart = microtime(true);
foreach (range(1, $max, 2) as $number) {
}
$simpleEnd = microtime(true);
$c->timeEnd();
print_r($c->showStatus());
// 使用协程
$c = new codeStatus(true);
$c->timeStart();
$start = microtime(true);
foreach (xrange(1, $max, 2) as $number) {
}
$end = microtime(true);
$c->timeEnd();
print_r($c->showStatus());
/*
结果如下:
Array
(
[0] => 耗时14.484毫秒
[1] => 占用内存:389.875KB
)
Array
(
[0] => 耗时19.184毫秒
[1] => 占用内存:33.125KB
)
*/
/**
* 程序耗时统计
*
* @version 1.0
*/
class codeStatus
{
/**
* @param:boolen $time_type时间类型, false是秒,true是毫秒,
* boolen $show_m是否显示内存,
* boolen $show_type,false是array,ture为json,
* $regmax是数据保留几位
*/
public $regmax;
public $runTime = 0;
public $time_type;
public $is_show_memory;
public $show_type;
private static $t1;
private static $t2;
public function __construct($time_type = false, $show_m = true, $show_type = false, $regmax = 3)
{
$this->regmax = $regmax;
$this->is_show_memory = $show_m;
$this->time_type = $time_type;
$this->show_type = $show_type;
}
public function timeStart()
{
self::$t1 = microtime(true);
}
public function timeEnd()
{
self::$t2 = microtime(true);
}
private function getTime()
{
if (self::$t1 != '' && self::$t2 != '') {
if ($this->time_type == false) {
return '耗时' . round(self::$t2 - self::$t1, $this->regmax) . '秒';
} else if ($this->time_type == true) {
return '耗时' . round(self::$t2 - self::$t1, ($this->regmax + 3)) * 1000 . '毫秒';
}
} else {
return "error param";
}
}
private function getmemory()
{
$memory = (!function_exists('memory_get_usage')) ? '0' : round(memory_get_usage() / 1024, $this->regmax) . 'KB';
return '占用内存:' . $memory;
}
public function showStatus()
{
if ($this->is_show_memory == true) {
$arr = array (self::getTime(), self::getmemory());
} else {
$arr = array (self::getTime());
}
if ($this->show_type == false) {
return $arr;
} else {
return json_encode($arr);
}
}
}
其他
数组双向队列
用PHP实现一个双向队列:
class Deque
{
private $queue = array();
public function addFirst ( $item )
{
return array_unshift( $this->queue, $item );
}
public function addLast ( $item )
{
return array_push( $this->queue, $item );
}
public function removeFirst ()
{
return array_shift( $this->queue );
}
public function removeLast ()
{
return array_pop( $this->queue );
}
}
线性表删除
/**
* 线性表的删除(数组中实现),删除数组中指定的键的值
* @param $array
* @param $i
* @return mixed
*/
function delete_array_element($array, $i)
{
$len = count($array);
for ( $j = $i; $j < $len; $j++ )
{
$array[ $j ] = $array [ $j + 1 ];
}
array_pop($array);
return $array;
}
举例:
$array = array(2, 4, 6, 8, 10);
$array = delete_array_element($array, 2);
print_r($array); // 输出 Array ( [0] => 2 [1] => 4 [2] => 8 [3] => 10 )
动态规划
参阅 https://ibaiyang.github.io/blog/算法/2022/01/25/图解动态规划.html
参考资料
PHP 手册 函数参考 变量与类型相关扩展 数组 数组 函数 https://www.php.net/manual/zh/ref.array.php
用 PHP 的方式实现的各类算法合集 https://github.com/m9rco/algorithm-php
PHP实现八大算法 https://www.cnblogs.com/zixuanfy/p/7617451.html
PHP的基本算法合集 https://www.php.cn/php-weizijiaocheng-394062.html
PHP算法 https://www.jianshu.com/p/cb2ad99029c8
php数据结构和算法 https://www.csdn.net/gather_21/MtTacg3sMzkxNy1ibG9n.html
七大常用PHP算法 http://www.sohu.com/a/118661179_468191
堆排序算法与PHP实现 https://www.cnblogs.com/iampeter/p/3223487.html
PHP实现排序算法—-堆排序(Heap Sort) https://blog.csdn.net/baidu_30000217/article/details/53087079
PHP实现堆排序 https://www.cnblogs.com/zhenbianshu/p/5273995.html
哪本《数据结构与算法》最好? https://www.zhihu.com/question/21628833/answer/54623559
数据结构与算法必备的 50 个代码实现 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/67490380
常见数据结构与算法整理总结(上) https://www.cnblogs.com/xkzhangsanx/p/10888179.html
PHP实现各种经典算法 http://www.cnblogs.com/hellohell/p/5718175.html
php面试题之二——数据结构和算法(高级部分) https://blog.csdn.net/s1070/article/details/51174725
阮一峰 字符串匹配的KMP算法 http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2013/05/Knuth%E2%80%93Morris%E2%80%93Pratt_algorithm.html
从头到尾彻底理解 KMP https://wiki.jikexueyuan.com/project/kmp-algorithm/
KMP算法—终于全部弄懂了 https://blog.csdn.net/dark_cy/article/details/88698736
PHP 手册 函数参考 其它基本扩展 SPL 数据结构 The SplStack class https://www.php.net/manual/zh/class.splstack.php