正文
查找篇
顺序查找
<?php
/**
* 顺序查找(数组里查找某个值的键)
* @param $array 给定数组
* @param $high 最大键,结束位置
* @param $value 要查找的值
* @return int
*/
function sequence_search($array, $high, $value)
{
for( $i=0; $i <= $high; $i++) {
if ($array[$i] == $value) {
break;
}
}
if ($i <= $high) {
return $i;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
举例:
$array = array(2, 4, 6, 8, 10);
$key = sequence_search($array, 3, 6);
echo $key; // 输出 2
二分查找
二分查找是在排好序的数组中查找指定值的数组键值。
/**
* 二分查找(数组里查找某个值的键),也叫半分法
* @param $array 给定数组
* @param $low 最小键,开始位置
* @param $high 最大键,结束位置
* @param $value 要查找的值
* @return int
*/
function binary_search($array, $low, $high, $value)
{
if ( $low <= $high ) {
$mid = intval( ($low+$high)/2 );
if ( $array[$mid] == $value ) {
return $mid;
} elseif ( $value < $array[$mid] ) {
return binary_search ( $array, $low, $mid-1, $value );
} else {
return binary_search ( $array, $mid+1, $high, $value );
}
}
return -1;
}
举例:
$array = array(2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14);
$key = binary_search($array, 2, 7 , 8);
echo $key; // 输出 3
特别说明,$value必须在数组$low与$high的值之间存在,否则都返回-1。
这里看到数组要是排好序的,如果是乱序的,可以用下面的函数排序(除了数字,也可对字符排序):
sort() - 对数组进行升序排列
rsort() - 对数组进行降序排列
/**
* 递归版 二分查找
*
* @param array $container
* @param $search
* @param int $low
* @param string $top
* @return int|string
*/
function BinaryQueryRecursive(array $container, $search, $low = 0, $top = 'default')
{
$top === 'default' && $top = count($container);
if ($low <= $top) {
$mid = intval(floor($low + $top) / 2);
if (!isset($container[$mid])) {
return '没找着哦';
}
if ($container[$mid] == $search) {
return $mid;
}
if ($container[$mid] < $search) {
return BinaryQueryRecursive($container, $search, $mid + 1, $top);
} else {
return BinaryQueryRecursive($container, $search, $low, $mid - 1);
}
}
}
function QuickQuery($array, $value, $low = 0, $high = 0)
{
//判断是否为第一次调用
if (count($array) != 0 and $high == 0) {
$high = count($array);
}
//如果还存在剩余的数组元素
if ($low <= $high) {
//取$low和$high的中间值
$mid = intval(($low + $high) / 2);
//如果找到则返回
if ($array[$mid] == $value) {
return $mid;
} else if ($value < $array[$mid]) {//如果没有找到,则继续查找
return QuickQuery($array, $value, $low, $mid - 1);
} else {
return QuickQuery($array, $value, $mid + 1, $high);
}
}
return -1;
}
echo QuickQuery([4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 8], 8);
/**
* 非递归版 二分查找
*
* @param array $container
* @param $search
* @return int|string
*/
function BinaryQuery(array $container, $search)
{
$top = count($container);
$low = 0;
while ($low <= $top) {
$mid = intval(floor(($low + $top) / 2));
if (!isset($container[$mid])) {
return '没找着哦';
}
if ($container[$mid] == $search) {
return $mid;
}
$container[$mid] < $search && $low = $mid + 1;
$container[$mid] > $search && $top = $mid - 1;
}
}
快速查询
快速选择是一种改进的快速排序算法,用于在未排序的列表中查找特定元素。它通过随机选择一个主元素, 将列表划分为小于、等于和大于主元素的子列表,然后递归地在相应的子列表中进行选择,直到找到目标元素。 PHP 中可以使用自定义函数来实现快速选择算法。
<?php
function quickSelect($arr, $target, $left, $right) {
}
$unsortedArray = [3, 5, 2, 1, 4];
$target = 3;
$index = quickSelect($unsortedArray, $target, 0, count($unsortedArray) - 1);
echo "找到目标元素,索引为:{$index}"; // 输出:2
插入查找
思路分析:对于数组长度比较大,关键字分布又是比较均匀的来说,插值查找的效率比折半查找的效率高。
它是二分查找的改进。 在英文词典里查找“apple”,你下意识里翻开词典是翻前面的书页还是后面的书页呢?如果再查“zoo”,你又会怎么查? 显然你不会从词典中间开始查起,而是有一定目的地往前或往后翻。
分布比较均匀的情况下,用密度乘以间隔长度就该是我们要找的值,理论根据:p = (yb - ya) / (xb - xa) = (yc - ya) / (xc - xa) 。
/**
* insertQuery
*
* @param array $container
* @param $num
* @return bool|float|int
*/
function insertQuery(array $container, $num)
{
$count = count($container);
$lower = 0;
$high = $count - 1;
while ($lower <= $high) {
if ($container[ $lower ] == $num) {
return $lower;
}
if ($container[ $high ] == $num) {
return $high;
}
// $left = intval($lower + $num - $container[ $lower ]);
// $right = ($container[ $high ] - $container[ $lower ]) * ($high - $lower);
// $middle = $left /$right;
// ($middle - $lower) / ($num - $container[ $lower ]) = ($high - $lower) / ($container[ $high ] - $container[ $lower ])
$middle = intval(($high - $lower) * ($num - $container[ $lower ]) / ($container[ $high ] - $container[ $lower ])) + $lower;
if ($num < $container[ $middle ]) {
$high = $middle - 1;
} else if ($num > $container[ $middle ]) {
$lower = $middle + 1;
} else {
return $middle;
}
}
return false;
}
斐波那契查找
思路分析:斐波那契查找 利用黄金分割原理
斐波那契数列,又称黄金分割数列,指的是这样一个数列:1、1、2、3、5、8、13、21、····,
在数学上,斐波那契被递归方法如下定义:F(1)=1,F(2)=1,F(n)=f(n-1)+F(n-2) (n>=2)。
该数列越往后相邻的两个数的比值越趋向于黄金比例值(0.618)。
斐波那契查找就是在二分查找的基础上根据斐波那契数列进行分割的。在斐波那契数列找一个等于略大于查找表中元素个数的数F[n], 将原查找表扩展为长度为F[n] (如果要补充元素,则补充重复最后一个元素,直到满足F[n]个元素),完成后进行斐波那契分割, 即F[n]个元素分割为前半部分F[n-1]个元素,后半部分F[n-2]个元素,找出要查找的元素在那一部分并递归,直到找到。
斐波那契查找的时间复杂度还是O(log 2 n ),但是 与折半查找相比,斐波那契查找的优点是它只涉及加法和减法运算, 而不用除法,而除法比加减法要占用更多的时间,因此,斐波那契查找的运行时间理论上比折半查找小,但是还是得视具体情况而定。
对于斐波那契数列:1、1、2、3、5、8、13、21、34、55、89……(也可以从0开始),前后两个数字的比值随着数列的增加,越来越接近黄金比值0.618。 比如这里的89,把它想象成整个有序表的元素个数,而89是由前面的两个斐波那契数34和55相加之后的和, 也就是说把元素个数为89的有序表分成由前55个数据元素组成的前半段和由后34个数据元素组成的后半段, 那么前半段元素个数和整个有序表长度的比值就接近黄金比值0.618,假如要查找的元素在前半段, 那么继续按照斐波那契数列来看,55 = 34 + 21,所以继续把前半段分成前34个数据元素的前半段和后21个元素的后半段, 继续查找,如此反复,直到查找成功或失败,这样就把斐波那契数列应用到查找算法中了。
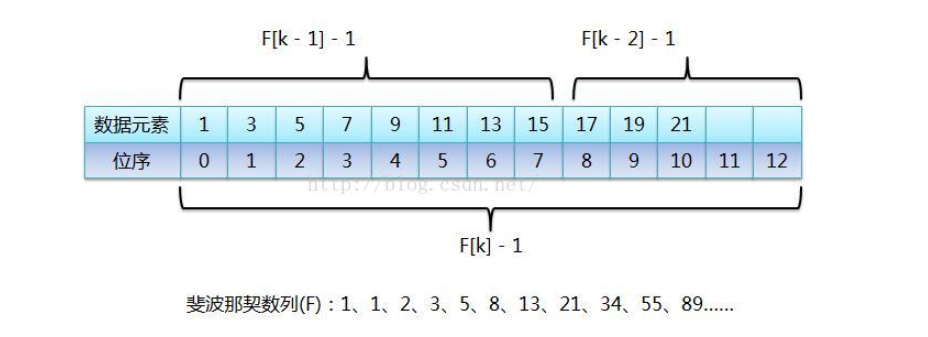
从图中可以看出,当有序表的元素个数不是斐波那契数列中的某个数字时,需要把有序表的元素个数长度补齐,让它成为斐波那契数列中的一个数值, 当然把原有序表截断肯定是不可能的,不然还怎么查找。然后图中标识每次取斐波那契数列中的某个值时(F[k]),都会进行-1操作, 这是因为有序表数组位序从0开始的,纯粹是为了迎合位序从0开始。
用迭代实现斐波那契查找算法如下
<?php
/**
* $num == $container[$mid],直接返回
* $num < $container[$mid],新范围是第 $low 个到 $mid-1 个,此时范围个数为 produced($key-1)-1 个
* $num > $container[$mid],新范围是第 $mid+1 个到 $high 个,此时范围个数为 produced($key-2)-1 个
*/
class FibonacciQuery
{
/**
* FibonacciQuery constructor.
*
* @param array $container
* @param $num
*/
public function __construct(array $container, $num)
{
$count = count($container);
$lower = $key = $result = 0;
$high = $count - 1;
//计算$count位于斐波那契数列的位置,$this->produced($key) - 1 是因为数组键名从0开始
while ($count > ($this->produced($key) - 1)) {
$key++;
}
//将不满的数值补全,补的数值为数组的最后一位
for ($j = $count; $j <= ($this->produced($key) - 1); $j++) {
$container[$j] = $container[$count - 1];
}
//查找开始
while ($lower <= $high) {
//计算当前分隔的下标
$mid = $lower + $this->produced($key - 1) - 1;
if ($num < $container[$mid]) {
$high = $mid - 1;
$key -= 1; //斐波那契数列数列下标减一位
} else if ($num > $container[$mid]) {
$lower = $mid + 1;
$key -= 2; //斐波那契数列数列下标减两位
} else {
if ($mid <= $count - 1) {
$result = $mid;
break;
} else { //这里$mid大于$count-1说明是补全数值,返回$count-1
$result = $count - 1;
break;
}
}
}
var_dump($result);
}
/**
* 创建一个生产斐波那契数列
*
* @param $length
* @return int
*/
public function produced($length)
{
if ($length < 2) {
return ($length == 0 ? 0 : 1);
}
return $this->produced($length - 1) + $this->produced($length - 2);
}
}
测试:
new FibonacciQuery([4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10], 8);
暴力匹配算法
暴力匹配算法是一种最容易想到的字符串匹配算法。
假设现在我们面临这样一个问题:有一个文本串 S,和一个模式串 P,现在要查找 P 在 S 中的位置,怎么查找呢?
如果用暴力匹配的思路,并假设现在文本串 S 匹配到 i 位置,模式串 P 匹配到 j 位置,则有:
- 如果当前字符匹配成功(即
S[i] == P[j]),则i++,j++,继续匹配下一个字符; - 如果失配(即
S[i]! = P[j]),令i = i - (j - 1),j = 0。相当于每次匹配失败时,i 回溯,j 被置为0。
理清楚了暴力匹配算法的流程及内在的逻辑,咱们可以写出暴力匹配的代码,如下:
function ViolentMatch($haystack, $needle) {
$haystackLen = mb_strlen($haystack, 'utf-8');
$needleLen = mb_strlen($needle, 'utf-8');
$i = $j = 0;
while ($i < $haystackLen && $j < $needleLen) {
if ($haystack[$i] == $needle[$j]) {
//①如果当前字符匹配成功(即S[i] == P[j]),则i++,j++
$i++;
$j++;
} else {
//②如果失配(即S[i]! = P[j]),令i = i - (j - 1),j = 0
$i = $i - $j + 1;
$j = 0;
}
}
// 匹配成功,返回模式串p在文本串s中的位置,否则返回-1
if ($j == $needleLen) {
return $i - $j;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
测试代码:
echo ViolentMatch("BBC ABCDAB ABCDABCDABDE", "ABCDABD");
整个过程如下所示:

KMP算法
KMP算法是一种改进的字符串匹配算法。
KMP 算法是 D.E.Knuth、J,H,Morris 和 V.R.Pratt 三人于 1977 年联合发表,称之为 Knuth-Morria-Pratt 算法,简称 KMP 算法。 该算法相对于 Brute-Force(暴力)算法有比较大的改进,主要是消除了主串指针的回溯,从而使算法效率有了某种程度的提高。
KMP精要:KMP在进行朴素匹配时,如果发现不匹配字符时,通过对已经匹配的那部分字符串的最大前缀来快速找到下一个模式串需要匹配的位置。 KMP对模式进行预处理时间复杂度O(m),匹配时间复杂度O(n),总的KMP时间复杂度为O(m+n)。 参考 阮一峰 字符串匹配的KMP算法 。 具体代码实现,参考从头到尾彻底理解 KMP 。
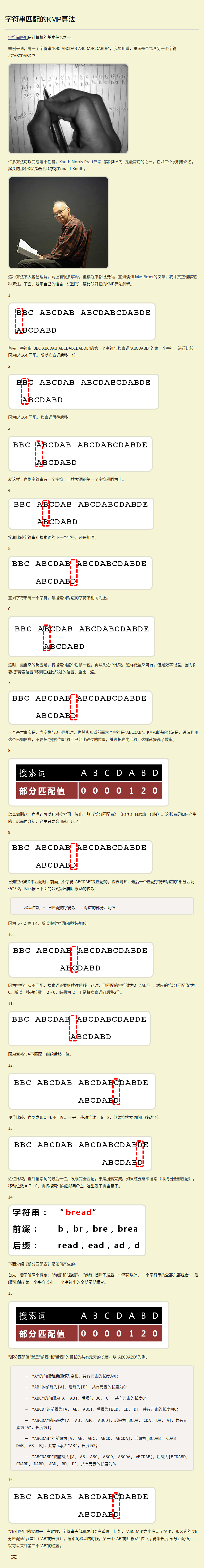
KMP 的算法流程:
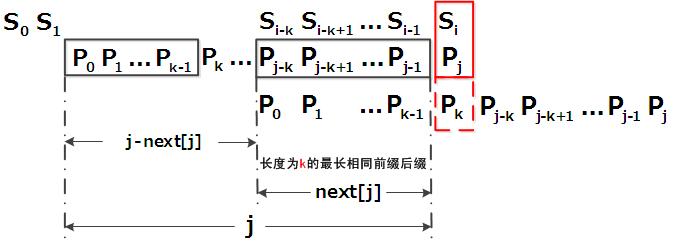
- 假设现在文本串 S 匹配到 i 位置,模式串 P 匹配到 j 位置
- 如果 j = -1,或者当前字符匹配成功(即 S[i] == P[j]),都令 i++,j++,继续匹配下一个字符;
- 如果 j != -1,且当前字符匹配失败(即 S[i] != P[j]),则令 i 不变,j = next[j]。此举意味着失配时,模式串 P 相对于文本串 S 向右移动了 j - next [j] 位。
- 换言之,当匹配失败时,模式串向右移动的位数为:失配字符所在位置 - 失配字符对应的 next 值(next 数组的求解会在下文的 3.3.3 节中详细阐述),即移动的实际位数为:j - next[j],且此值大于等于1。
代码类:
class KMP
{
public $haystack;
public $needle;
private $_haystackLen;
private $_needleLen;
private $_matchTable;
private $_isMatch;
//构造函数
function __construct($haystack, $needle)
{
$this->haystack = $haystack;
$this->needle = $needle;
//初始化一些参数
$this->_haystackLen = $this->getLen($this->haystack);
$this->_needleLen = $this->getLen($this->needle);
$this->_matchTable = $this->getMatchTable();
$this->_isMatch = false;
}
//类似strpos函数功能
public function strpos()
{
//haystack
$haystackIdx = $matchNum = 0;
while ($haystackIdx <= $this->_haystackLen - $this->_needleLen) {
//needle
$needIdx = 0;
for (; $needIdx < $this->_needleLen; $needIdx++) {
if (strcmp($this->haystack[$haystackIdx], $this->needle[$needIdx]) <> 0) {
if ($matchNum > 0) {
$lastMatchValue = $this->getLastMatchValue($needIdx - 1);
$haystackIdx += $this->getStep($matchNum, $lastMatchValue);
$matchNum = 0;
} else {
$haystackIdx++;
}
break;
} else {
$haystackIdx++;
$matchNum++;
if ($matchNum == $this->_needleLen) {
$this->_isMatch = true;
break;
}
}
}
if ($this->_isMatch == true) {
break;
}
}
return $this->_isMatch ? $haystackIdx - $this->_needleLen : false;
}
//获取字符长度
private function getLen($str)
{
return mb_strlen($str, 'utf-8');
}
//获取部分匹配表
private function getMatchTable()
{
$matchTable = [];
for ($i = 0; $i < $this->_needleLen; $i++) {
$intersectLen = 0;
$nowStr = mb_substr($this->needle, 0, $i + 1, 'utf-8');
$preFixArr = $this->getPreFix($nowStr);
$sufFixArr = $this->getSufFix($nowStr);
if ($preFixArr && $sufFixArr) {
$intersectArr = array_intersect($preFixArr, $sufFixArr);
if (!empty($intersectArr)) {
$intersect = array_pop($intersectArr); // 从栈中获取最上面一条,也就是最长的匹配
$intersectLen = mb_strlen($intersect, 'utf-8');
}
}
$matchTable[$i] = $intersectLen;
}
return $matchTable;
}
//获取前缀数组,从短到长
private function getPreFix($str)
{
$outArr = [];
$strLen = $this->getLen($str);
if ($strLen > 1) {
for ($i = 1; $i < $strLen; $i++) {
$outArr[] = mb_substr($str, 0, $i, 'utf-8');
}
}
return $outArr;
}
//获取后缀数组
private function getSufFix($str)
{
$outArr = [];
$strLen = $this->getLen($str);
if ($strLen > 1) {
for ($i = 1; $i < $strLen; $i++) {
$outArr[] = mb_substr($str, $i, null, 'utf-8');
}
}
return $outArr;
}
//计算步长
private function getStep($matchNum, $lastMatchValue)
{
return $matchNum - $lastMatchValue;
}
//获取最后匹配值
private function getLastMatchValue($index)
{
return isset($this->_matchTable[$index]) ? $this->_matchTable[$index] : 0;
}
}
测试类:
$str = 'a b a c a a b a c a b a c a b a a b b';
$subStr = 'a b a c a b';
$kmp = new KMP($str, $subStr);
var_dump($kmp->strpos());
$kmp->haystack = 'pull requests';
$kmp->needle = 'sts';
var_dump($kmp->strpos());
$kmp->haystack = 'i love you';
$kmp->needle = 'hate';
var_dump($kmp->strpos());
广度优先搜索
这里面涉及到 什么是 “图” , 深度优先遍历 和 广度优先遍历 , 等。
什么是 深度/广度 优先遍历?
深度优先遍历简称DFS(Depth First Search),广度优先遍历简称BFS(Breadth First Search),它们是遍历图当中所有顶点的两种方式。
深度优先遍历(DFS):先深入探索,走到头再回退寻找其他出路的遍历方式。 二叉树的前序、中序、后序遍历,本质上就是深度优先遍历。
广度优先遍历(BFS):一层一层由内而外的遍历方式。 二叉树的层序遍历,本质上就是广度优先遍历。
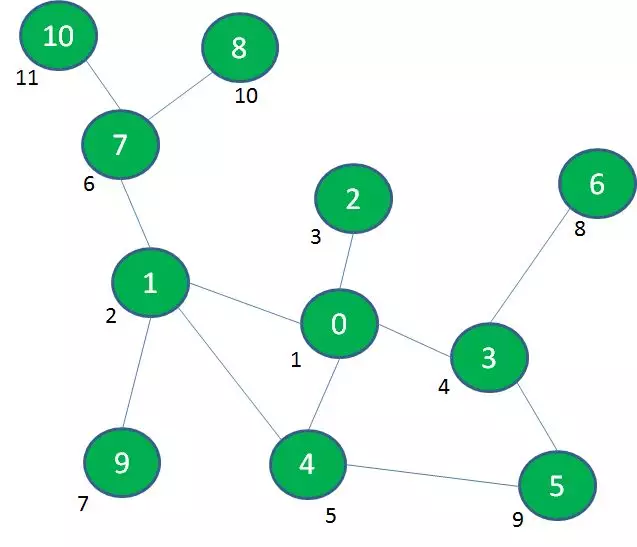
深度优先遍历,可以使用回溯:自后向前追溯曾经访问过的路径,就叫做回溯。 要想实现回溯,可以利用栈的先入后出特性,也可以采用递归的方式(因为递归本身就是基于方法调用栈来实现)。
广度优先遍历,可以使用重放:把遍历过的顶点按照之前的遍历顺序重新回顾,就叫做重放。 同样的,要实现重放也需要额外的存储空间,可以利用队列的先入先出特性来实现。
下面实现广度优先遍历。
思路分析: BFS并不使用经验法则算法。从算法的观点,所有因为展开节点而得到的子节点都会被加进一个先进先出的队列中
时间复杂度:O(n)
宽度优先搜索算法(又称广度优先搜索)是最简便的图的搜索算法之一,这一算法也是很多重要的图的算法的原型。 Dijkstra单源最短路径算法和Prim最小生成树算法都采用了和宽度优先搜索类似的思想。 其别名又叫BFS,属于一种盲目搜寻法,目的是系统地展开并检查图中的所有节点,以找寻结果。 换句话说,它并不考虑结果的可能位置,彻底地搜索整张图,直到找到结果为止。
<?php
class BFSQuery
{
/**
* @var array 关系网络
*/
protected $relationship;
/**
* @var \SplQueue 处理队列
*/
protected $queue;
/**
* @var string 搜索结果
*/
protected $target;
/**
* BFSQuery constructor.
*
* @param array $relationship
* @param string $target
*/
public function __construct(array $relationship, $target)
{
$this->relationship = $relationship;
$this->queue = new SplQueue();
$this->target = $target;
$this->generator($this->relationship);
}
/**
* 开始入列
*
* @param array $relation
* @return \Generator
*/
public function generator($relation)
{
foreach ($relation as $value) {
$this->schedule($value);
}
}
/**
* 队列入队
*
* @param $item
* @return int
*/
public function schedule($item)
{
$this->queue->enqueue($item);
}
/**
* 队列中查找符合条件
*
* @return string
*/
public function run()
{
$result = $this->target . '没有人有~!';
while (!$this->queue->isEmpty()) {
// 出队列
$item = $this->queue->dequeue();
if (!isset($item['friend'])) {
continue;
}
if (!isset($item['fruit'])) {
continue;
}
$totalFruit = count($item['fruit']);
$mark = 0;
while ($totalFruit > $mark) {
if ($item['fruit'][$mark] === $this->target) {
$result = '找到了~!';
break 2;
}
$mark++;
}
$this->generator($item['friend']);
}
return $result;
}
}
方案测试:你现在需要一个 mango ,所以你需要在你的朋友圈里搜刮,你可以先从Jack 与 tom 身上找,
然后再从他们的朋友身上找,然后再从他们朋友的朋友哪里找:
$me = array (
'jack' => array (
'fruit' => array ('apple', 'banana', 'dragon'),
'friend' => array (
'lucy' => array (
'fruit' => array ('bear', 'watermelon'),
'friend' => array (
'marco' => array (
'fruit' => array ('mango', 'cherry'), // Mango 在这儿
'friend' => array (
'...',
)
),
),
),
'bob' => array (
'fruit' => array ('orange', 'mangosteen', 'peach'),
'friend' => array (
'',
),
),
),
),
'tom' => array (
'fruit' => array (
'apple',
'banana',
),
'friend' => array (
'lucy' => array (
'fruit' => array (),
'friend' => array (
'lucy' => array (
'fruit' => array ('bear', 'watermelon'),
'friend' => array (
'marco' => array (
'fruit' => array ('mango', 'cherry'), // Mango 在这儿也有
'friend' => array (
'...',
)
),
),
),
),
),
'bob' => array (
'fruit' => array ('apple', 'peach'),
'friend' => array (
'marco' => array (
'fruit' => array ('mango', 'cherry'), // Mango 在这儿也有
'friend' => array (
'Marco 有无数多的盆友...',
)
),
)
),
),
)
);
echo (new BFSQuery($me, 'mango'))->run();
SplQueue标准类:
/**
* The SplDoublyLinkedList class provides the main functionalities of a doubly linked list.
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/class.spldoublylinkedlist.php
*/
class SplDoublyLinkedList implements Iterator, Countable, ArrayAccess, Serializable
{
const IT_MODE_LIFO = 2;
const IT_MODE_FIFO = 0;
const IT_MODE_DELETE = 1;
const IT_MODE_KEEP = 0;
/**
* Add/insert a new value at the specified index
* @param mixed $index The index where the new value is to be inserted.
* @param mixed $value The new value for the index.
* @link https://php.net/spldoublylinkedlist.add
* @return void
* @since 5.5
*/
public function add($index, $value) {}
/**
* Pops a node from the end of the doubly linked list
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.pop.php
* @return mixed The value of the popped node.
*/
public function pop () {}
/**
* Shifts a node from the beginning of the doubly linked list
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.shift.php
* @return mixed The value of the shifted node.
*/
public function shift () {}
/**
* Pushes an element at the end of the doubly linked list
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.push.php
* @param mixed $value <p>
* The value to push.
* </p>
* @return void
*/
public function push ($value) {}
/**
* Prepends the doubly linked list with an element
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.unshift.php
* @param mixed $value <p>
* The value to unshift.
* </p>
* @return void
*/
public function unshift ($value) {}
/**
* Peeks at the node from the end of the doubly linked list
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.top.php
* @return mixed The value of the last node.
*/
public function top () {}
/**
* Peeks at the node from the beginning of the doubly linked list
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.bottom.php
* @return mixed The value of the first node.
*/
public function bottom () {}
/**
* Counts the number of elements in the doubly linked list.
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.count.php
* @return int the number of elements in the doubly linked list.
*/
public function count () {}
/**
* Checks whether the doubly linked list is empty.
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.isempty.php
* @return bool whether the doubly linked list is empty.
*/
public function isEmpty () {}
/**
* Sets the mode of iteration
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.setiteratormode.php
* @param int $mode <p>
* There are two orthogonal sets of modes that can be set:
* </p>
* The direction of the iteration (either one or the other):
* <b>SplDoublyLinkedList::IT_MODE_LIFO</b> (Stack style)
* @return void
*/
public function setIteratorMode ($mode) {}
/**
* Returns the mode of iteration
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.getiteratormode.php
* @return int the different modes and flags that affect the iteration.
*/
public function getIteratorMode () {}
/**
* Returns whether the requested $index exists
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.offsetexists.php
* @param mixed $index <p>
* The index being checked.
* </p>
* @return bool true if the requested <i>index</i> exists, otherwise false
*/
public function offsetExists ($index) {}
/**
* Returns the value at the specified $index
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.offsetget.php
* @param mixed $index <p>
* The index with the value.
* </p>
* @return mixed The value at the specified <i>index</i>.
*/
public function offsetGet ($index) {}
/**
* Sets the value at the specified $index to $newval
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.offsetset.php
* @param mixed $index <p>
* The index being set.
* </p>
* @param mixed $value <p>
* The new value for the <i>index</i>.
* </p>
* @return void
*/
public function offsetSet ($index, $value) {}
/**
* Unsets the value at the specified $index
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.offsetunset.php
* @param mixed $index <p>
* The index being unset.
* </p>
* @return void
*/
public function offsetUnset ($index) {}
/**
* Rewind iterator back to the start
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.rewind.php
* @return void
*/
public function rewind () {}
/**
* Return current array entry
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.current.php
* @return mixed The current node value.
*/
public function current () {}
/**
* Return current node index
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.key.php
* @return string|float|int|bool|null The current node index.
*/
public function key () {}
/**
* Move to next entry
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.next.php
* @return void
*/
public function next () {}
/**
* Move to previous entry
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.prev.php
* @return void
*/
public function prev () {}
/**
* Check whether the doubly linked list contains more nodes
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.valid.php
* @return bool true if the doubly linked list contains any more nodes, false otherwise.
*/
public function valid () {}
/**
* Unserializes the storage
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.serialize.php
* @param string $data The serialized string.
* @return void
* @since 5.4
*/
public function unserialize($data) {}
/**
* Serializes the storage
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.unserialize.php
* @return string The serialized string.
* @since 5.4
*/
public function serialize () {}
/**
* @return array
* @since 7.4
*/
public function __debugInfo(){}
/**
* @return array
* @since 7.4
*/
public function __serialize(): array {}
/**
* @param array $data
* @since 7.4
*/
public function __unserialize(array $data): void {}
}
/**
* The SplQueue class provides the main functionalities of a queue implemented using a doubly linked list.
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/class.splqueue.php
*/
class SplQueue extends SplDoublyLinkedList {
/**
* Adds an element to the queue.
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/splqueue.enqueue.php
* @param mixed $value <p>
* The value to enqueue.
* </p>
* @return void
*/
public function enqueue ($value) {}
/**
* Dequeues a node from the queue
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/splqueue.dequeue.php
* @return mixed The value of the dequeued node.
*/
public function dequeue () {}
/**
* Sets the mode of iteration
* @link https://php.net/manual/en/spldoublylinkedlist.setiteratormode.php
* @param int $mode <p>
* There are two orthogonal sets of modes that can be set:
* </p>
* The direction of the iteration (either one or the other):
* <b>SplDoublyLinkedList::IT_MODE_LIFO</b> (Stack style)
* @return void
*/
public function setIteratorMode ($mode) {}
}
迪克斯特拉算法
这里面涉及到图的 “最短路径” 问题 , Dijkstra 算法的优化 , 还有图的 “多源” 最短路径 , 等。
思路分析:单源最短路径问题
Dijkstra 算法一般的表述通常有两种方式,一种用永久和临时标号方式,一种是用OPEN, CLOSE表的方式, 这里均采用永久和临时标号的方式。注意该算法要求图中不存在负权边。 因此,在包含负权边的图中要找出最短路径,可以使用另一种算法 – 贝克曼-福德算法
<?php
class DijkstraQuery
{
/**
* @var array
*/
protected $graph;
/**
* @var array
*/
protected $processed;
/**
* @var int
*/
protected $infinity;
/**
* @var string
*/
protected $start;
/**
* @var string
*/
protected $end;
/**
* DijkstraQuery constructor.
*
* @param array $graph
* @param $start
* @param $end
*/
public function __construct(array $graph, $start, $end)
{
$this->graph = $graph; // 图
$this->start = $start;
$this->end = $end;
$this->processed = array ();
$this->infinity = mt_getrandmax(); // 无穷大数
}
/**
* 最短路径
*
* @return string
*/
public function calculate()
{
// 开始人结构
$costs = $this->graph[$this->start];
// 终点也放进来,不过距离为最大
$costs[$this->end] = $this->infinity;
// 在开始人结构中找到最小的邻居点
$node = $this->findLowestCostNode($costs);
while ($node !== null) {
// 距离
$cost = $costs[$node];
// 邻居结构
$neighbors = $this->graph[$node] ?? array ();
foreach ($neighbors as $neighbor => $distance) {
// 新距离
$newCost = $cost + $distance;
// 如果这个邻居还没有包含进来,那么包含进来,变相补充开始人的邻居及距离
if (!isset($costs[$neighbor])) {
$costs[$neighbor] = $newCost;
}
// 开始人到邻居的距离比新距离大,则开始人到邻居的距离取新距离,变相修改开始人到邻居的最短距离
if ($costs[$neighbor] > $newCost) {
$costs[$neighbor] = $newCost;
}
}
// 把算过的邻居计入过程
array_push($this->processed, $node);
// 继续选择里面最近的邻居,直到所有邻居都计算完
$node = $this->findLowestCostNode($costs);
}
return 'The shortest distance for:' . $costs[$this->end];
}
/**
* findLowestCostNode
* 寻找最小邻居节点
*
* @param $costs
* @return null
*/
protected function findLowestCostNode($costs)
{
// 当前最小距离
$lowestCost = $this->infinity;
// 最小邻居
$lowestCostNode = null;
foreach ($costs as $node => $cost) {
if ($cost < $lowestCost && !in_array($node, $this->processed)) {
$lowestCost = $cost;
$lowestCostNode = $node;
}
}
return $lowestCostNode;
}
}
// +--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// | 验证 me --> claire
// +--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// ∞
$graph = array (
'me' => array (
'alice' => 6,
'bob' => 2,
),
'alice' => array (
'claire' => 1,
),
'bob' => array (
'alice' => 3,
'claire' => 5,
),
'claire' => array (// 没有任何邻居
),
);
echo (new DijkstraQuery($graph, 'me', 'claire'))->calculate();
输出:6,从 me -> bob -> alice -> claire 。
二叉搜索树
<?php
/**
* 二叉搜索树
*
* 二叉搜索树或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树:
* 1.每个结点都有一个作为搜索依据的关键码(value),所有结点的关键码互不相同。
* 2.左子树(如果非空)上所有结点的关键码都小于根结点的关键码。
* 3.右子树(如果非空)上所有结点的关键码都大于根结点的关键码。
* 4.左子树和右子树也是二叉搜索树。
*
* class Node {
* public $value;
* public $left = null;
* public $right = null;
* }
*/
class BinarySearchTree
{
/**
* @var $root 根节点
*/
public $root = null;
/**
* 创建新节点
* @param $data 关键码
*/
protected function createNode($data)
{
$node = new stdClass();
$node->value = $data;
$node->left = null;
$node->right = null;
return $node;
}
/**
* 插入节点
* @param $node 根节点
* @param $value 关键值
*/
public function insert(&$node, $value)
{
// $value为 null、 '' 的情况
if (empty($value) && $value !== 0) {
return ;
}
if ($node == null) {
// 创建结点
$node = $this->createNode($value);
} else if ($value < $node->value) {
$this->insert($node->left, $value);
} else {
$this->insert($node->right, $value);
}
}
/**
* 先序遍历
* @param $node 根节点
*/
public function preOrder(&$node)
{
if ($node != null) {
echo $node->value . PHP_EOL ;
$this->preOrder($node->left);
$this->preOrder($node->right);
}
}
/**
* 中序遍历
* @param $node 根节点
*/
public function middleOrder(&$node)
{
if ($node != null) {
$this->middleOrder($node->left);
echo $node->value . PHP_EOL ;
$this->middleOrder($node->right);
}
}
/**
* 后序遍历
* @param $node 根节点
*/
public function afterOrder(&$node)
{
if ($node != null) {
$this->afterOrder($node->left);
$this->afterOrder($node->right);
echo $node->value . PHP_EOL;
}
}
/**
* 获取最大值
* @param $node 根节点
*/
public function findMax(&$node)
{
while ($node->right != null) {
$node = $node->right;
}
return $node->value;
}
}
$tree = new BinarySearchTree();
$tree->insert($tree->root, 3);
$tree->insert($tree->root, 9);
$tree->insert($tree->root, 2);
$tree->insert($tree->root, 20);
echo "先序遍历".PHP_EOL;
$tree->preOrder($tree->root);
echo "中序遍历" . PHP_EOL;
$tree->middleOrder($tree->root);
echo "后序遍历" . PHP_EOL;
$tree->afterOrder($tree->root);
$max = $tree->findMax($tree->root);
var_dump($max);
输出:
先序遍历
3
2
9
20
中序遍历
2
3
9
20
后序遍历
2
20
9
3
int(20)
参考资料
PHP 手册 函数参考 变量与类型相关扩展 数组 数组 函数 https://www.php.net/manual/zh/ref.array.php
用 PHP 的方式实现的各类算法合集 https://github.com/m9rco/algorithm-php
PHP实现八大算法 https://www.cnblogs.com/zixuanfy/p/7617451.html
PHP的基本算法合集 https://www.php.cn/php-weizijiaocheng-394062.html
PHP算法 https://www.jianshu.com/p/cb2ad99029c8
php数据结构和算法 https://www.csdn.net/gather_21/MtTacg3sMzkxNy1ibG9n.html
七大常用PHP算法 http://www.sohu.com/a/118661179_468191
堆排序算法与PHP实现 https://www.cnblogs.com/iampeter/p/3223487.html
PHP实现排序算法—-堆排序(Heap Sort) https://blog.csdn.net/baidu_30000217/article/details/53087079
PHP实现堆排序 https://www.cnblogs.com/zhenbianshu/p/5273995.html
哪本《数据结构与算法》最好? https://www.zhihu.com/question/21628833/answer/54623559
数据结构与算法必备的 50 个代码实现 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/67490380
常见数据结构与算法整理总结(上) https://www.cnblogs.com/xkzhangsanx/p/10888179.html
PHP实现各种经典算法 http://www.cnblogs.com/hellohell/p/5718175.html
php面试题之二——数据结构和算法(高级部分) https://blog.csdn.net/s1070/article/details/51174725
阮一峰 字符串匹配的KMP算法 http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2013/05/Knuth%E2%80%93Morris%E2%80%93Pratt_algorithm.html
从头到尾彻底理解 KMP https://wiki.jikexueyuan.com/project/kmp-algorithm/
KMP算法—终于全部弄懂了 https://blog.csdn.net/dark_cy/article/details/88698736
PHP 手册 函数参考 其它基本扩展 SPL 数据结构 The SplStack class https://www.php.net/manual/zh/class.splstack.php