正文
Elasticsearch中有个元数据的概念:元数据(Metadata),又称中介数据、中继数据,为描述数据的数据(data about data), 主要是描述数据属性(property)的信息,用来支持如指示存储位置、历史数据、资源查找、文件记录等功能;元数据算是一种电子式目录, 为了达到编制目录的目的,必须在描述并收藏数据的内容或特色,进而达成协助数据检索的目的。
元数据是关于数据的组织、数据域及其关系的信息,简言之,元数据就是关于数据的数据。
Elasticsearch中的元数据有:
_index
- 代表一个document存储在哪个index中。
- 类似的数据(document)放在同一个index,不同类型的数据放在不同的index。
- 索引名必须是小写,不能用下划线(_)开头,不能包含逗号。
_type
- 代表document属于index下 的哪个类别(type)。
- 一个index通常包含多个type。
- type名称可以大写或小写,不能用下划线(_)开头,不能包含逗号。
_id
- 代表document的唯一标识,与index和type一起确定一个唯一的document。
- 可以手动指定,也可es自动生成。 手动指定:PUT /index/type/id; 自动生成: PUT /index/type/ 生成base64编码的20长度的字符串ID,分布式集群下不可能重复。
_score
- 相关度分数:匹配程度,分数越高越相关。
_source
- 代表一个document,是一个json对象({json}),包含一个实例对象。
引导
在PHP代码中查找Elasticsearch数据,我们可以用已经写好的vendor类库——elasticsearch/elasticsearch。 首先需要知道安装的Elasticsearch版本,然后选择对应elasticsearch/elasticsearch。
假设Elasticsearch Version >= 5.0, < 6.0 。我们选择Elasticsearch-PHP Branch 5.0
composer.json中:
"require": {
"elasticsearch/elasticsearch": "~5.0"
}
安装项目拓展:
php composer.phar install
载入引导:
<?php
require 'vendor/autoload.php';
use Elasticsearch\ClientBuilder;
$client = ClientBuilder::create()->build();
在elasticsearch-php中,几乎所有东西都是由关联数组配置的。 REST端,文档和可选参数,一切都是一个关联数组。
创建index索引
$params = [
'index' => 'my_index',
'body' => [
'settings' => [
'number_of_shards' => 2,
'number_of_replicas' => 0
]
]
];
$response = $client->indices()->create($params);
print_r($response);
输出:
Array
(
[acknowledged] => 1
)
通过上面这些操作可以看出,elasticsearch-php这个拓展中,可以实现对文档及索引的增删改查,我们实际情况下,新增文档都是通过kafka 、 logstash中转实现的, 项目中不直接写入文档。一般在项目中都是搜索文档。
mapping
删除index索引
$deleteParams = [
'index' => 'my_index'
];
$response = $client->indices()->delete($deleteParams);
print_r($response);
输出:
Array
(
[acknowledged] => 1
)
写入文档
导入单条数据
要为文档建立索引,我们需要指定三项信息:index, id 和 body文档主体:
$params = [
'index' => 'my_index',
'id' => 'my_id',
'body' => ['testField' => 'abc']
];
$response = $client->index($params);
print_r($response);
输出:
Array
(
[_index] => my_index
[_type] => _doc
[_id] => my_id
[_version] => 1
[result] => created
[_shards] => Array
(
[total] => 1
[successful] => 1
[failed] => 0
)
[_seq_no] => 0
[_primary_term] => 1
)
批量导入数据
bulk
获取文档
$params = [
'index' => 'my_index',
'id' => 'my_id'
];
$response = $client->get($params);
print_r($response);
输出:
Array
(
[_index] => my_index
[_type] => _doc
[_id] => my_id
[_version] => 1
[_seq_no] => 0
[_primary_term] => 1
[found] => 1
[_source] => Array
(
[testField] => abc
)
)
如果要直接检索_source字段,则有getSource方法:
$params = [
'index' => 'my_index',
'id' => 'my_id'
];
$source = $client->getSource($params);
print_r($source);
输出:
Array
(
[testField] => abc
)
搜索文档
搜索是Elasticsearch的标志,因此让我们执行搜索。
$params = [
'index' => 'my_index',
'body' => [
'query' => [
'match' => [
'testField' => 'abc'
]
]
]
];
$response = $client->search($params);
print_r($response);
和上面的返回不同:
Array
(
[took] => 33,
[timed_out] => false,
[_shards] => Array
(
[total] => 1
[successful] => 1
[skipped] => 0
[failed] => 0
),
[hits] => Array
(
[total] => Array
(
[value] => 1
[relation] => eq
),
[max_score] => 0.2876821,
[hits] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[_index] => my_index
[_type] => _doc
[_id] => my_id
[_score] => 0.2876821
[_source] => Array
(
[testField] => abc
)
)
)
)
)
took是耗时,单位是ms。 hits.total 表示有多少个 Document。
删除文档
$params = [
'index' => 'my_index',
'id' => 'my_id'
];
$response = $client->delete($params);
print_r($response);
输出:
Array
(
[_index] => my_index
[_type] => _doc
[_id] => my_id
[_version] => 2
[result] => deleted
[_shards] => Array
(
[total] => 1
[successful] => 1
[failed] => 0
)
[_seq_no] => 1
[_primary_term] => 1
)
具体使用
读取代码中:
use Elasticsearch\ClientBuilder;
......
$type = 'adminWeb'
$start = strtotime(date('Y-m-d'));
$con = [
'index' => 'weberror-*',
'type' => $type,
'from' => 0,
'size' => 100,
'body' => [
'query' => [
'bool'=>[
'filter'=> [
'range' => [
'time_created'=>[
'gte' => $start,
'lte' => $start + 3600*24
]
]
],
]
],
'sort' => [
"time_created" =>[
"order"=>"desc"
]
]
]
];
$client = ClientBuilder::create()->setHosts(['192.168.0.11'])->build();
$response = $client->search($con);
return $this->renderPartial('api-error-data',[
'total'=> $response['hits']['total'],
'data'=> $response['hits']['hits']
]);
这里query还可以这样组织:
$clientId = 101;
$type = 'client';
'body' => [
'query' => [
'bool' => [
'must' => [
['match' => [ 'client_id' => intval($clientId) ]],
['match' => [ 'role' => $type ]],
]
]
]
]
其他查询语句,自己可以对照文档摸索。
渲染试图中:
<p class="bg-blue fit-width">总共过滤出来数据:<?=$total?>条,系统默认显示100条</p>
<table class="table table-hover table-portal">
<thead>
<tr>
<td style="width: 120px;">日期</td>
<td style="width: 120px;">用户</td>
<td style="width: 60px;">错误码</td>
<td>错误地址</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<?php foreach ($data as $item):?>
<tr>
<td><?= date('Y-m-d H:i',$item['_source']['time_created']) ?></td>
<td><?= $item['_source']['uid'] ?> - <?= empty($item['_source']['name']) ? "none" : $item['_source']['name'] ?></td>
<td><?= $item['_source']['error_code'] ?></td>
<td>
<p class="font-blue"><?= $item['_source']['error_url'] ?></p>
<p class="font-blue break-all">参数:<?= $item['_source']['error_param'] ?></p>
<p class="font-red">错误:<?= $item['_source']['error_msg'] ?></p>
<p class="font-yellow">路径:<?= $item['_source']['error_file'] ?></p>
</td>
</tr>
<?php endforeach;?>
</tbody>
</table>
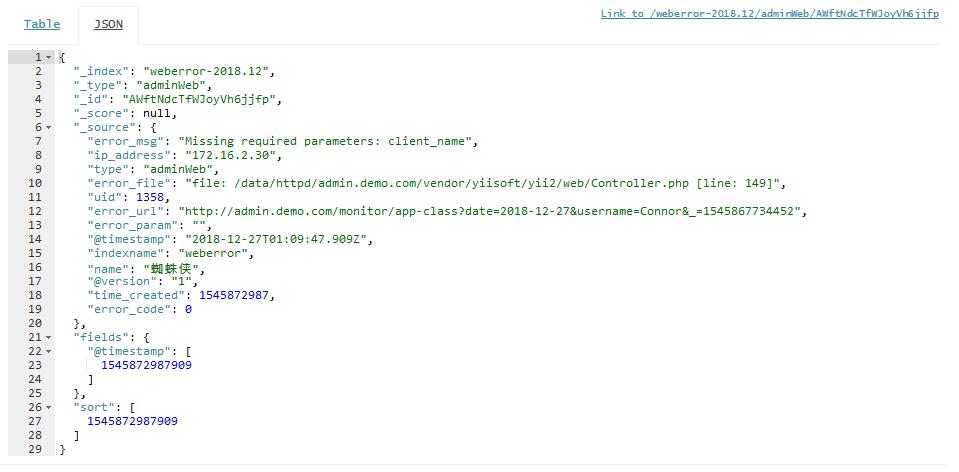
看一下Elasticsearch储存的数据结构实例:
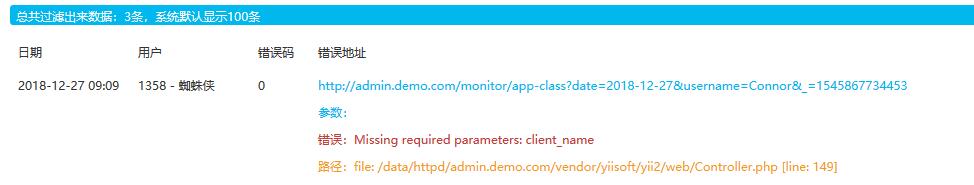
看一下视图渲染的效果:
合并语句查询
我们一般多用合并语句查询,这些语句可以是如下形式:
1、叶子语句(Leaf clauses) (就像 match 语句) 被用于将查询字符串和一个字段(或者多个字段)对比。
{
"query": {
"match": {
"tweet": "elasticsearch"
}
}
}
2、复合(Compound) 语句 主要用于 合并其它查询语句。 比如,一个 bool 语句 允许在你需要的时候组合其它语句, 无论是 must 匹配、 must_not 匹配还是 should 匹配,同时它可以包含不评分的过滤器(filters):
{
"bool": {
"must": { "match": { "tweet": "elasticsearch" }},
"must_not": { "match": { "name": "mary" }},
"should": { "match": { "tweet": "full text" }},
"filter": { "range": { "age" : { "gt" : 30 }} }
}
}
3、一条复合语句可以合并 任何 其它查询语句,包括复合语句,了解这一点是很重要的。这就意味着, 复合语句之间可以互相嵌套,可以表达非常复杂的逻辑。 例如,以下查询是为了找出信件正文包含 business opportunity 的星标邮件, 或者在收件箱正文包含 business opportunity 的非垃圾邮件:
{
"bool": {
"must": { "match": { "email": "business opportunity" }},
"should": [
{ "match": { "starred": true }},
{ "bool": {
"must": { "match": { "folder": "inbox" }},
"must_not": { "match": { "spam": true }}
}}
],
"minimum_should_match": 1
}
}
你要理解到,一条复合语句可以将多条语句 — 叶子语句和其它复合语句 — 合并成一个单一的查询语句。
查询关键字
match_all 查询:简单的 匹配所有文档
match 查询:匹配查询
multi_match 查询:多个字段上执行相同的 match 查询
{
"multi_match": {
"query": "full text search",
"fields": [ "title", "body" ]
}
}
range 查询:落在指定区间的数据
{
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 20,
"lt": 30
}
}
}
被允许的操作符如下: gt 大于 gte 大于等于 lt 小于 lte 小于等于
term 查询:精确值 匹配
terms 查询:和 term 查询一样,但它允许你指定多值进行匹配
exists 查询、missing 查询:用于查找那些指定字段中有值 (exists) 或无值 (missing) 的文档
{
"exists": {
"field": "title"
}
}
组合多查询
现实的查询需求从来都没有那么简单;它们需要在多个字段上查询多种多样的文本, 并且根据一系列的标准来过滤。为了构建类似的高级查询,你需要一种能够将多查询组合成单一查询的查询方法。
你可以用 bool 查询来实现你的需求。这种查询将多查询组合在一起,成为用户自己想要的布尔查询。它接收以下参数:
must 文档 必须 匹配这些条件才能被包含进来。 must_not 文档 必须不 匹配这些条件才能被包含进来。 should 如果满足这些语句中的任意语句,将增加 _score ,否则,无任何影响。它们主要用于修正每个文档的相关性得分。 filter 必须 匹配,但它以不评分、过滤模式来进行。这些语句对评分没有贡献,只是根据过滤标准来排除或包含文档。
如:
{
"bool": {
"must": { "match": { "title": "how to make millions" }},
"must_not": { "match": { "tag": "spam" }},
"should": [
{ "match": { "tag": "starred" }}
],
"filter": {
"range": { "date": { "gte": "2014-01-01" }}
}
}
}
通过将 range 查询移到 filter 语句中,我们将它转成不评分的查询,将不再影响文档的相关性排名。 由于它现在是一个不评分的查询,可以使用各种对 filter 查询有效的优化手段来提升性能。
如:
{
"bool": {
"must": { "match": { "title": "how to make millions" }},
"must_not": { "match": { "tag": "spam" }},
"should": [
{ "match": { "tag": "starred" }}
],
"filter": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "range": { "date": { "gte": "2014-01-01" }}},
{ "range": { "price": { "lte": 29.99 }}}
],
"must_not": [
{ "term": { "category": "ebooks" }}
]
}
}
}
}
constant_score 查询:
尽管没有 bool 查询使用这么频繁,constant_score 查询也是你工具箱里有用的查询工具。 它将一个不变的常量评分应用于所有匹配的文档。 它被经常用于你只需要执行一个 filter 而没有其它查询(例如,评分查询)的情况下。
可以使用它来取代只有 filter 语句的 bool 查询。在性能上是完全相同的, 但对于提高查询简洁性和清晰度有很大帮助。
{
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"term": { "category": "ebooks" }
}
}
}
term 查询被放置在 constant_score 中,转成不评分的 filter。 这种方式可以用来取代只有 filter 语句的 bool 查询。
wildcard模糊查询:
{
"must":{
"wildcard": {"content": "*abc123*"}
}
}
看一个例子:
{
"index":"logs-*",
"from":0,
"size":100,
"body":{
"query":{
"constant_score":{
"filter":{
"bool":{
"must":{
"term":{
"logId":"f5d891bed00e001"
}
},
"should":[
{"term":{"type":1}},
{"range":{"spendTime":{"gt":-1}}}
]
}
}
}
}
}
}
聚合分析
aggs
通过kibana进行聚合分析查询时,POST提交格式,如:
{"index":"nginx-ingress-*","ignore_unavailable":true,"timeout":30000,"preference":1596525370968}
{
"size":0,"_source":{"excludes":[]},
"aggs":{
"2":{
"terms":{"field":"url.keyword","size":100,"order":{"_count":"desc"}},
"aggs":{
"7":{
"terms":{"field":"http_host.keyword","size":100,"order":{"_count":"desc"}},
"aggs":{
"3":{"avg":{"field":"responsetime"}},
"4":{"max":{"field":"responsetime"}},
"5":{"min":{"field":"responsetime"}},
"6":{
"percentiles":{"field":"responsetime","percents":[90,95,99],"keyed":false}
}
}
}
}
}
},
"stored_fields":["*"],"script_fields":{},"docvalue_fields":["@timestamp","time"],
"query":{
"bool":{
"must":[
{"query_string":{"query":"\"wx.test.com\" OR \"wx.test.work\"","analyze_wildcard":true,"default_field":"*"}},
{"range":{"@timestamp":{"gte":1596384000000,"lte":1596470399999,"format":"epoch_millis"}}}
],
"filter":[],
"should":[],
"must_not":[]
}
}
}
然后kibana进行分析,再调用Es进行查询,不过调用Es的格式具体是怎样的,需要我们分析。
Es支持的聚合分析的语法如:
[
"index" => "indexlog-*",
'from' => 0,
'size' => 3,
"body" => [
"aggs" => [
"options" => [
"terms" => [
"field" => "action_url.keyword",
"size" => 100,
"order" => [
"_count" => "desc"
]
]
]
]
]
]
后记
用户认证
在一次项目对接中用到了ES,连接时报了错,用curl请求报错是一样的:
[root@localhost]$ curl -XGET '172.16.0.1:9200/longlat-*'
{"error":{"root_cause":[{"type":"security_exception","reason":"missing authentication token for REST request [/longlat-*]",
"header":{"WWW-Authenticate":"Basic realm=\"security\" charset=\"UTF-8\""}}],"type":"security_exception",
"reason":"missing authentication token for REST request [/longlat-*]",
"header":{"WWW-Authenticate":"Basic realm=\"security\" charset=\"UTF-8\""}},"status":401}
查询后,说是Elasticsearch安装x-pack插件后,无法正常按照之前的参数来进行CRUL操作,因为安装的x-pack的插件中新增了Shield的安全机制。
解决方法:在使用crul命令的时候加入两个参数:-u username:password ,格式如下:
curl -u lastic:changeme -XGET '172.16.0.1:9200/longlat-*'
请求时发现的确可以了。
但是vendor类库elasticsearch/elasticsearch 怎么把认证信息加上呢?
查询后,发现在setHosts()时就把用户认证信息放入了:
$hosts = [
'http://user:pass@localhost:9200', // HTTP Basic Authentication
'http://user2:pass2@other-host.com:9200' // Different credentials on different host
];
$client = ClientBuilder::create()->setHosts($hosts)->build();
如:
$hosts = [
"lastic:changeme@172.16.0.1:9200"
];
参考资料
elastic/elasticsearch-php https://github.com/elastic/elasticsearch-php
Packagist elasticsearch/elasticsearch https://packagist.org/packages/elasticsearch/elasticsearch
Elasticsearch-PHP https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/client/php-api/current/index.html
Elasticsearch 中文官方 https://www.elastic.co/cn/
Elasticsearch: 权威指南 https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/index.html
该怎么学elasticsearch? https://www.zhihu.com/question/323811022/answer/981341195
filter和query的不同 https://blog.csdn.net/laoyang360/article/details/80468757
filters特性 https://www.cnblogs.com/bmaker/p/5480006.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/query-filter-context.html
使用 ElasticSearch Aggregations 进行统计分析 https://blog.csdn.net/zxjiayou1314/article/details/53837719?utm_source=blogxgwz6
Elasticsearch实用的聚合操作Aggs https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/37500880
ElasticSearch聚合aggs入门 https://www.cnblogs.com/pilihaotian/p/5845754.html
Elasticsearch: 权威指南 » 聚合 https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/aggregations.html
Elasticsearch安装后x-pack插件后使用CRUL https://blog.csdn.net/u012332735/article/details/56475522
Elasticsearch-PHP » 配置 https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/php/current/_configuration.html
Elasticsearch-PHP » 安全 https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/php/current/_security.html