正文
jwt,全程 JSON WEB Token,是一种基于JSON的、用于在网络上声明某种主张的令牌(token)。 JWT通常由三部分组成: 头信息(header), 消息体(payload)和签名(signature)。
php中,我们使用 lcobucci/jwt 这个库。 Packagist地址 https://packagist.org/packages/lcobucci/jwt , Github地址 https://github.com/lcobucci/jwt , 文档地址 https://lcobucci-jwt.readthedocs.io/en/latest/。
下面举个Yii2中使用的例子。浏览器访问指定地址获取token,以后访问时在header中带上token。
composer.json中require引入:"lcobucci/jwt": "^3.2"
用user/get-jwt-token获取token,在这个方法中调用TokenService生成token:
<?php
namespace common\service;
use Lcobucci\JWT\Builder;
use Lcobucci\JWT\Signer\Hmac\Sha256;
use Lcobucci\JWT\Parser;
use Lcobucci\JWT\ValidationData;
use \Exception;
use Yii;
class LTokenService
{
/**
* 生成令牌
* @param $from_type 来源
* @param $department_id 部门
* @param $position 职位
* @param $worker_id 员工id
* @return string
*/
public static function createToken( $from_type, $department_id, $position, $worker_id )
{
$jwt = Yii::$app->params['jwt'];
$jwt['aud'] = Yii::$app->request->getUserIP();
$jwt['jti'] = uniqid() . mt_rand(100000, 999999);
$jwt['iat'] = time();
$jwt['nbf'] = time();
$jwt['exp'] = $jwt['iat'] + $jwt['sur'];
$jwt['src'] = $from_type;
$jwt['worker_id'] = $worker_id;
$jwt['department_id'] = $department_id;
$jwt['position'] = $position;
$signer = new Sha256();
$token = (new Builder())->setIssuer($jwt['iss']) // 签发者
->setAudience( $jwt['aud'] ) // 接受者
->setId( $jwt['jti'], true ) // 唯一标识
->setIssuedAt( $jwt['iat'] ) // 签发时间
->setNotBefore( $jwt['nbf']) // 过去时间不可用
->setExpiration( $jwt['exp'] ) // 截至时间
->set('worker_id', $jwt['worker_id']) // 员工id
->set('src', $jwt['src']) // 来源
->set('department_id', $jwt['department_id']) //部门
->set('position', $jwt['position']) //职位
->set('jti', $jwt['jti']) // 唯一标识
->sign($signer, $jwt['sign']) // 加盐字符串
->getToken();
// $token->getHeaders(); // Retrieves the token headers
// $token->getClaims(); // Retrieves the token claims
return (string)$token;
}
/**
* 检测Token是否过期与篡改
* @param null $token
* @return array
* @throws Exception
*/
public static function validateToken( $token = null )
{
$token = (new Parser())->parse($token); // Parses from a string
$signer = new Sha256();
if (!$token->verify($signer, Yii::$app->params['jwt']['sign'])) {
throw new Exception('签名不正确');
}
$jwt = Yii::$app->params['jwt'];
$aud = Yii::$app->request->getUserIP();
$validationData = new ValidationData();
$validationData->setIssuer( $jwt['iss'] );
$validationData->setAudience( $aud ); // 令牌异地检查
$validationData->setId( $token->getClaim('jti') ); // 唯一标识
if ( $token->validate($validationData) ) {
return [
'src' => $token->getClaim('src'),
'department_id' => $token->getClaim('department_id'),
'position' => $token->getClaim('position'),
'worker_id' => $token->getClaim('worker_id'),
];
} else {
throw new Exception('令牌异地或过时');
}
}
}
配置参数:
'params' => [
'jwt' => [
'iss' => 'https://abc.test.com', // 签发者
'exp' => 0, // 过期时间戳
'sub' => 0, //面向的用户
'sur' => 86400, // 过期事件一天
'src' => 'lmn', // 来源
'aud' => 'http://xyz.test.com', // 接收方
'iat' => '', //签发时间
"sign" => "test123456", // 签名
],
],
之后其他所有访问都检验token。所有控制器都继承自LController(包括user控制器),节选:
use Yii;
use yii\web\Controller;
use common\service\LTokenService;
class LController extends Controller
{
protected $global_src = ''; // 来源项目
protected $global_dpt_id = 0; // 部门id
protected $global_position = 0; // 职位
protected $global_wid = 0; // 员工id, worker.id
public function beforeAction( $action )
{
$controllerName = $action->controller->id;
$actionName = $action->id;
if ( $action->actionMethod != 'actionGetJwtToken' && $action->controller->id != 'user' ) {
/***** 检查令牌 ******/
$jwtToken = Yii::$app->request->headers->get('jwt-token');
if ( isset($jwtToken) ) {
try {
$res = LTokenService::validateToken( $jwtToken );
$this->global_src = $res['src'];
$this->global_dpt_id = $res['department_id'];
$this->global_position = $res['position'];
$this->global_wid = $res['worker_id'];
$this->global_stu_id = $res['student_id'];
} catch ( \Exception $e ) {
$result = [
'code' => 401,
'msg' => '授权失败,请刷新页面后重新操作',
'data' => [],
];
Yii::$app->response->format = Response::FORMAT_JSON;
Yii::$app->response->data = $result;
return false;
}
} else {
return $this->ajaxReturn( LError::ERROR, '用户未授权' );
}
}
return parent::beforeAction($action);
}
}
解说2
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/RqGJMkCCeGtR1zjrALuVNw
一、什么是JWT
1、简介
JWT(JSON Web Token)是为了在网络应用环境间传递声明而执行的一种基于JSON的开放标准。
简单的说,JWT就是一种Token的编码算法,服务器端负责根据一个密码和算法生成Token,然后发给客户端, 客户端只负责后面每次请求都在HTTP header里面带上这个Token,服务器负责验证这个Token是不是合法的, 有没有过期等,并可以解析出subject和claim里面的数据。
2、JWT的组成
第一部分为头部(header),第二部分我们称其为载荷(payload),第三部分是签证(signature)。【中间用 . 分隔】
一个标准的JWT生成的token格式如下:
eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsImp0aSI6IjRmMWcyM2ExMmFhMTEifQ.eyJpc3MiOiJodHRwOlwvXC9leGFtcGxlLmNvbSIsImF1ZCI6Imh0dHA6XC9cL2V4YW1wbGUub3JnIiwianRpIjoiNGYxZzIzYTEyYWExMSIsImlhdCI6MTY0MDE3MTA1MywibmJmIjoxNjQwMTcxMDU0LCJleHAiOjE2NDAxNzQ2NTMsInVpZCI6MjAsInVzZXJuYW1lIjoiTWFrZSJ9.bysUwNIyhqqEyL0JecSHdplSTfE6G6zuCsrAn6eyrQM
使用 https://jwt.io/ 这个网站对JWT Token进行解析的结果如下
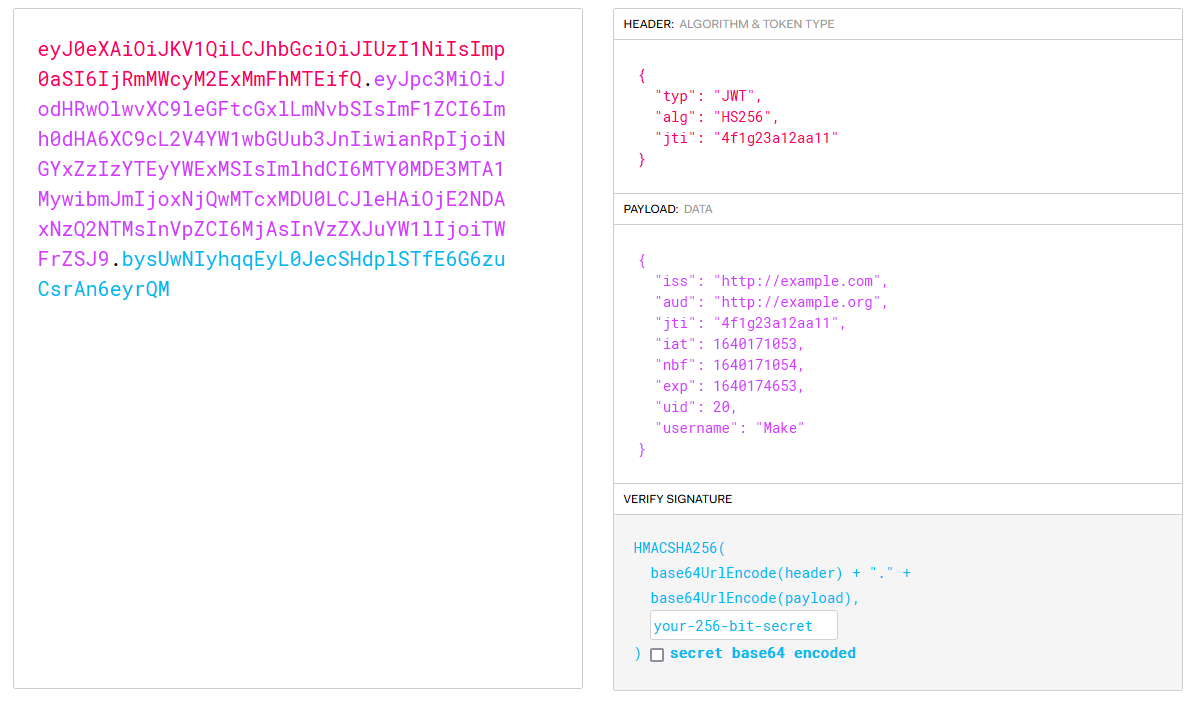
3、JWT验证流程和特点
验证流程:
- 在头部信息中声明加密算法和常量, 然后把header使用json转化为字符串
- 在载荷中声明用户信息,同时还有一些其他的内容;再次使用json 把载荷部分进行转化,转化为字符串
- 使用在header中声明的加密算法和每个项目随机生成的secret来进行加密, 把第一步分字符串和第二部分的字符串进行加密, 生成新的字符串。该字符串是独一无二的。
- 解密的时候,只要客户端带着JWT来发起请求,服务端就直接使用secret进行解密。
特点:
- 三部分组成,每一部分都进行字符串的转化
- 解密的时候没有使用数据库,仅仅使用的是secret进行解密
- JWT的secret千万不能泄密!
- 不依赖数据库,而是直接根据token取出保存的用户信息,以及对token可用性校验,校验方式更加简单便捷化,单点登录更为简单。
二、相关问题
1、JWT Token需要持久化在redis、Memcached中吗?
- 不应该这样做,无状态的jwt变成了有状态了,背离了JWT通过算法验证的初心。
2、在退出登录时怎样实现JWT Token失效呢?
- 退出登录, 只要客户端端把Token丢弃就可以了,服务器端不需要废弃Token。
3、怎样保持客户端长时间保持登录状态?
- 服务器端提供刷新Token的接口, 客户端负责按一定的逻辑刷新服务器Token。
三、PHP实现
1、引入依赖
composer require lcobucci/jwt 3.*
2、功能实现
- 签发token, 设置签发人、接收人、唯一标识、签发时间、立即生效、过期时间、用户id、用户username、签名。 其中,用户id、用户username是特意存储在token中的信息,也可以增加一些其他信息, 这样在解析的时候就可以直接获取到这些信息,不能是敏感数据
- 验证令牌验证这个Token是不是合法的,有没有过期等,并可以解析出subject和claim里面的数据, 传递jwt token的方式为Authorization中的Bearer Token,如下
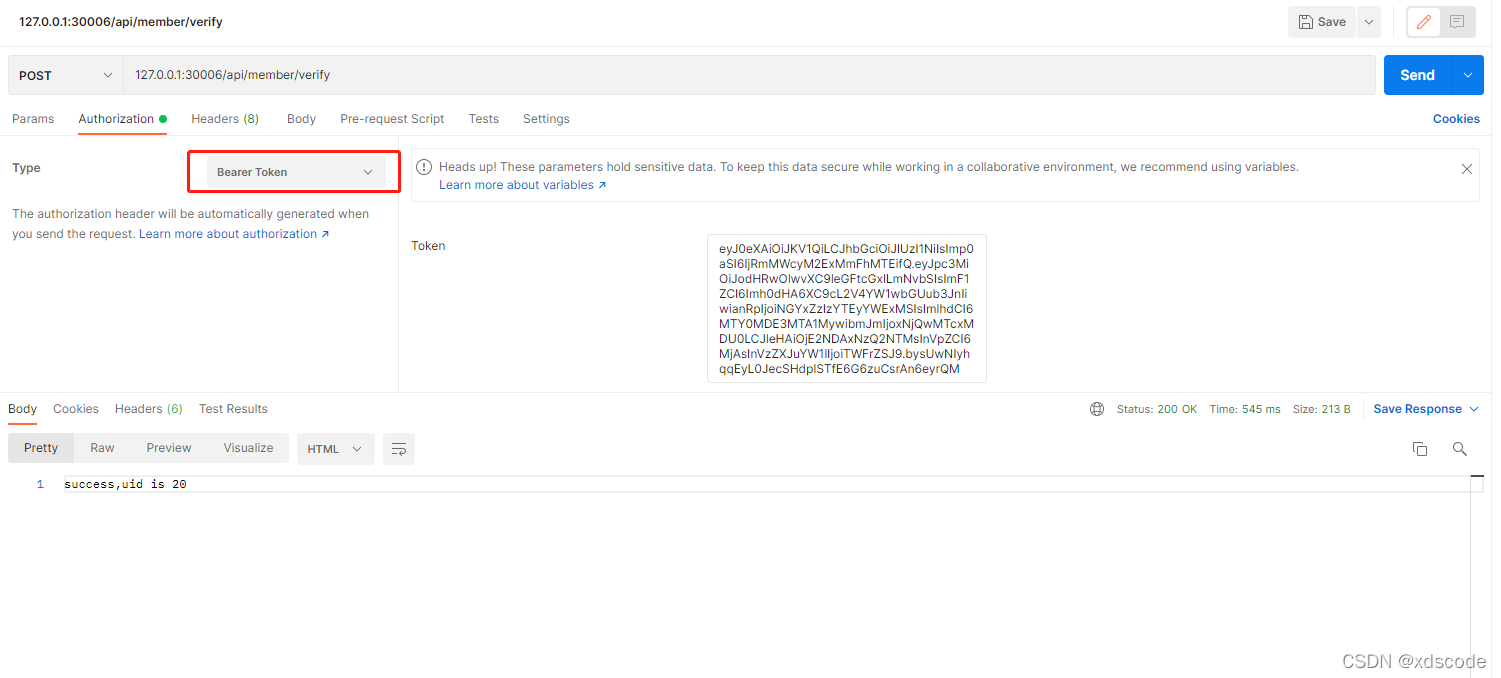
3、封装工具类如下
<?php
/**
* Created by PhpStorm
* @author sxd
*/
namespace App\Utils;
use Lcobucci\JWT\Configuration;
use Lcobucci\JWT\Parser;
use Lcobucci\JWT\Signer\Hmac\Sha256;
use Lcobucci\JWT\Signer\Key\InMemory;
use Lcobucci\JWT\Token\Plain;
use Lcobucci\JWT\Validation\Constraint\IdentifiedBy;
use Lcobucci\JWT\Validation\Constraint\IssuedBy;
use Lcobucci\JWT\Validation\Constraint\PermittedFor;
use Lcobucci\JWT\ValidationData;
class JwtUtil
{
// jwt github: https://github.com/lcobucci/jwt https://jwt.io/
protected $issuer = "http://example.com";
protected $audience = "http://example.org";
protected $id = "4f1g23a12aa11";
// key 是绝对不允许泄露的
protected static $key = "8swQsm1Xb0TA0Jw5ASPwClKVZPoTyS7GvhtaW0MxzKEihs1BNpcS2q3FYMJ11111";
/**
* 签发令牌
*/
public function getToken()
{
$time = time();
$config = self::getConfig();
assert($config instanceof Configuration);
// 签发token, 设置签发人、接收人、唯一标识、签发时间、立即生效、过期时间、用户id、用户username、签名
$token = $config->builder()
->issuedBy($this->issuer) // Configures the issuer (iss claim)
->permittedFor($this->audience) // Configures the audience (aud claim)
->identifiedBy($this->id, true) // Configures the id (jti claim), replicating as a header item
->issuedAt($time) // Configures the time that the token was issue (iat claim)
->canOnlyBeUsedAfter($time + 1) // Configures the time that the token can be used (nbf claim) 签发x秒钟后生效
->expiresAt($time + 3600) // Configures the expiration time of the token (exp claim)
->withClaim('uid', 20) // Configures a new claim, called "uid"
->withClaim('username', "Make") // Configures a new claim, called "uid"
->getToken($config->signer(), $config->signingKey()); // Retrieves the generated token
return $token->toString();
}
/**
* 验证 jwt token 并返回其中的用户id
* verify token
*/
public function verifyToken_bak($token)
{
try {
$config = self::getConfig();
assert($config instanceof Configuration);
$token = $config->parser()->parse($token);
assert($token instanceof Plain);
//Lcobucci\JWT\Validation\Constraint\IdentifiedBy: 验证jwt id是否匹配
//Lcobucci\JWT\Validation\Constraint\IssuedBy: 验证签发人参数是否匹配
//Lcobucci\JWT\Validation\Constraint\PermittedFor: 验证受众人参数是否匹配
//Lcobucci\JWT\Validation\Constraint\RelatedTo: 验证自定义cliam参数是否匹配
//Lcobucci\JWT\Validation\Constraint\SignedWith: 验证令牌是否已使用预期的签名者和密钥签名
//Lcobucci\JWT\Validation\Constraint\StrictValidAt: ::验证存在及其有效性的权利要求中的iat,nbf和exp(支持余地配置
//Lcobucci\JWT\Validation\Constraint\LooseValidAt: 验证的权利要求iat,nbf和exp,当存在时(支持余地配置)
//验证jwt id是否匹配
$validate_jwt_id = new IdentifiedBy($this->id);
//验证签发人url是否正确
$validate_issued = new IssuedBy($this->issuer);
//验证客户端url是否匹配
$validate_aud = new PermittedFor($this->audience);
$config->setValidationConstraints($validate_jwt_id, $validate_issued, $validate_aud);
$constraints = $config->validationConstraints();
if (!$config->validator()->validate($token, ...$constraints)) {
die("token invalid!");
}
} catch (\Exception $e) {
die("error:" . $e->getMessage());
}
$jwtInfo = $token->claims(); // 这是jwt token中存储的所有信息
return $jwtInfo->get("uid"); // 获取uid
}
/**
* 加密解密使用的配置
* @return Configuration
*/
public static function getConfig()
{
$configuration = Configuration::forSymmetricSigner(
// You may use any HMAC variations (256, 384, and 512)
new Sha256(),
// replace the value below with a key of your own!
InMemory::base64Encoded(self::$key)
// You may also override the JOSE encoder/decoder if needed by providing extra arguments here
);
return $configuration;
}
/**
* 另一种验证方法,但是已经弃用
* verify token
*/
public function verifyToken($token)
{
$token = (new Parser())->parse((string)$token);
//验证token
$data = new ValidationData();
$data->setIssuer($this->issuer);//验证的签发人
$data->setAudience($this->audience);//验证的接收人
$data->setId($this->id);//验证token标识
if (!$token->validate($data)) {
//token验证失败
die("token invalid!");
}
$jwtInfo = $token->claims(); // 这是jwt token中存储的所有信息
return $jwtInfo->get("uid"); // 获取uid
}
}
README 文件
Basic usage
Creating
Just use the builder to create a new JWT/JWS tokens:
use Lcobucci\JWT\Builder;
$time = time();
$token = (new Builder())->issuedBy('http://example.com') // Configures the issuer (iss claim)
->permittedFor('http://example.org') // Configures the audience (aud claim)
->identifiedBy('4f1g23a12aa', true) // Configures the id (jti claim), replicating as a header item
->issuedAt($time) // Configures the time that the token was issue (iat claim)
->canOnlyBeUsedAfter($time + 60) // Configures the time that the token can be used (nbf claim)
->expiresAt($time + 3600) // Configures the expiration time of the token (exp claim)
->withClaim('uid', 1) // Configures a new claim, called "uid"
->getToken(); // Retrieves the generated token
$token->getHeaders(); // Retrieves the token headers
$token->getClaims(); // Retrieves the token claims
echo $token->getHeader('jti'); // will print "4f1g23a12aa"
echo $token->getClaim('iss'); // will print "http://example.com"
echo $token->getClaim('uid'); // will print "1"
echo $token; // The string representation of the object is a JWT string (pretty easy, right?)
Parsing from strings
Use the parser to create a new token from a JWT string (using the previous token as example):
use Lcobucci\JWT\Parser;
$token = (new Parser())->parse((string) $token); // Parses from a string
$token->getHeaders(); // Retrieves the token header
$token->getClaims(); // Retrieves the token claims
echo $token->getHeader('jti'); // will print "4f1g23a12aa"
echo $token->getClaim('iss'); // will print "http://example.com"
echo $token->getClaim('uid'); // will print "1"
Validating
We can easily validate if the token is valid (using the previous token and time as example):
use Lcobucci\JWT\ValidationData;
$data = new ValidationData(); // It will use the current time to validate (iat, nbf and exp)
$data->setIssuer('http://example.com');
$data->setAudience('http://example.org');
$data->setId('4f1g23a12aa');
var_dump($token->validate($data)); // false, because token cannot be used before now() + 60
$data->setCurrentTime($time + 61); // changing the validation time to future
var_dump($token->validate($data)); // true, because current time is between "nbf" and "exp" claims
$data->setCurrentTime($time + 4000); // changing the validation time to future
var_dump($token->validate($data)); // false, because token is expired since current time is greater than exp
// We can also use the $leeway parameter to deal with clock skew (see notes below)
// If token's claimed time is invalid but the difference between that and the validation time is less than $leeway,
// then token is still considered valid
$dataWithLeeway = new ValidationData($time, 20);
$dataWithLeeway->setIssuer('http://example.com');
$dataWithLeeway->setAudience('http://example.org');
$dataWithLeeway->setId('4f1g23a12aa');
var_dump($token->validate($dataWithLeeway)); // false, because token can't be used before now() + 60, not within leeway
$dataWithLeeway->setCurrentTime($time + 51); // changing the validation time to future
var_dump($token->validate($dataWithLeeway)); // true, because current time plus leeway is between "nbf" and "exp" claims
$dataWithLeeway->setCurrentTime($time + 3610); // changing the validation time to future but within leeway
var_dump($token->validate($dataWithLeeway)); // true, because current time - 20 seconds leeway is less than exp
$dataWithLeeway->setCurrentTime($time + 4000); // changing the validation time to future outside of leeway
var_dump($token->validate($dataWithLeeway)); // false, because token is expired since current time is greater than exp
Important
- You have to configure
ValidationDatainforming all claims you want to validate the token. - If
ValidationDatacontains claims that are not being used in token or token has claims that are not configured inValidationDatathey will be ignored byToken::validate(). exp,nbfandiatclaims are configured by default inValidationData::__construct()with the current UNIX time (time()).- The optional
$leewayparameter ofValidationDatawill cause us to use that number of seconds of leeway when validating the time-based claims, pretending we are further in the future for the “Issued At” (iat) and “Not Before” (nbf) claims and pretending we are further in the past for the “Expiration Time” (exp) claim. This allows for situations where the clock of the issuing server has a different time than the clock of the verifying server, as mentioned in section 4.1 of RFC 7519.
Token signature
We can use signatures to be able to verify if the token was not modified after its generation. This library implements Hmac, RSA and ECDSA signatures (using 256, 384 and 512).
Important
Do not allow the string sent to the Parser to dictate which signature algorithm to use, or else your application will be vulnerable to a critical JWT security vulnerability.
The examples below are safe because the choice in Signer is hard-coded and
cannot be influenced by malicious users.
Hmac
Hmac signatures are really simple to be used:
use Lcobucci\JWT\Builder;
use Lcobucci\JWT\Signer\Key;
use Lcobucci\JWT\Signer\Hmac\Sha256;
$signer = new Sha256();
$time = time();
$token = (new Builder())->issuedBy('http://example.com') // Configures the issuer (iss claim)
->permittedFor('http://example.org') // Configures the audience (aud claim)
->identifiedBy('4f1g23a12aa', true) // Configures the id (jti claim), replicating as a header item
->issuedAt($time) // Configures the time that the token was issue (iat claim)
->canOnlyBeUsedAfter($time + 60) // Configures the time that the token can be used (nbf claim)
->expiresAt($time + 3600) // Configures the expiration time of the token (exp claim)
->withClaim('uid', 1) // Configures a new claim, called "uid"
->getToken($signer, new Key('testing')); // Retrieves the generated token
var_dump($token->verify($signer, 'testing 1')); // false, because the key is different
var_dump($token->verify($signer, 'testing')); // true, because the key is the same
RSA and ECDSA
RSA and ECDSA signatures are based on public and private keys so you have to generate using the private key and verify using the public key:
use Lcobucci\JWT\Builder;
use Lcobucci\JWT\Signer\Key;
use Lcobucci\JWT\Signer\Rsa\Sha256; // you can use Lcobucci\JWT\Signer\Ecdsa\Sha256 if you're using ECDSA keys
$signer = new Sha256();
$privateKey = new Key('file://{path to your private key}');
$time = time();
$token = (new Builder())->issuedBy('http://example.com') // Configures the issuer (iss claim)
->permittedFor('http://example.org') // Configures the audience (aud claim)
->identifiedBy('4f1g23a12aa', true) // Configures the id (jti claim), replicating as a header item
->issuedAt($time) // Configures the time that the token was issue (iat claim)
->canOnlyBeUsedAfter($time + 60) // Configures the time that the token can be used (nbf claim)
->expiresAt($time + 3600) // Configures the expiration time of the token (exp claim)
->withClaim('uid', 1) // Configures a new claim, called "uid"
->getToken($signer, $privateKey); // Retrieves the generated token
$publicKey = new Key('file://{path to your public key}');
var_dump($token->verify($signer, $publicKey)); // true when the public key was generated by the private one =)
It’s important to say that if you’re using RSA keys you shouldn’t invoke ECDSA signers (and vice-versa), otherwise sign() and verify() will raise an exception!
参考资料
Packagist jwt https://packagist.org/packages/lcobucci/jwt
github jwt https://github.com/lcobucci/jwt
Documentation https://lcobucci-jwt.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
lcobucci/jwt的安装和使用 https://www.cnblogs.com/jurij/p/jwt.html
lcobucci/jwt —— 一个轻松生成jwt token的插件 http://www.koukousky.com/back/2483.html
https://blog.csdn.net/HobHunter/article/details/78524922
https://github.com/lcobucci/jwt/blob/3.2/README.md#basic-usage
https://blog.csdn.net/maxsky/article/details/80036512
初步理解JWT并实践使用 https://www.jianshu.com/p/2fdc20a42c41
https://www.jianshu.com/p/af8360b83a9f
https://cnodejs.org/topic/5b0c4a7b8a4f51e140d942fc
读懂JWT的使用,你就会用PHP https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/166279165
前后端分离项目token自动续期的解决方案 https://juejin.cn/post/6854573211451916301
PHP实现JWT登录鉴权 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/RqGJMkCCeGtR1zjrALuVNw
PHP实现JWT登录鉴权 https://blog.csdn.net/xiaodong_526/article/details/122178578