正文
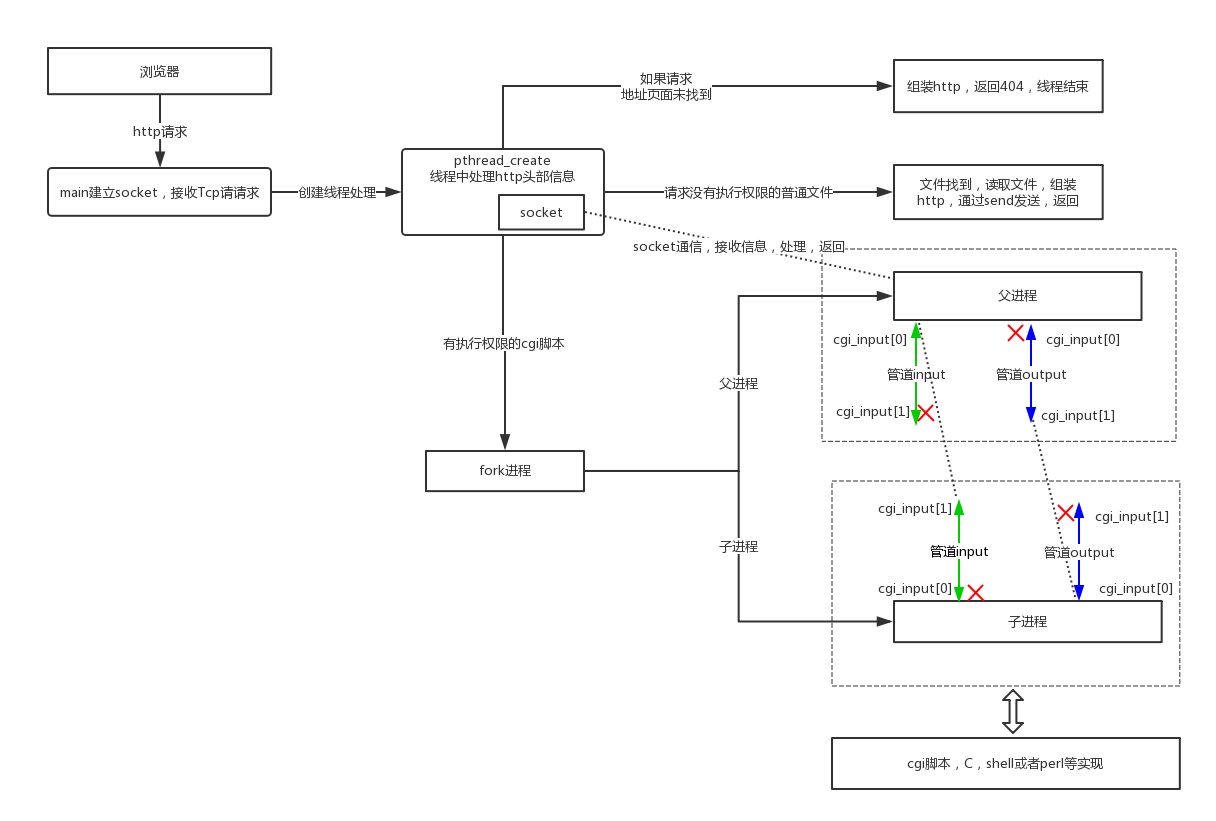
先看一下浏览器和tinyhttpd交互的整个流程:
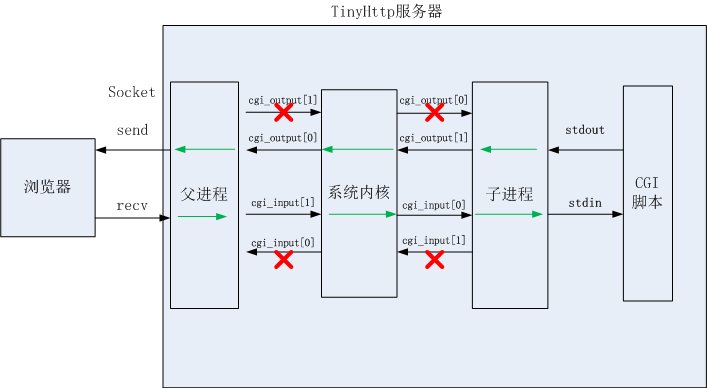
再看一下Tinyhttp的运作模型:
Tiny HTTPd 的函数有:
void accept_request(int);//处理从套接字上监听到的一个 HTTP 请求
void bad_request(int);//返回给客户端这是个错误请求,400响应码
void cat(int, FILE *);//读取服务器上某个文件写到 socket 套接字
void cannot_execute(int);//处理发生在执行 cgi 程序时出现的错误
void error_die(const char *);//把错误信息写到 perror
void execute_cgi(int, const char *, const char *, const char *);//运行cgi脚本,这个非常重要,涉及动态解析
int get_line(int, char *, int);//读取一行HTTP报文
void headers(int, const char *);//返回HTTP响应头
void not_found(int);//返回找不到请求文件
void serve_file(int, const char *);//调用 cat 把服务器文件内容返回给浏览器。
int startup(u_short *);//开启http服务,包括绑定端口,监听,开启线程处理链接
void unimplemented(int);//返回给浏览器表明收到的 HTTP 请求所用的 method 不被支持。
建议源码阅读顺序: main -> startup -> accept_request -> serve_file -> execute_cgi
httpd.c 源码:
/* J. David's webserver */
/* This is a simple webserver.
* Created November 1999 by J. David Blackstone.
* CSE 4344 (Network concepts), Prof. Zeigler
* University of Texas at Arlington
*/
/* This program compiles for Sparc Solaris 2.6.
* To compile for Linux:
* 1) Comment out the #include <pthread.h> line.
* 2) Comment out the line that defines the variable newthread.
* 3) Comment out the two lines that run pthread_create().
* 4) Uncomment the line that runs accept_request().
* 5) Remove -lsocket from the Makefile.
* 1)注释掉#include <pthread.h>行。
* 2)注释掉定义变量newthread的行。
* 3)注释掉运行pthread_create()的两行。
* 4)取消注释运行accept_request()的行。
* 5)从Makefile中删除-lsocket。
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
// #include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define ISspace(x) isspace((int)(x))
//函数说明:检查参数c是否为空格字符,
//也就是判断是否为空格(' ')、定位字符(' \t ')、CR(' \r ')、换行(' \n ')、垂直定位字符(' \v ')或翻页(' \f ')的情况。
//返回值:若参数c 为空白字符,则返回非 0,否则返回 0。
#define SERVER_STRING "Server: jdbhttpd/0.1.0\r\n"
//定义server名称
void accept_request(int);
void bad_request(int);
void cat(int, FILE *);
void cannot_execute(int);
void error_die(const char *);
void execute_cgi(int, const char *, const char *, const char *);
int get_line(int, char *, int);
void headers(int, const char *);
void not_found(int);
void serve_file(int, const char *);
int startup(u_short *);
void unimplemented(int);
/**********************************************************************/
/* A request has caused a call to accept() on the server port to
* return. Process the request appropriately.
* Parameters: the socket connected to the client */
/**********************************************************************/
//接收客户端的连接,并读取请求数据
void accept_request(int client)
{
char buf[1024];
int numchars;
char method[255];
char url[255];
char path[512];
size_t i, j;
struct stat st;
int cgi = 0; /* becomes true if server decides this is a CGI program */
char *query_string = NULL;
//获取一行HTTP报文数据
numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf));
i = 0; j = 0;
//对于HTTP报文来说,第一行的内容即为报文的起始行,格式为<method> <request-URL> <version>,每个字段用空白字符相连
while (!ISspace(buf[j]) && (i < sizeof(method) - 1))
{
//提取其中的请求方式是GET还是POST
method[i] = buf[j];
i++; j++;
}
method[i] = '\0';
//函数说明:strcasecmp()用来比较参数s1 和s2 字符串,比较时会自动忽略大小写的差异。
//返回值:若参数s1 和s2 字符串相同则返回0。s1 长度大于s2 长度则返回大于0 的值,s1 长度若小于s2 长度则返回小于0 的值。
if (strcasecmp(method, "GET") && strcasecmp(method, "POST"))
{
//tinyhttp仅仅实现了GET和POST
unimplemented(client);
return;
}
//cgi为标志位,置1说明开启cgi解析
if (strcasecmp(method, "POST") == 0)
//如果请求方法为POST,需要cgi解析
cgi = 1;
i = 0;
//将method后面的后边的空白字符略过
while (ISspace(buf[j]) && (j < sizeof(buf)))
j++;
//继续读取request-URL
while (!ISspace(buf[j]) && (i < sizeof(url) - 1) && (j < sizeof(buf)))
{
url[i] = buf[j];
i++; j++;
}
url[i] = '\0';
//如果是GET请求,url可能会带有?,有查询参数
if (strcasecmp(method, "GET") == 0)
{
query_string = url;
while ((*query_string != '?') && (*query_string != '\0'))
query_string++;
if (*query_string == '?')
{
//如果带有查询参数,需要执行cgi,解析参数,设置标志位为1
cgi = 1;
//将解析参数截取下来
*query_string = '\0';
query_string++;
}
}
//以上已经将起始行解析完毕
//url中的路径格式化到path
sprintf(path, "htdocs%s", url);
//如果path只是一个目录,默认设置为首页index.html
if (path[strlen(path) - 1] == '/')
strcat(path, "index.html");
//函数定义: int stat(const char *file_name, struct stat *buf);
//函数说明: 通过文件名filename获取文件信息,并保存在buf所指的结构体stat中
//返回值: 执行成功则返回0,失败返回-1,错误代码存于errno(需要include <errno.h>)
if (stat(path, &st) == -1) {
//假如访问的网页不存在,则不断的读取剩下的请求头信息,并丢弃即可
while ((numchars > 0) && strcmp("\n", buf)) /* read & discard headers */
numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf));
//最后声明网页不存在
not_found(client);
}
else
{
//如果访问的网页存在则进行处理
if ((st.st_mode & S_IFMT) == S_IFDIR) //S_IFDIR代表目录
//如果路径是个目录,那就将主页进行显示
strcat(path, "/index.html");
if ((st.st_mode & S_IXUSR) ||
(st.st_mode & S_IXGRP) ||
(st.st_mode & S_IXOTH) )
//S_IXUSR:文件所有者具可执行权限
//S_IXGRP:用户组具可执行权限
//S_IXOTH:其他用户具可读取权限
cgi = 1;
if (!cgi)
//将静态文件返回
serve_file(client, path);
else
//执行cgi动态解析
execute_cgi(client, path, method, query_string);
}
//因为http是面向无连接的,所以要关闭
close(client);
}
/**********************************************************************/
/* Inform the client that a request it has made has a problem.
* Parameters: client socket */
/**********************************************************************/
void bad_request(int client)
{
char buf[1024];
//发送400
sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 400 BAD REQUEST\r\n");
send(client, buf, sizeof(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "Content-type: text/html\r\n");
send(client, buf, sizeof(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "\r\n");
send(client, buf, sizeof(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "<P>Your browser sent a bad request, ");
send(client, buf, sizeof(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "such as a POST without a Content-Length.\r\n");
send(client, buf, sizeof(buf), 0);
}
/**********************************************************************/
/* Put the entire contents of a file out on a socket. This function
* is named after the UNIX "cat" command, because it might have been
* easier just to do something like pipe, fork, and exec("cat").
* Parameters: the client socket descriptor
* FILE pointer for the file to cat */
/**********************************************************************/
//读取服务器上某个文件写到 socket 套接字
void cat(int client, FILE *resource)
{
//发送文件的内容
char buf[1024];
//读取文件到buf中
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), resource);
while (!feof(resource)) //判断文件是否读取到末尾
{
//读取并发送文件内容
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), resource);
}
}
/**********************************************************************/
/* Inform the client that a CGI script could not be executed.
* Parameter: the client socket descriptor. */
/**********************************************************************/
void cannot_execute(int client)
{
char buf[1024];
//发送500
sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 500 Internal Server Error\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "Content-type: text/html\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "<P>Error prohibited CGI execution.\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
}
/**********************************************************************/
/* Print out an error message with perror() (for system errors; based
* on value of errno, which indicates system call errors) and exit the
* program indicating an error. */
/**********************************************************************/
void error_die(const char *sc)
{
perror(sc);
exit(1);
}
/**********************************************************************/
/* Execute a CGI script. Will need to set environment variables as
* appropriate.
* Parameters: client socket descriptor
* path to the CGI script */
/**********************************************************************/
//执行cgi动态解析
void execute_cgi(int client, const char *path,
const char *method, const char *query_string)
{
char buf[1024];
int cgi_output[2]; //声明的读写管道,切莫被名称给忽悠
int cgi_input[2];
pid_t pid;
int status;
int i;
char c;
int numchars = 1;
int content_length = -1;
buf[0] = 'A'; buf[1] = '\0';
//如果是GET请求
if (strcasecmp(method, "GET") == 0)
while ((numchars > 0) && strcmp("\n", buf)) /* read & discard headers 读取并且丢弃头信息 */
numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf));
//处理的请求为POST
else /* POST */
{
numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf));
//循环读取头信息找到Content-Length字段的值
while ((numchars > 0) && strcmp("\n", buf))
{
buf[15] = '\0'; //目的是为了截取Content-Length:
if (strcasecmp(buf, "Content-Length:") == 0)
//"Content-Length: 15"
content_length = atoi(&(buf[16])); //获取Content-Length的值
numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf));
}
if (content_length == -1) {
//错误请求
bad_request(client);
return;
}
}
//返回正确响应码200
sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
//#include<unistd.h>
//int pipe(int filedes[2]);
//返回值:成功,返回0,否则返回-1。参数数组包含pipe使用的两个文件的描述符。fd[0]:读管道,fd[1]:写管道。
//必须在fork()中调用pipe(),否则子进程不会继承文件描述符。
//两个进程不共享祖先进程,就不能使用pipe。但是可以使用命名管道。
//pipe(cgi_output)执行成功后,cgi_output[0]:读通道 cgi_output[1]:写通道,这就是为什么说不要被名称所迷惑
if (pipe(cgi_output) < 0) {
cannot_execute(client);
return;
}
if (pipe(cgi_input) < 0) {
cannot_execute(client);
return;
}
if ( (pid = fork()) < 0 ) {
cannot_execute(client);
return;
}
//fork出一个子进程运行cgi脚本
if (pid == 0) /* child: CGI script 子进程: 运行CGI 脚本 */
{
char meth_env[255];
char query_env[255];
char length_env[255];
dup2(cgi_output[1], 1); //1代表着stdout,0代表着stdin,将系统标准输出重定向为cgi_output[1]
dup2(cgi_input[0], 0); //将系统标准输入重定向为cgi_input[0],这一点非常关键,cgi程序中用的是标准输入输出进行交互
close(cgi_output[0]); //关闭了cgi_output中的读通道
close(cgi_input[1]); //关闭了cgi_input中的写通道
//CGI标准需要将请求的方法存储环境变量中,然后和cgi脚本进行交互
//存储REQUEST_METHOD
sprintf(meth_env, "REQUEST_METHOD=%s", method);
putenv(meth_env);
if (strcasecmp(method, "GET") == 0) {
//存储QUERY_STRING
sprintf(query_env, "QUERY_STRING=%s", query_string);
putenv(query_env);
}
else { /* POST */
//存储CONTENT_LENGTH
sprintf(length_env, "CONTENT_LENGTH=%d", content_length);
putenv(length_env);
}
// 表头文件#include<unistd.h>
// 定义函数
// int execl(const char * path,const char * arg,....);
// 函数说明
// execl()用来执行参数path字符串所代表的文件路径,接下来的参数代表执行该文件时传递过去的argv(0)、argv[1]……,最后一个参数必须用空指针(NULL)作结束。
// 返回值
// 如果执行成功则函数不会返回,执行失败则直接返回-1,失败原因存于errno中。
execl(path, path, NULL); //执行CGI脚本
exit(0);
} else { /* parent 父进程 */
close(cgi_output[1]); //关闭了cgi_output中的写通道,注意这是父进程中cgi_output变量和子进程要区分开
close(cgi_input[0]); //关闭了cgi_input中的读通道
if (strcasecmp(method, "POST") == 0)
for (i = 0; i < content_length; i++) {
//开始读取POST中的内容
recv(client, &c, 1, 0);
//将数据发送给cgi脚本
write(cgi_input[1], &c, 1);
}
//读取cgi脚本返回数据
while (read(cgi_output[0], &c, 1) > 0)
//发送给浏览器
send(client, &c, 1, 0);
//运行结束关闭
close(cgi_output[0]);
close(cgi_input[1]);
//定义函数:pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int * status, int options);
//函数说明:waitpid()会暂时停止目前进程的执行, 直到有信号来到或子进程结束.
//如果在调用wait()时子进程已经结束, 则wait()会立即返回子进程结束状态值. 子进程的结束状态值会由参数status 返回,
//而子进程的进程识别码也会一快返回.
//如果不在意结束状态值, 则参数status 可以设成NULL. 参数pid 为欲等待的子进程识别码, 其他数值意义如下:
//1、pid<-1 等待进程组识别码为pid 绝对值的任何子进程.
//2、pid=-1 等待任何子进程, 相当于wait().
//3、pid=0 等待进程组识别码与目前进程相同的任何子进程.
//4、pid>0 等待任何子进程识别码为pid 的子进程.
waitpid(pid, &status, 0);
}
}
/**********************************************************************/
/* Get a line from a socket, whether the line ends in a newline,
* carriage return, or a CRLF combination. Terminates the string read
* with a null character. If no newline indicator is found before the
* end of the buffer, the string is terminated with a null. If any of
* the above three line terminators is read, the last character of the
* string will be a linefeed and the string will be terminated with a
* null character.
* Parameters: the socket descriptor
* the buffer to save the data in
* the size of the buffer
* Returns: the number of bytes stored (excluding null) */
/**********************************************************************/
//解析一行http报文
int get_line(int sock, char *buf, int size)
{
int i = 0;
char c = '\0';
int n;
while ((i < size - 1) && (c != '\n'))
{
n = recv(sock, &c, 1, 0);
/* DEBUG printf("%02X\n", c); */
if (n > 0)
{
if (c == '\r')
{
n = recv(sock, &c, 1, MSG_PEEK);
/* DEBUG printf("%02X\n", c); */
if ((n > 0) && (c == '\n'))
recv(sock, &c, 1, 0);
else
c = '\n';
}
buf[i] = c;
i++;
}
else
c = '\n';
}
buf[i] = '\0';
return(i);
}
/**********************************************************************/
/* Return the informational HTTP headers about a file. */
/* Parameters: the socket to print the headers on
* the name of the file */
/**********************************************************************/
void headers(int client, const char *filename)
{
char buf[1024];
(void)filename; /* could use filename to determine file type */
//发送HTTP头
strcpy(buf, "HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
strcpy(buf, SERVER_STRING);
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "Content-Type: text/html\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
strcpy(buf, "\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
}
/**********************************************************************/
/* Give a client a 404 not found status message. */
/**********************************************************************/
void not_found(int client)
{
char buf[1024];
//返回404
sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 404 NOT FOUND\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, SERVER_STRING);
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "Content-Type: text/html\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "<HTML><TITLE>Not Found</TITLE>\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "<BODY><P>The server could not fulfill\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "your request because the resource specified\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "is unavailable or nonexistent.\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "</BODY></HTML>\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
}
/**********************************************************************/
/* Send a regular file to the client. Use headers, and report
* errors to client if they occur.
* Parameters: a pointer to a file structure produced from the socket
* file descriptor
* the name of the file to serve */
/**********************************************************************/
//将请求的文件发送回浏览器客户端
void serve_file(int client, const char *filename)
{
FILE *resource = NULL;
int numchars = 1;
char buf[1024];
buf[0] = 'A'; buf[1] = '\0';
while ((numchars > 0) && strcmp("\n", buf)) /* read & discard headers 将HTTP请求头读取并丢弃 */
numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf));
//打开文件
resource = fopen(filename, "r");
if (resource == NULL)
//如果文件不存在,则返回not_found
not_found(client);
else
{
//添加HTTP头
headers(client, filename);
//并发送文件内容
cat(client, resource);
}
//关闭文件句柄
fclose(resource);
}
/**********************************************************************/
/* This function starts the process of listening for web connections
* on a specified port. If the port is 0, then dynamically allocate a
* port and modify the original port variable to reflect the actual
* port.
* Parameters: pointer to variable containing the port to connect on
* Returns: the socket */
/**********************************************************************/
//启动服务端。开启http服务,包括绑定端口,监听,开启线程处理链接
int startup(u_short *port)
{
int httpd = 0;
struct sockaddr_in name;
//设置http socket
httpd = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (httpd == -1)
error_die("socket");
memset(&name, 0, sizeof(name));
name.sin_family = AF_INET; // AF_INET Supported address families -> Internet IP Protocol
name.sin_port = htons(*port);
name.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
//绑定端口
if (bind(httpd, (struct sockaddr *)&name, sizeof(name)) < 0)
error_die("bind");
/*动态分配一个端口 */
if (*port == 0) /* if dynamically allocating a port */
{
int namelen = sizeof(name);
if (getsockname(httpd, (struct sockaddr *)&name, &namelen) == -1)
error_die("getsockname");
*port = ntohs(name.sin_port);
}
//监听连接
if (listen(httpd, 5) < 0)
error_die("listen");
return(httpd);
}
/**********************************************************************/
/* Inform the client that the requested web method has not been
* implemented.
* Parameter: the client socket */
/**********************************************************************/
//返回给浏览器表明收到的 HTTP 请求所用的 method 不被支持。
void unimplemented(int client)
{
char buf[1024];
//发送501说明相应方法没有实现
sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 501 Method Not Implemented\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, SERVER_STRING);
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "Content-Type: text/html\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "<HTML><HEAD><TITLE>Method Not Implemented\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "</TITLE></HEAD>\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "<BODY><P>HTTP request method not supported.\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "</BODY></HTML>\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
}
/**********************************************************************/
int main(void)
{
int server_sock = -1;
u_short port = 0; // unsigned short
int client_sock = -1;
struct sockaddr_in client_name;
int client_name_len = sizeof(client_name);
// pthread_t newthread;
server_sock = startup(&port);
printf("httpd running on port %d\n", port);
while (1)
{
//接受请求,函数原型
//#include <sys/types.h>
//#include <sys/socket.h>
//int accept(int sockfd, struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t *addrlen);
//接受客户端连接
client_sock = accept(server_sock,
(struct sockaddr *)&client_name,
&client_name_len);
if (client_sock == -1)
error_die("accept");
accept_request(client_sock);
// 启动线程处理新的连接。 每次收到请求,创建一个线程来处理接受到的请求,把client_sock转成地址作为参数传入pthread_create
// if (pthread_create(&newthread , NULL, accept_request, client_sock) != 0)
// perror("pthread_create");
}
//关闭server socketss
close(server_sock);
return(0);
}
Makefile 编译文件内容:
all: httpd
httpd: httpd.c
gcc -W -Wall -lpthread -o httpd httpd.c
clean:
rm httpd
命令行 make 编译,然后 ./httpd 运行服务器。
通过浏览器访问 127.0.0.1:端口/index2.html 访问指定文件,post提交可以查看cgi处理结果。
cgi脚本
原项目中cgi是perl写的:
#!/usr/local/bin/perl -Tw
use strict;
use CGI;
my($cgi) = new CGI;
print $cgi->header;
my($color) = "blue";
$color = $cgi->param('color') if defined $cgi->param('color');
print $cgi->start_html(-title => uc($color),
-BGCOLOR => $color);
print $cgi->h1("This is $color");
print $cgi->end_html;
cgi文件改成支持php的:
#!/usr/bin/env php
<?php
echo "<html>";
echo "<head>";
echo "<title>POST</title>";
echo "</head>";
echo "<body>";
echo "<CENTER>Today is:</CENTER>";
echo "<CENTER><B>";
echo date('Y-m-d H:i:s');
echo "</B></CENTER>";
echo "</body></html>";
cgi文件改成支持shell的:
#!/bin/bash
echo "Content-Type: text/html"
echo
echo "<HTML><BODY>"
echo "<CENTER>Today is:</CENTER>"
echo "<CENTER><B>"
date
echo "</B></CENTER>"
echo "</BODY></HTML>"
cgi文件改成支持python的:
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf-8
import sys,os
length = os.getenv('CONTENT_LENGTH')
if length:
postdata = sys.stdin.read(int(length))
print "Content-type:text/html\n"
print '<html>'
print '<head>'
print '<title>POST</title>'
print '</head>'
print '<body>'
print '<h2> POST data </h2>'
print '<ul>'
for data in postdata.split('&'):
print '<li>'+data+'</li>'
print '</ul>'
print '</body>'
print '</html>'
else:
print "Content-type:text/html\n"
print 'no found'
简单客户端
上面是服务端的例子,下面看一个简单的客户端,也是项目自带的示例:
simpleclient.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int sockfd;
int len;
struct sockaddr_in address;
int result;
char ch = 'A';
sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
address.sin_family = AF_INET;
address.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1");
address.sin_port = htons(9734);
len = sizeof(address);
result = connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&address, len);
if (result == -1)
{
perror("oops: client1");
exit(1);
}
write(sockfd, &ch, 1);
read(sockfd, &ch, 1);
printf("char from server = %c\n", ch);
close(sockfd);
exit(0);
}
参考资料
Tiny HTTPd 分析源码 https://github.com/iBaiYang/TinyHTTPd
Tiny HTTPd’s tiny homepage https://sourceforge.net/projects/tinyhttpd/files/
HTTP服务器的本质:tinyhttpd源码分析及拓展 https://www.cnblogs.com/qiyeboy/p/6296387.html
HTTP服务器的本质:tinyhttpd源码分析及拓展源码 https://github.com/qiyeboy/SourceAnalysis
Tinyhttpd精读解析 https://www.cnblogs.com/nengm1988/p/7816618.html
Tinyhttpd精读解析git源码 https://github.com/nengm/Tinyhttpd
十个最值得阅读学习的C开源项目代码 https://blog.csdn.net/deeplee021/article/details/40583877
源码阅读——十个C开源项目 https://my.oschina.net/zhoukuo/blog/335788
linux c——dup( )和dup2( )函数详解 https://blog.csdn.net/tiandc/article/details/81489447
Linux pipe详解 https://blog.csdn.net/acs713/article/details/27500663